Palo Alto Networks Decryption Concepts
Introduction: Why Decrypt?
Encryption (SSL/TLS, SSH) is essential for protecting data confidentiality and integrity during transmission. However, attackers leverage this same encryption to hide malware, command-and-control communication, and data exfiltration from traditional security inspection tools. Without visibility into encrypted traffic, firewalls operate with significant blind spots.
Palo Alto Networks Decryption allows the NGFW and Prisma Access to inspect encrypted traffic, enabling features like App-ID, Threat Prevention (Antivirus, Anti-Spyware, Vulnerability Protection), WildFire, Advanced URL Filtering, DNS Security, and Data Filtering to function effectively on traffic that would otherwise be opaque.
Core Decryption Concepts
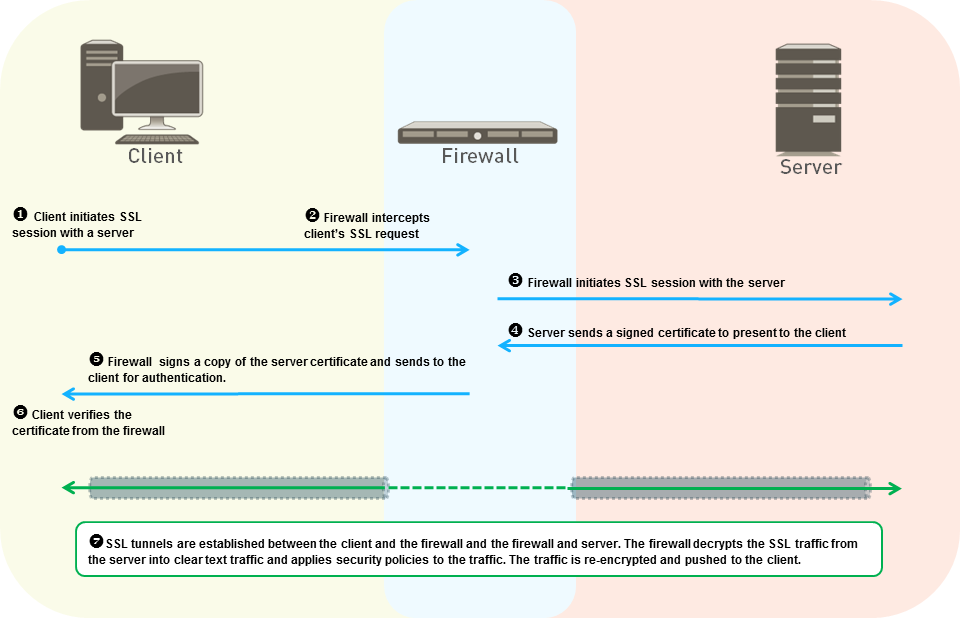
- SSL Forward Proxy: Decrypts outbound traffic from internal users to external sites. The firewall acts as a proxy, terminating the client's TLS connection and initiating a new one to the server, using specific certificates (Forward Trust/Untrust) to manage trust.
- SSL Inbound Inspection: Decrypts inbound traffic destined for internal servers (e.g., company web servers). Requires importing the server's certificate and private key onto the firewall.
- SSH Proxy: Decrypts SSH traffic, primarily to detect and block unauthorized SSH tunneling (port forwarding), rather than inspecting the interactive shell content itself.
PCNSE Focus: Be clear on which mode applies to which traffic direction. Forward Proxy = Outbound user traffic. Inbound Inspection = Inbound traffic to *your* servers (requires server cert/key).
The Role of Certificates in SSL/TLS Decryption
SSL/TLS decryption fundamentally relies on Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) concepts and digital certificates to establish trust and enable the firewall to act as a transparent intermediary.
Certificate Types and Requirements
Understanding certificate roles is critical for the PCNSE exam and real-world deployment:
- CA Certificate (Certificate Authority): Issues and signs other certificates, establishing a chain of trust. Can be a Root CA or an Intermediate/Subordinate CA.
- End-Entity Certificate (Server/Leaf): Presented by a web server to identify itself and facilitate TLS encryption. Signed by a CA.
-
Forward Trust Certificate:
- Purpose: Used by the firewall in SSL Forward Proxy to generate *impersonation* certificates for websites whose original server certificate is signed by a CA that the *firewall trusts*.
- Type Required: Must be a CA certificate (either self-signed generated on the firewall, or preferably, a subordinate CA issued by your enterprise PKI).
- Client Trust: Client browsers/systems *must* trust the CA that issued the Forward Trust certificate to avoid warnings.
- Private Key: Requires the private key to be on the firewall to sign the impersonation certificates.
-
Forward Untrust Certificate:
- Purpose: Used by the firewall in SSL Forward Proxy to generate *impersonation* certificates for websites whose original server certificate is *not* trusted by the firewall (e.g., expired, unknown issuer, self-signed).
- Type Required: Typically a self-signed CA certificate generated on the firewall.
- Client Trust: Should *not* be trusted by clients; its purpose is to present a certificate that *will* trigger a browser warning, alerting the user to the untrusted nature of the original site.
- Private Key: Requires the private key to be on the firewall.
-
SSL Inbound Inspection Certificate:
- Purpose: Used by the firewall in SSL Inbound Inspection to decrypt traffic destined for an internal server.
- Type Required: The actual end-entity (server) certificate used by the internal server, along with its corresponding private key .
- Trust: External clients connecting to the server must trust the CA that originally issued this server certificate.
Summary Table: Keys Required
| Certificate Purpose | Private Key Required on Firewall? | Typical Certificate Type |
|---|---|---|
| Forward Trust | Yes | CA (Subordinate or Self-Signed Root) |
| Forward Untrust | Yes | CA (Self-Signed Root) |
| SSL Inbound Inspection | Yes | End-Entity (Server) |
| Trusted Root CAs (for validation) | No | CA (Root or Intermediate) |
PCNSE Focus: Remember which certificates need their private key imported onto the firewall: Forward Trust, Forward Untrust, and the Server Certificate used for Inbound Inspection.
PKI Strategy:
- Enterprise PKI (Recommended): Issue a subordinate CA certificate from your internal Root CA to use as the Forward Trust certificate. Clients already trust the Root CA, simplifying deployment. Use a separate self-signed CA for Forward Untrust.
- Self-Signed (Firewall Generated): Generate a self-signed Root CA directly on the firewall, then generate Forward Trust/Untrust CAs signed by it. Requires distributing and installing the firewall's self-signed Root CA onto *all* client devices that will have their traffic decrypted. More suitable for labs/POCs.
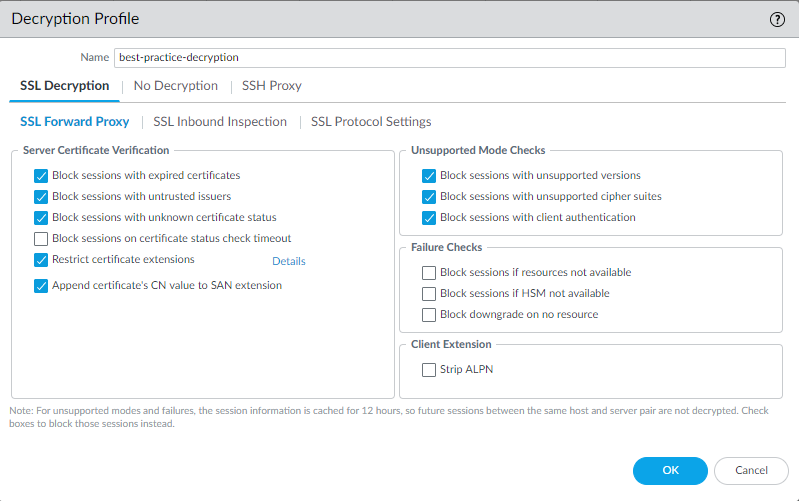
Decryption Profiles: Controlling Decryption Behavior
Decryption Profiles are attached to Decryption Policy rules and define *how* the firewall handles specific aspects of the SSL/TLS or SSH session, especially regarding security checks and protocol parameters. They allow granular control over decrypted traffic.
Profile Checks and Actions
Key settings within Decryption Profiles allow you to:
-
Block Sessions Based on Certificate Status (SSL Forward Proxy & No Decrypt for TLS 1.2-):
- Expired Certificates
- Untrusted Issuers
- Unknown Status (OCSP/CRL failure)
-
Block Sessions Based on Unsupported Modes:
- Unsupported Protocol Versions (e.g., block TLS 1.0/1.1)
- Unsupported Cipher Suites/Algorithms (e.g., block RC4, 3DES)
- Client Authentication Required (for Forward Proxy)
-
Block Sessions Based on Resource/Failure Checks:
- Block if decryption resources exhausted.
- Block if required HSM is unavailable.
- Protocol Settings (Min/Max Version, Algorithms): Define allowed TLS/SSH versions and cryptographic algorithms.
Different profiles (SSL Forward Proxy, SSL Inbound Inspection, SSH Proxy, No Decryption) expose different subsets of these controls.
PCNSE Focus: Understand that a "No Decrypt" profile still allows security checks (like expired/untrusted certs) for TLS 1.2 and earlier, providing some security even without full inspection.
TLS 1.3 Decryption: Enhancements and Challenges
TLS 1.3 enhances speed and security but encrypts the server certificate, impacting decryption.
- Performance: Faster native handshake, but decryption overhead remains. ECDHE is mandatory and efficient on modern hardware.
- Certificate Visibility Issue: Encrypted certificates limit pre-decryption checks (e.g., issuer validation in "No Decrypt" profiles is ineffective for TLS 1.3). Automatic technical exclusions based on cert details are less feasible.
- Certificate Pinning: More likely to cause issues; requires explicit exclusions.
- Configuration: Use Decryption Profiles (Min/Max Version). Recommend Min: TLS 1.2, Max: Max for general use. Consider setting Max to TLS 1.2 for mobile app compatibility if pinning is an issue.
PCNSE Focus: Key trade-off: TLS 1.3 is more secure but reduces pre-decryption visibility for the firewall, making exclusions for technical reasons more reliant on manual configuration or observed failures.
Decryption Exclusions: When NOT to Decrypt
Traffic might be excluded from decryption for technical or policy reasons.
Reasons for Exclusion
- Technical Reasons (Use Global Exclusion List): Certificate Pinning, Mutual Authentication (mTLS), Unsupported Ciphers/Protocols by firewall decryption engine.
- Policy Reasons (Use 'No Decrypt' Policy Rule): Privacy/Compliance (Financial, Health), Sensitive internal traffic, User Experience.
Exclusion Decision Flow
graph TD
A[SSL/TLS Traffic Matches Decrypt Rule] --> B{Technical Issue?};
B -- Yes --> C[Add to Global Exclusion List];
B -- No --> D{Policy/Privacy Reason?};
D -- Yes --> E[Create 'No Decrypt' Policy Rule + Profile];
D -- No --> F[Attempt Decryption];
C --> G[Traffic Bypasses Decryption];
E --> G;
F --> H[Inspect & Forward];
style G fill:#fcf8e3,stroke:#f0ad4e,stroke-width:2px;
style H fill:#dff0d8,stroke:#3c763d,stroke-width:2px;
Verification and Troubleshooting
Using Logs
- Traffic Logs: Primary source to verify if a *specific session* was decrypted (look for flags/fields), encountered an error, or matched a 'No Decrypt' rule.
- Decryption Logs: Primarily logs *handshake failures* (by default) or successes (if enabled). Useful for identifying systemic decryption issues (e.g., cert problems, resource exhaustion) rather than individual session status.
PCNSE Focus: Know that the Traffic Log is the place to confirm decryption status for specific, completed sessions.