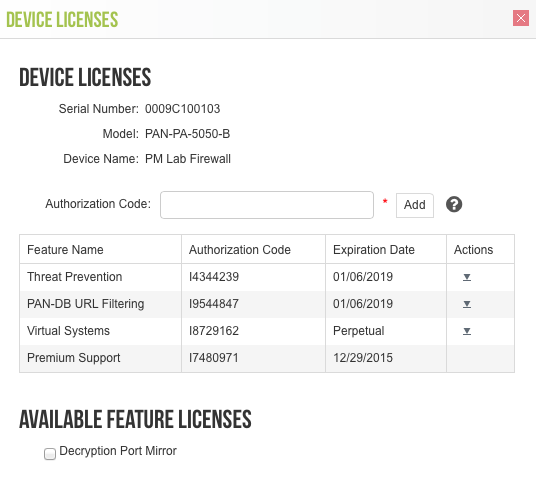
Mermaid Diagrams: Visualizing Decryption Flows
Decryption Mirror Process (Sequence Diagram)
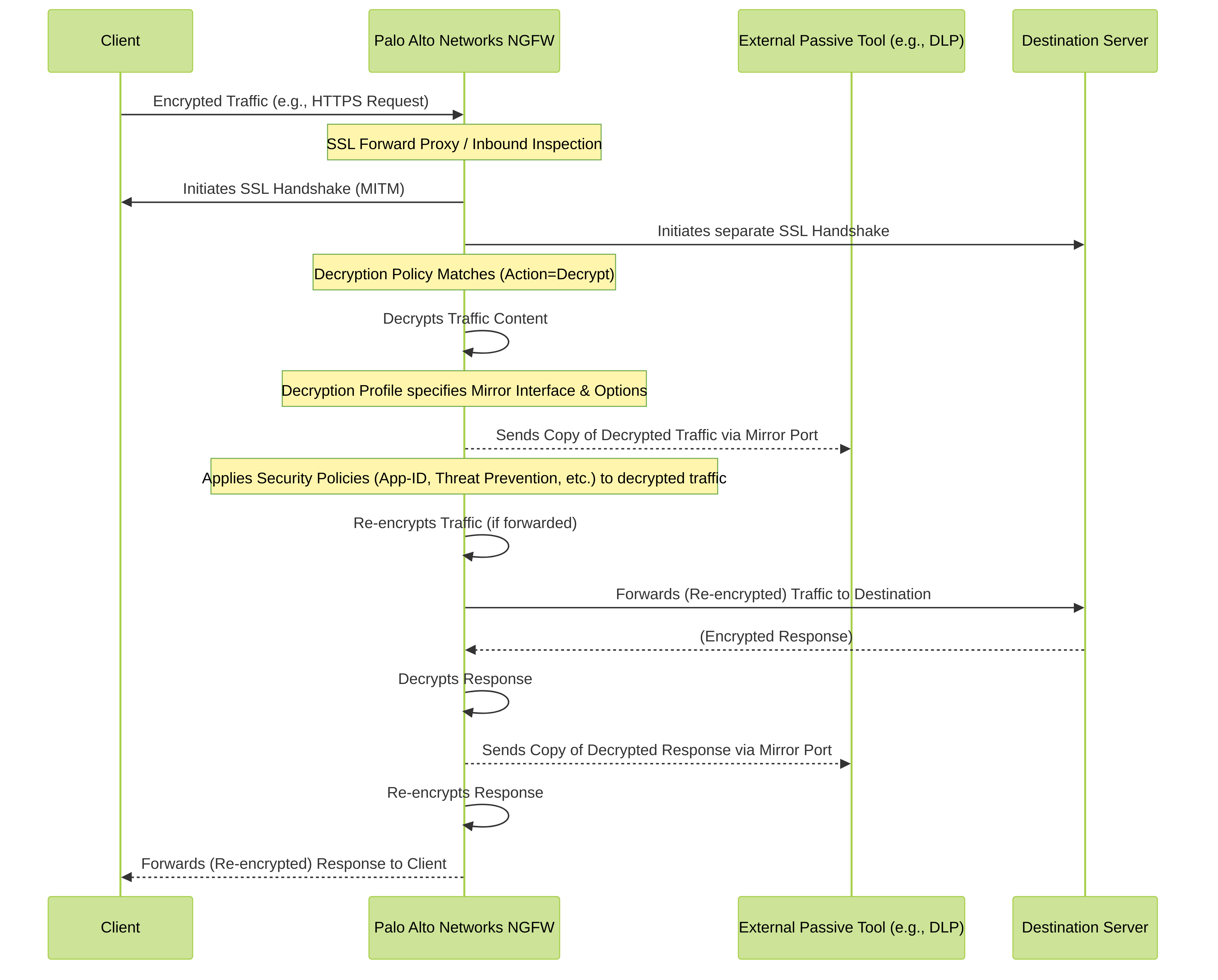
Sequence of operations in Palo Alto Networks Decryption Mirroring, showing passive copying of decrypted traffic to an external tool.
Decryption Mirror Configuration Flow (Flowchart)
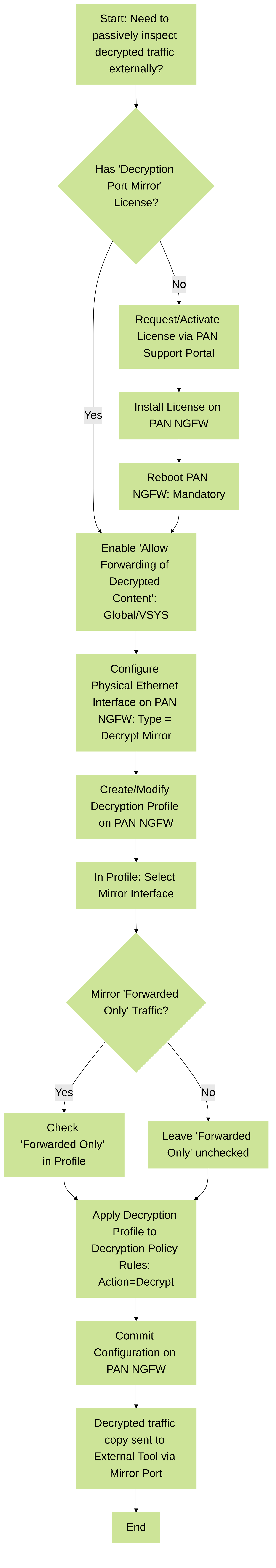
Palo Alto Networks Decryption Mirroring configuration workflow.
Decryption Broker: Inline Security Chain (Transparent Bridge Mode)
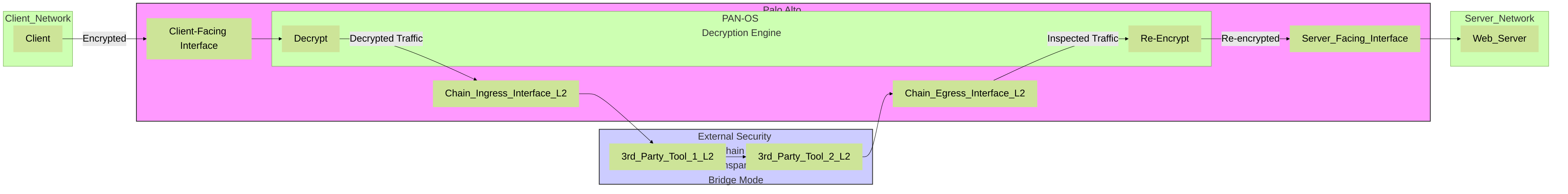
Palo Alto Networks Decryption Broker traffic flow with an external security chain in Transparent Bridge mode. The PAN NGFW forwards decrypted traffic through inline Layer 2 tools.
Decryption Broker: Inline Security Chain (Layer 3 Mode)
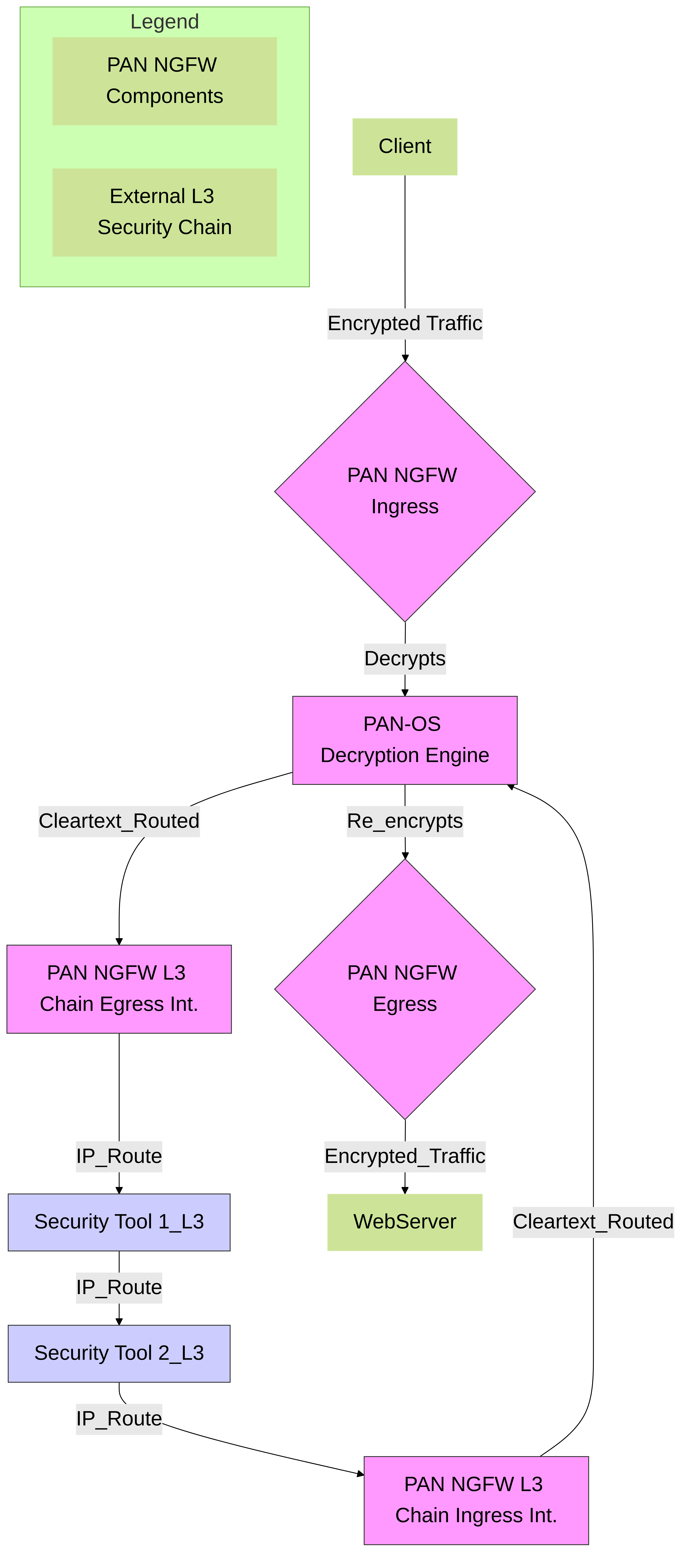
Palo Alto Networks Decryption Broker traffic flow with an external security chain in Layer 3 mode. Decrypted traffic is routed to and from IP-addressable security tools.
Decision Flow: Decryption Mirror vs. Decryption Broker
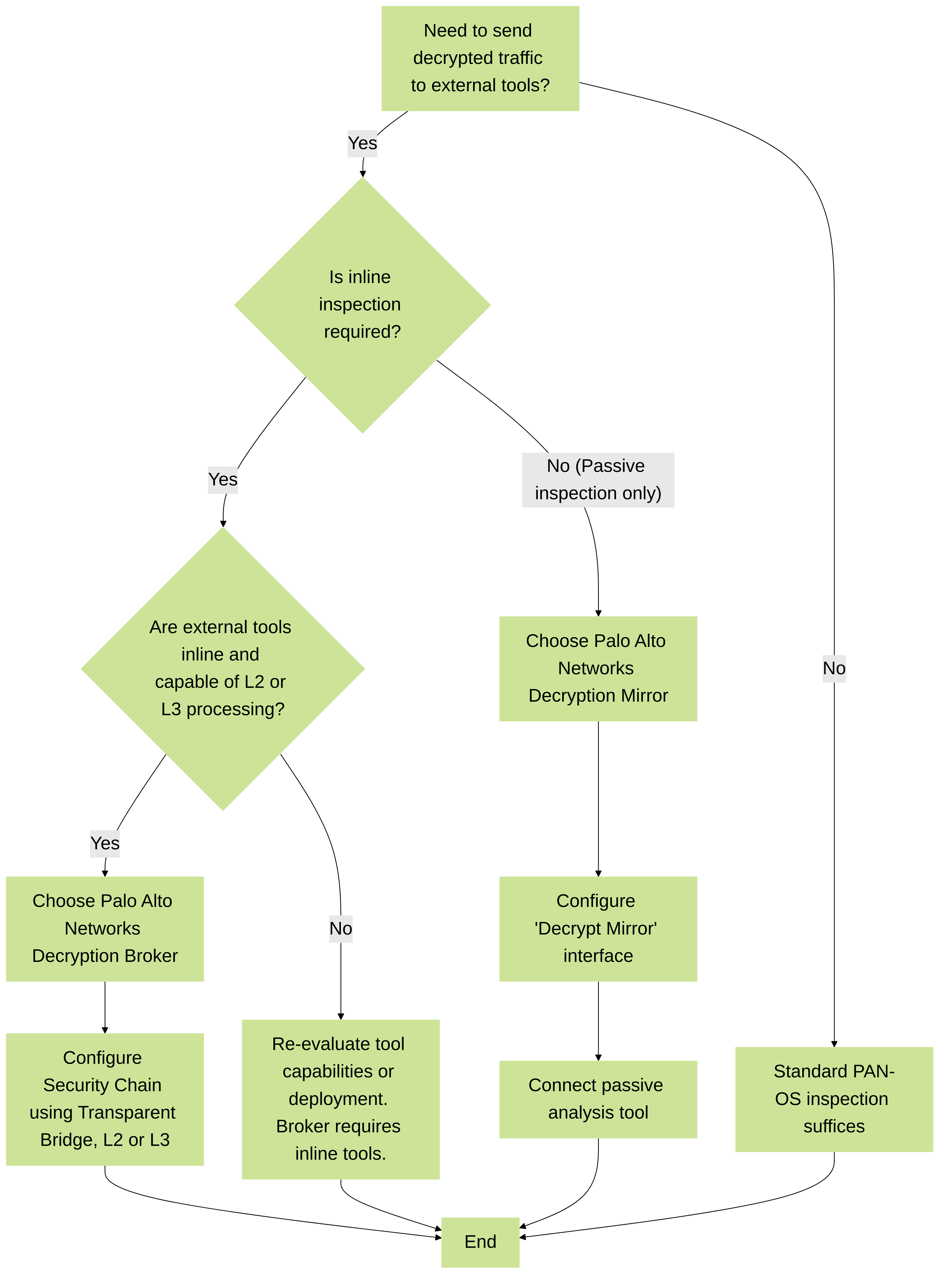
Decision tree for selecting between Palo Alto Networks Decryption Mirror and Decryption Broker based on inspection requirements.