Advanced Threat Prevention Deep Dive (PCNSE Focus)
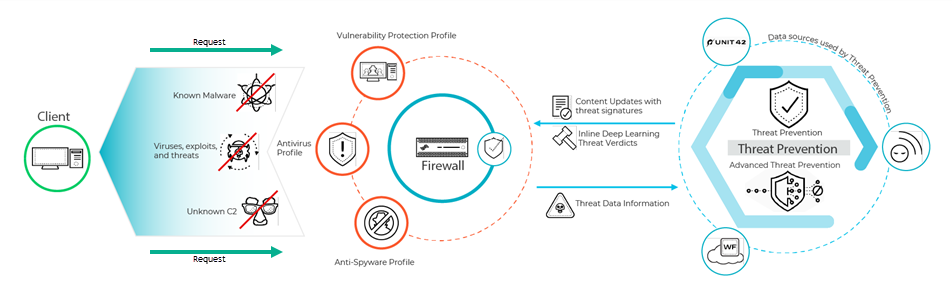
Advanced Threat Prevention (ATP) is Palo Alto Networks' enhanced Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) capability. It builds upon the standard Threat Prevention subscription by adding cloud-based machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) engines for inline, real-time detection and prevention of unknown and evasive threats, especially Command-and-Control (C2) and certain classes of exploits, often before traditional signatures are available.
Core Concepts and Architecture
- Layered Prevention: ATP works alongside existing signature-based engines (Antivirus, Anti-Spyware, Vulnerability Protection). Signatures block known threats quickly.
-
Inline Cloud Analysis:
For traffic not matching known signatures but deemed suspicious (based on heuristics or specific protocol analysis), the firewall can send metadata or payload snippets to the ATP cloud for real-time analysis by advanced ML/DL models. This targets:
- Unknown C2: Detects patterns indicative of C2 communication over HTTP, HTTP/2, SSL, unknown-UDP, and unknown-TCP, even if the destination domain/IP isn't yet known malicious.
- Command Injection & SQL Injection: Analyzes web requests (HTTP/HTTPS) for patterns matching these common web vulnerability exploit techniques, blocking zero-day attempts.
- DNS Relay Threats: (Mentioned in original text, likely part of broader C2 detection).
- Local Deep Learning (Content Release Dependent): Some PAN-OS versions/content releases include on-box deep learning models for analyzing specific traffic types (like suspicious PE files or scripts) locally, providing faster verdicts for certain zero-day threats without requiring a cloud query for every file. Traffic requiring further analysis may still be sent to the cloud.
- Cloud-Delivered Updates: The ML/DL models in the cloud are continuously updated by Palo Alto Networks based on data from WildFire, Unit 42 threat research, and global telemetry, providing evolving protection without requiring firewall content updates for model enhancements. New *types* of detectors might still arrive via content updates.
- MITRE ATT&CK® Integration: ATP provides context for detected threats by mapping them to relevant MITRE ATT&CK® tactics and techniques, aiding in incident response and understanding attacker behavior.
Signature Types (Foundation for ATP)
ATP complements, but does not replace, the standard threat signature categories configured in Security Profiles:
- Antivirus Signatures: Detect known malware in files (executables, documents, archives, etc.). Delivered via Antivirus content updates.
- Anti-Spyware Signatures: Detect known C2 traffic patterns, spyware activity, adware, keyloggers, botnets, etc. Includes DNS-based signatures. Delivered via Applications and Threats and Antivirus content updates.
- Vulnerability Signatures: Detect attempts to exploit known software or protocol flaws (buffer overflows, code execution, DoS, SQL injection, info leaks, etc.). Delivered via Applications and Threats content updates.
Signatures have default severities (Critical, High, Medium, Low, Informational) and default actions (e.g.,
alert
,
block
,
reset-client
,
reset-server
,
reset-both
). These defaults can be overridden in Security Profiles.
Threat Signature Categories Table (Detailed)
This table provides more detail on the categories used by standard Threat Prevention, which ATP builds upon.
| Threat Category | Content Update Source | Description & Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Antivirus Signatures | ||
| apk | Antivirus, WildFire | Malicious Android Application (APK) files. |
| MacOSX | Antivirus, WildFire | Malicious MacOSX files (DMG, Mach-O, PKG). |
| flash | Antivirus, WildFire | Malicious Adobe Flash applets (SWF). |
| jar | Antivirus, WildFire | Malicious Java archives (JAR, class files). |
| ms-office | Antivirus, WildFire | Malicious Microsoft Office files (DOC, XLS, PPT, DOCX, XLSX, PPTX, RTF), including macro-based threats. |
| Antivirus, WildFire | Malicious Portable Document Format (PDF) files, often containing exploits or embedded scripts. | |
| pe | Antivirus, WildFire | Malicious Portable Executable files for Windows (EXE, DLL, SCR, SYS, CPL, OCX, FON, DRV, EFI, PIF). |
| linux | Antivirus, WildFire | Malicious Executable and Linkable Format (ELF) files for Linux. |
| archive | Antivirus, WildFire | Malicious RAR and 7z archive files (containing malware). |
| Anti-Spyware Signatures | ||
| adware | Applications and Threats | Programs displaying unwanted ads, potentially modifying browser behavior. |
| autogen | Antivirus | Automatically generated payload-based signatures detecting C2 traffic, effective against unknown/changing C2 hosts. |
| backdoor | Applications and Threats | Programs allowing unauthorized remote access/control. |
| botnet | Applications and Threats | Communication associated with known botnet C2 infrastructure or behavior. |
| browser-hijack | Applications and Threats | Software modifying browser settings (homepage, search engine) without consent. |
| cryptominer | Applications and Threats | Unauthorized use of system resources for cryptocurrency mining (often via scripts or malware). |
| data-theft | Applications and Threats | Detection of known patterns associated with exfiltration of sensitive data to unauthorized destinations. |
| dns | Antivirus | DNS requests matching known malicious domains (from daily Antivirus updates). |
| dns-security | Antivirus | Comprehensive category including signatures from `dns`, `dns-wildfire`, and DNS Security service analysis (requires DNS Security license). |
| dns-wildfire | WildFire | DNS requests matching known malicious domains (from frequent WildFire updates, requires WildFire license). |
| downloader | Applications and Threats | Programs (scripts, trojans, maldocs) designed to download and execute further malicious payloads (second-stage). |
| fraud | Applications and Threats | Activity related to phishing, scams, or form-jacking (stealing payment info from web forms). |
| hacktool | Applications and Threats | Traffic generated by tools commonly used for hacking (scanning, exploitation, C2). Use might be legitimate (pen testing) or malicious. |
| keylogger | Applications and Threats | Software secretly recording keystrokes and potentially taking screenshots, often exfiltrating data via C2. |
| networm | Applications and Threats | Self-replicating malware that spreads across networks, often exploiting vulnerabilities. |
| phishing-kit | Applications and Threats | Detection of connections to known phishing kit landing pages designed to steal credentials. |
| post-exploitation | Applications and Threats | Activity indicating an attacker exploring a compromised system (reconnaissance, privilege escalation attempts). |
| webshell | Applications and Threats | Detection of web shell uploads or C2 communication with implanted web shells on servers (PHP, ASP, etc.). |
| spyware | Applications and Threats | General category for outbound C2 communication detected by manually crafted or standard signatures. |
| Vulnerability Signatures | ||
| brute-force | Applications and Threats | Detects repeated failed attempts (logins, requests) exceeding a threshold in a time window. Configurable trigger conditions. |
| code-execution | Applications and Threats | Detects attempts to exploit vulnerabilities allowing arbitrary code execution on the target system. |
| code-obfuscation | Applications and Threats | Detects techniques used to hide malicious code (JavaScript obfuscation, etc.) to evade detection. |
| dos | Applications and Threats | Detects patterns associated with Denial-of-Service attacks attempting to overwhelm system resources. |
| exploit-kit | Applications and Threats | Detects connections to known exploit kit landing pages which probe for multiple vulnerabilities. |
| info-leak | Applications and Threats | Detects attempts to exploit vulnerabilities that reveal sensitive system information. |
| insecure-credentials | Applications and Threats | Detects use of weak, default, or known compromised credentials for devices/services (e.g., default IoT passwords). |
| overflow | Applications and Threats | Detects attempts to exploit buffer overflow vulnerabilities. |
| phishing | Applications and Threats | (Similar to phishing-kit under Anti-Spyware) Detects connections to known phishing sites based on vulnerability signatures. |
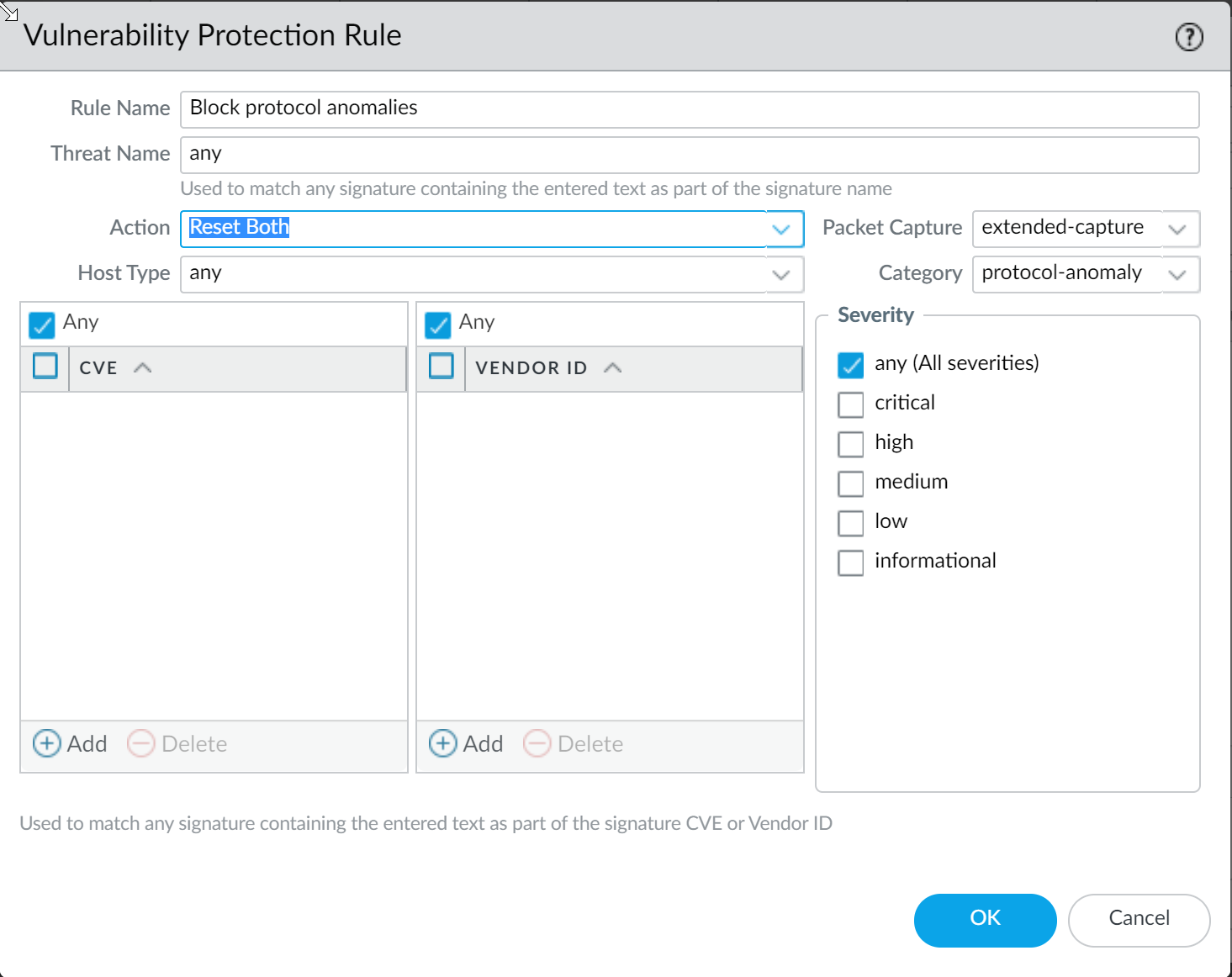
| protocol-anomaly | Applications and Threats | Detects deviations from standard protocol behavior (malformed packets, non-standard ports). Blocking this category is a key best practice. |
| sql-injection | Applications and Threats | Detects attempts to inject malicious SQL queries into web application inputs to manipulate databases. |
Best Practices for Securing Your Network from Layer 4 and Layer 7 Evasions
ATP complements foundational security best practices:
- Keep Updated: Maintain current PAN-OS versions and Content Releases (Antivirus, Apps & Threats).
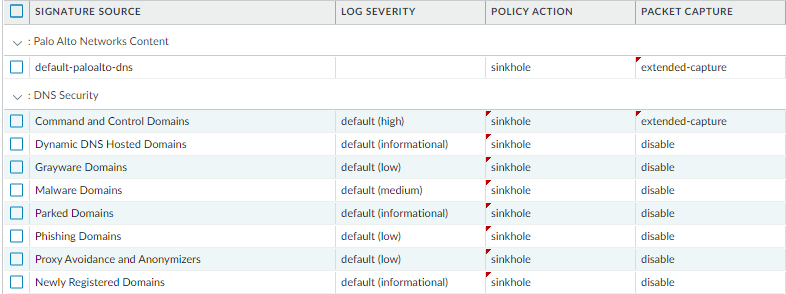
- Enable DNS Security:** Configure Anti-Spyware profiles to sinkhole or block malicious DNS categories (C2, Malware, Phishing, DGA, Tunneling etc.) as per best practices. Use the Palo Alto sinkhole IP ( 72.5.65.111 ) if clients might bypass internal DNS.
-
Enable ATP Inline Analysis (if licensed):**
- In relevant Security Profiles (Anti-Spyware for C2, Vulnerability Protection for Injection): Enable Inline Cloud Analysis .
- Set the action for detected inline threats (e.g., `Inline Cloud Analysis - C2`, `Inline Cloud Analysis - Command Injection`) typically to reset-both or block for maximum protection.
- Enable Local Deep Learning Analysis if available/supported for faster local verdicts on certain file types/scripts.
-
Use DNS Proxy & Enable Evasion Signatures:**
- Configure the firewall as a DNS Proxy ( Network > DNS Proxy ) for internal clients. This gives the firewall visibility into hostname-to-IP mappings.
- In the Anti-Spyware profile ( DNS Policies tab), enable relevant Evasion Signatures (like HTTP Evasion, TLS Evasion). These require DNS Proxy visibility to detect mismatches between DNS resolution and actual connection destinations.
-
Apply Strict Security Policies:**
- Allow only necessary applications using App-ID .
- Use specific Service objects instead of `any`. Use `application-default` where appropriate.
- Block unknown applications (unknown-tcp, unknown-udp). Create custom App-IDs or Application Override policies only for necessary, trusted internal apps initially identified as unknown.
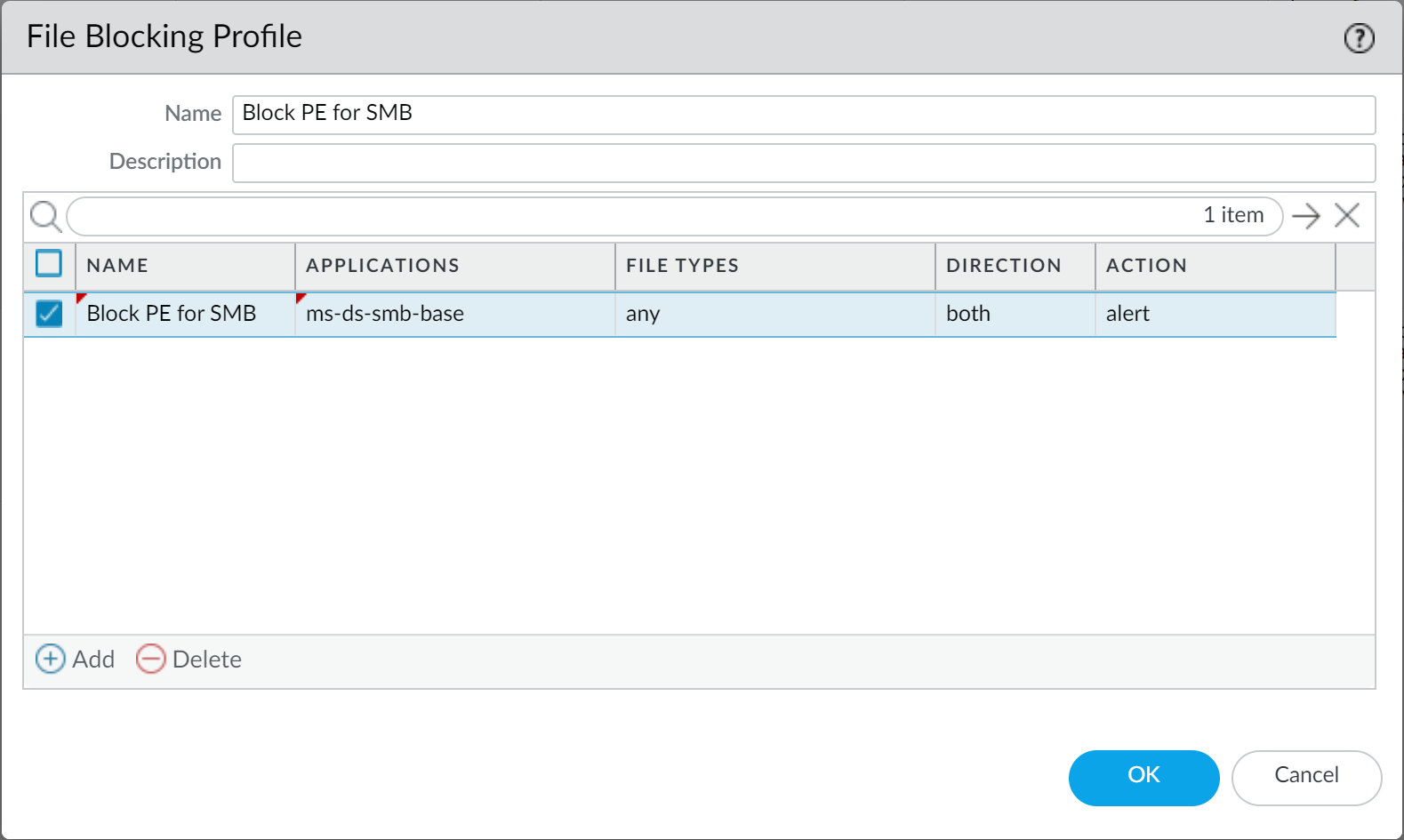
- Apply File Blocking profiles to block dangerous executables (PE, ELF, scripts) over protocols like SMB, especially from untrust zones.
- Enable WildFire Inline ML in Antivirus profiles for real-time blocking of malicious PE, Office, script files.
-
Configure Zone Protection:** Apply Zone Protection profiles to interfaces, especially external-facing ones (
Network > Network Profiles > Zone Protection
).
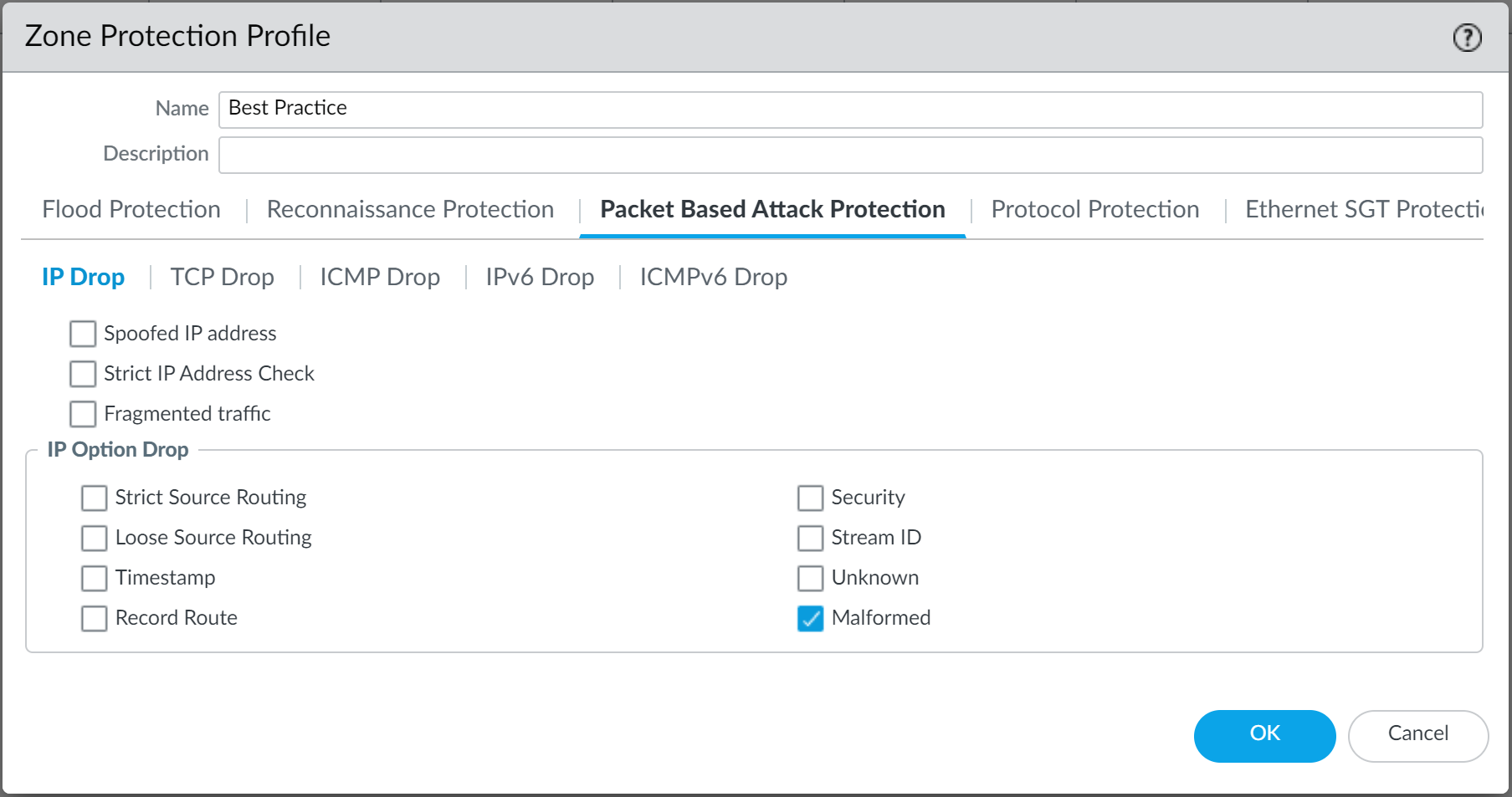
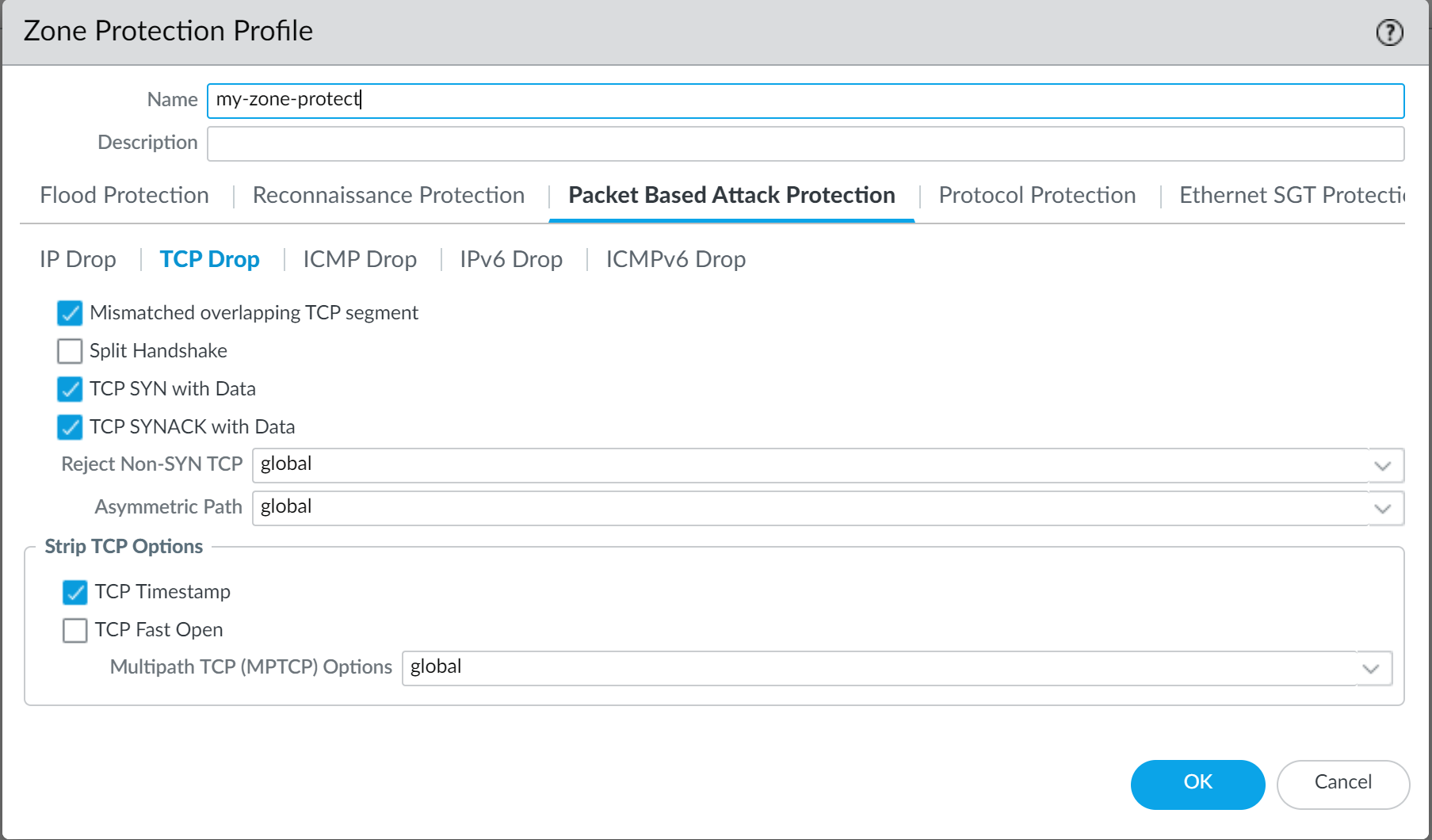
- Under Packet Based Attack Protection : Drop Malformed IP packets, Mismatched overlapping TCP segments , TCP SYN with Data , TCP SYNACK with Data . Strip TCP Timestamps .
- Network Segmentation & IPv6:** Use zones and appropriate policies for segmentation. Enable IPv6 filtering if IPv6 is used or to prevent tunneling attacks ( Network > Interfaces > Ethernet > IPv6 ).
-
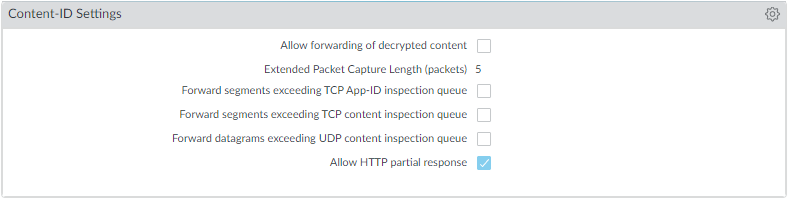
Content-ID Settings:** (
Device > Setup > Content-ID > Content-ID Settings
)
- Disable "Forward datagrams exceeding UDP content inspection queue".
- Disable "Forward segments exceeding TCP content inspection queue". (Ensures all allowed traffic gets inspected, potentially impacting performance on under-sized firewalls).
- Disable "Allow HTTP partial response". (Prevents clients from reassembling malicious files after an initial block). Verify impact on critical apps relying on HTTP Range requests. Use targeted Application Override *only if absolutely necessary* for specific apps that break.
-
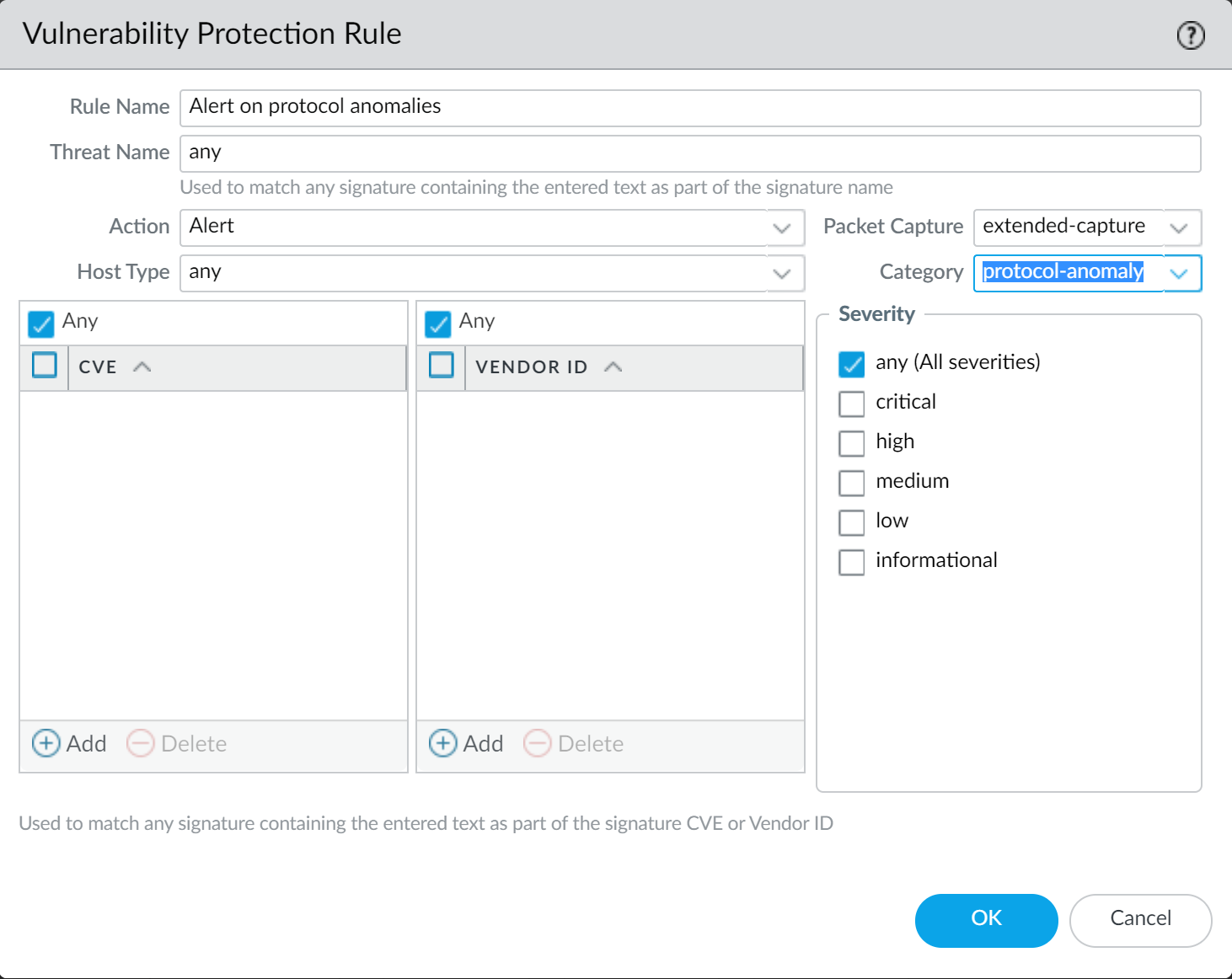
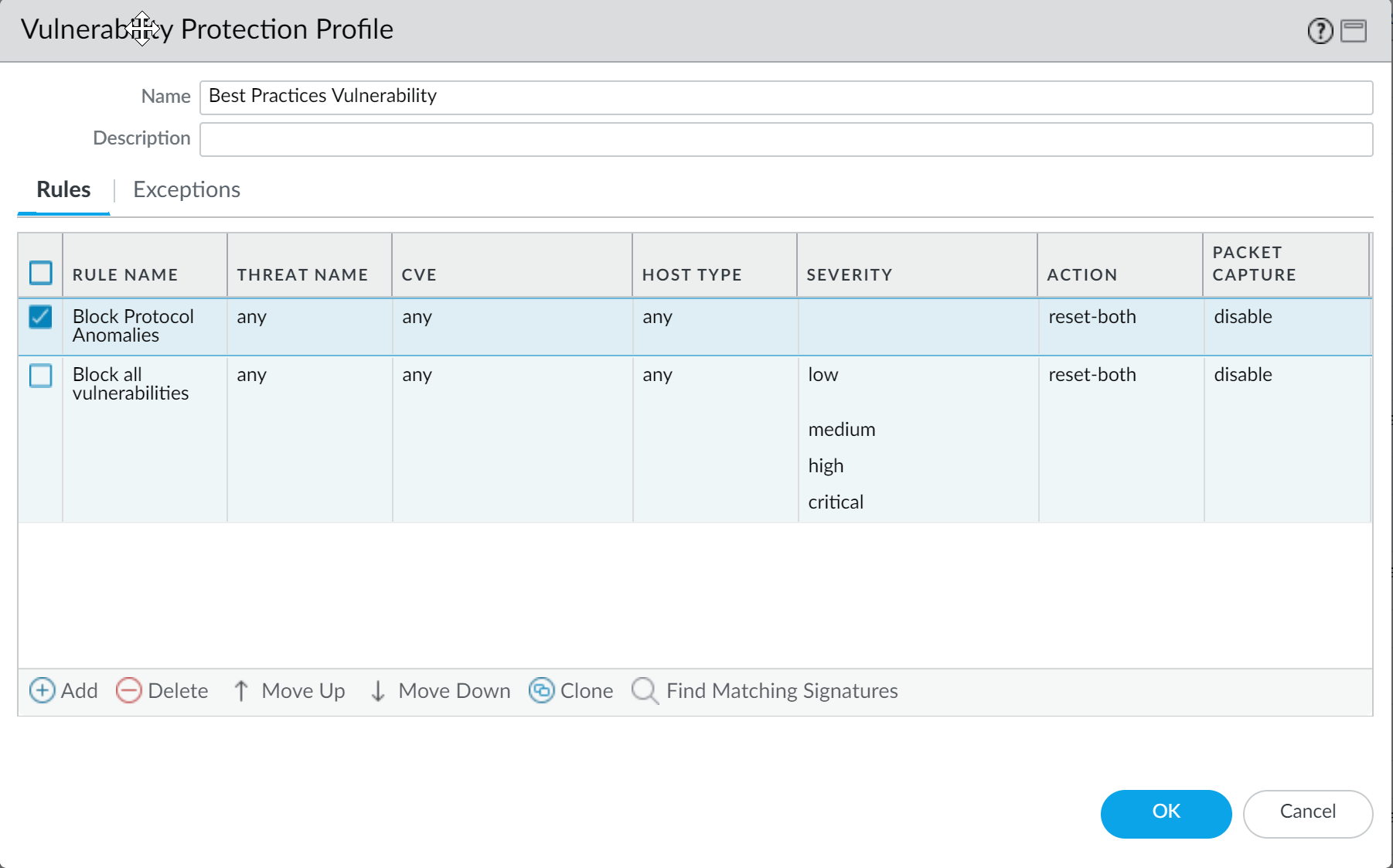
Vulnerability Protection Best Practices:** Apply a Vulnerability Protection profile that blocks:
- Protocol Anomalies (all severities). Start with 'alert' in sensitive environments to identify impact on custom/legacy apps, then move to 'block'.
- All vulnerabilities with critical, high, and medium severity. Optionally block 'low' as well.
- Share Telemetry:** Enable Device Telemetry ( Device > Setup > Telemetry ) to contribute threat intelligence back to Palo Alto Networks, improving protections for everyone.