Configuring Shared Gateway with Palo Alto Networks Multi-VSYS Implementation
Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs) offer powerful virtualization capabilities through Multiple Virtual Systems (multi-VSYS). This feature allows a single physical firewall to be partitioned into multiple independent, logical firewalls, each with its own discrete administrative domain, security policies, interfaces, and routing instances. A common and highly practical use case within a multi-VSYS environment is the configuration of a **Shared Gateway**. This allows multiple tenant VSYS instances to share common resources, most notably an internet connection, managed by a dedicated Shared Gateway VSYS. This guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough of the concepts, design considerations, and configuration steps (both GUI and CLI) for implementing a Shared Gateway on a Palo Alto Networks firewall.1. Understanding VSYS and Shared Gateway in Palo Alto Networks
1.1. Virtual Systems (VSYS)
On Palo Alto Networks firewalls, a Virtual System (VSYS) is a logical firewall instance that operates independently within a single physical firewall. Each VSYS maintains its own:
- Security Policies (including App-ID, User-ID, Content-ID)
- NAT Policies
- Network Interfaces (logical or physical segments)
- Virtual Routers
- Reporting and Logging
- Administrative access (role-based access control can be applied per VSYS)
1.2. Shared Gateway Concept
A
Shared Gateway
configuration in a Palo Alto Networks multi-VSYS environment designates one VSYS (often referred to as the "Shared VSYS" or "Gateway VSYS," e.g.,
vsys1
by default or a custom-named one like
vsys-shared
) to provide access to common resources for other "tenant" VSYS instances. The most common shared resource is internet access. Instead of each tenant VSYS having its own dedicated external interface and public IP address, they route their internet-bound traffic through the Shared Gateway VSYS.
Benefits of using a Shared Gateway:
- Resource Optimization: Conserves public IP addresses and reduces the number of physical interfaces needed for external connectivity.
- Centralized Management of Common Services: Security services like WildFire, DNS Security, URL Filtering, and Threat Prevention for internet-bound traffic can be managed centrally in the Shared Gateway VSYS.
- Simplified Routing for Tenants: Tenant VSYSs typically only need a default route pointing to the Shared Gateway VSYS for external access.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces the operational overhead of managing multiple independent internet connections.
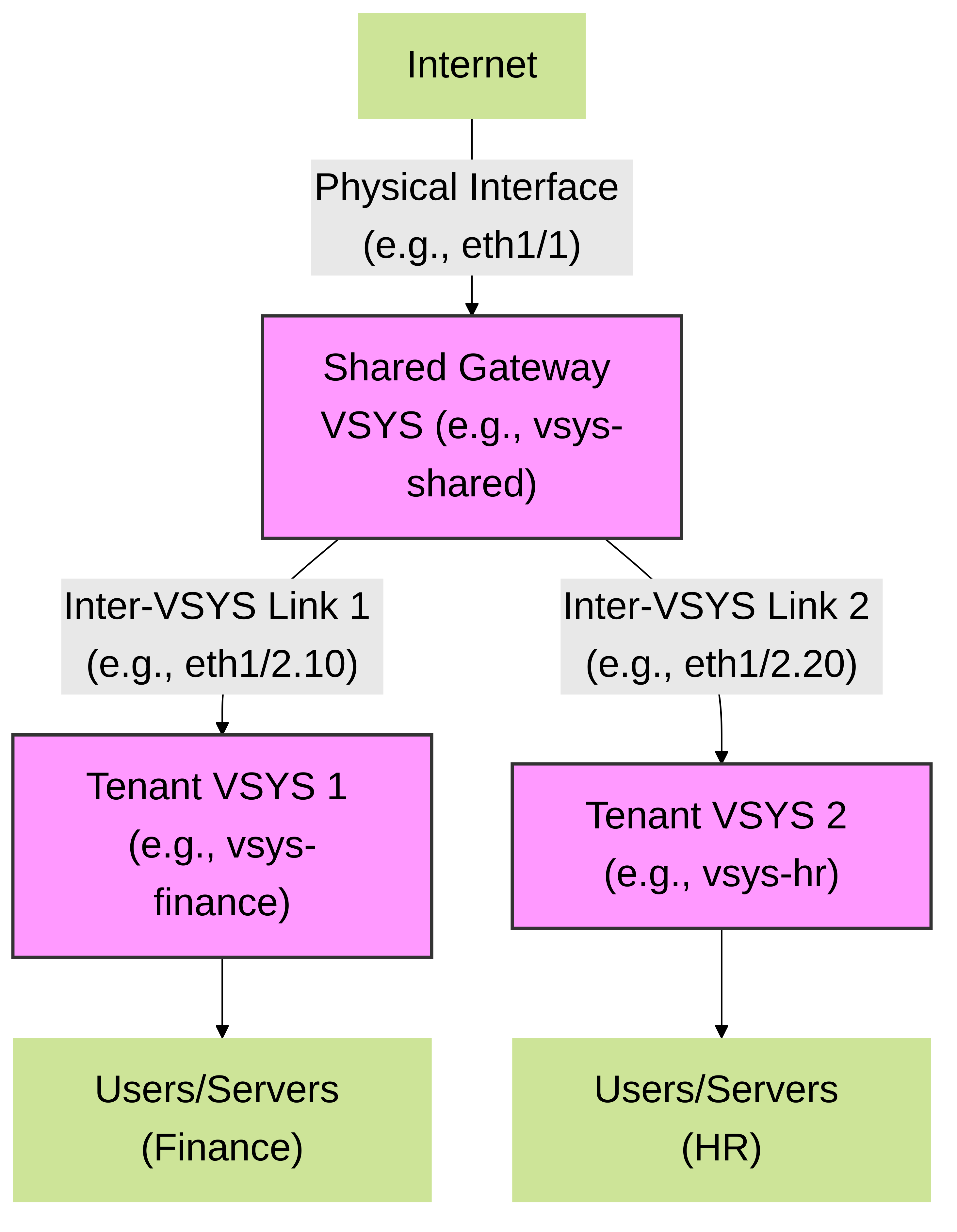
Figure 1: High-level architecture of a Palo Alto Networks Multi-VSYS environment with a Shared Gateway. The Shared Gateway VSYS handles external connectivity, while tenant VSYSs connect to it via inter-VSYS links.
2. Prerequisites and Design Considerations
- PAN-OS Version: Ensure your PAN-OS version supports multi-VSYS and Shared Gateway functionalities as described. Functionality is generally consistent across modern PAN-OS versions (8.1+).
- Platform Support: Multi-VSYS is supported on mid-range (e.g., PA-3200, PA-3400 Series) and high-end PA-Series firewalls (e.g., PA-5200, PA-5400, PA-7000 Series). Check Palo Alto Networks datasheets for specific platform capabilities. VM-Series firewalls also support multi-VSYS.
-
Licensing:
- A specific license is required to enable more than the default number of VSYS instances (typically, one base VSYS is included; additional VSYS capacity requires licensing).
- Shared Gateway functionality itself doesn't require a separate license beyond the VSYS capacity license.
- Subscription licenses (Threat Prevention, WildFire, URL Filtering, etc.) are generally applied per VSYS or globally, depending on the configuration and license type. For shared internet access, these are often crucial in the Shared Gateway VSYS.
- Resource Allocation: Each VSYS consumes hardware resources (CPU, memory, sessions). Carefully plan resource allocation, especially for the Shared Gateway VSYS, which will handle aggregated traffic. Panorama can be used to monitor and manage resource utilization.
- IP Addressing: Plan IP address schemes for inter-VSYS links (transit networks) and for any networks hosted within the Shared Gateway VSYS.
- Routing: Determine the routing design. Static routes are common for simplicity, but dynamic routing protocols (OSPF, BGP) can be used within and between VSYSs if needed.
-
Security Policies:
Design security policies for:
- Tenant VSYS to Shared Gateway VSYS traffic.
- Shared Gateway VSYS to external network traffic.
- Return traffic from the external network and Shared Gateway VSYS back to tenant VSYSs.
- NAT: Typically, Source NAT (SNAT) for outbound internet traffic from tenant VSYSs is configured in the Shared Gateway VSYS.
3. Configuration Steps: Enabling Multi-VSYS Mode
Before configuring a Shared Gateway, the firewall must be in multi-VSYS mode.3.1. GUI Steps: Enable Multi-VSYS Mode
- Navigate to Device > Setup > Management .
- Click the gear icon next to General Settings to edit.
- In the General Settings dialog, check the Multiple Virtual Systems Capability box.
- Click OK .
- A warning will appear stating that a reboot is required. Click OK or Yes .
- Commit the changes. The firewall will prompt for a reboot. Proceed with the reboot.
3.2. CLI Steps: Enable Multi-VSYS Mode
configure set system setting multi-vsys on commit request restart system
After the reboot, the firewall will operate in multi-VSYS mode. You can then proceed to create and configure VSYS instances.
4. Configuring the Shared Gateway and Tenant VSYSs
Let's assume:-
vsys1will be our Shared Gateway VSYS. -
vsys2will be a tenant VSYS (e.g., "Finance"). -
External (Internet) interface:
ethernet1/1(assigned tovsys1). -
Inter-VSYS link interface:
ethernet1/2. We will use subinterfaces onethernet1/2for inter-VSYS communication.-
ethernet1/2.10: Assigned tovsys1, IP:10.254.254.1/30, Zone:INTERNAL-SHARED. -
ethernet1/2.20: Assigned tovsys2, IP:10.254.254.2/30, Zone:TO-SHAREDGW.
-
-
vsys2internal network:192.168.20.0/24on interfaceethernet1/3(assigned tovsys2), Zone:FINANCE-LAN.
4.1. Create Tenant VSYS (e.g., vsys2) - GUI
- Navigate to Device > Virtual Systems .
- Click Add at the bottom.
-
Name:
vsys2(or a descriptive name likeFinance-VSYS). - Display Name: A user-friendly name.
-
Interfaces:
Initially, you might not assign interfaces here if you plan to do it from the Network tab later. Or, you can pre-assign interfaces that will exclusively belong to this VSYS. For our example, we will assign
ethernet1/3and the subinterfaceethernet1/2.20later. - Configure other VSYS-specific settings (DNS, permitted protocols, etc.) as needed.
- Click OK .
4.2. Create Tenant VSYS (e.g., vsys2) - CLI
configure set vsys vsys2 display-name Finance-VSYS # Add other vsys specific settings as needed # Example: set vsys vsys2 setting dns-proxy primary-dns 8.8.8.8 exit
4.3. Configure Network Interfaces - GUI
Interfaces must be assigned to their respective VSYS before they can be configured within that VSYS context.
4.3.1. Assign Interfaces to VSYS (Global Context)
- Navigate to Network > Interfaces > Ethernet .
-
Select
ethernet1/1. In the configuration window, set Virtual System tovsys1. Click OK . -
Select
ethernet1/2. This physical interface will host subinterfaces for inter-VSYS links. It does not need to be assigned to a VSYS at the parent level if only its subinterfaces are used. -
Select
ethernet1/3. Set Virtual System tovsys2. Click OK .
4.3.2. Configure Interfaces in
vsys1
(Shared Gateway VSYS)
Switch context to
vsys1
using the Virtual System dropdown at the top right of the WebUI.
-
External Interface (ethernet1/1):
-
Navigate to
Network > Interfaces > Ethernet
. Select
ethernet1/1. - Interface Type: Layer3.
-
Config Tab:
Assign to Virtual Router (e.g.,
defaultor a dedicatedVR-SHARED). Assign to Security Zone (e.g.,UNTRUST). - IPv4 Tab: Assign IP address (e.g., DHCP client or static IP from ISP).
- Click OK .
-
Navigate to
Network > Interfaces > Ethernet
. Select
-
Inter-VSYS Subinterface (ethernet1/2.10):
-
Navigate to
Network > Interfaces > Ethernet
. Select
ethernet1/2. Click Add Subinterface . -
Interface Name / Tag:
10(becomesethernet1/2.10). - Interface Type: Layer3.
-
Config Tab:
Assign to Virtual Router (e.g.,
defaultorVR-SHARED). Assign to Security Zone (e.g.,INTERNAL-SHARED). -
IPv4 Tab:
IP Address:
10.254.254.1, Netmask:255.255.255.252(or/30). - Click OK .
-
Navigate to
Network > Interfaces > Ethernet
. Select
4.3.3. Configure Interfaces in
vsys2
(Tenant VSYS)
Switch context to
vsys2
using the Virtual System dropdown.
-
Inter-VSYS Subinterface (ethernet1/2.20):
-
Navigate to
Network > Interfaces > Ethernet
. Select
ethernet1/2(it should be available if not assigned to a VSYS at parent level, or if subinterface assignment is allowed across VSYS from parent).Gotcha! (Palo Alto Networks): For subinterfaces on the same physical port to be in different VSYS, the parent physical interface (ethernet1/2in this case) should typically remain unassigned to any specific VSYS at its top-level configuration or be configured in a way that allows subinterface distribution. Alternatively, use separate physical interfaces or an Aggregate Ethernet (AE) interface whose members are distributed or subinterfaced per VSYS. The most common method is that the parent interface is not assigned to any VSYS if its subinterfaces are to be distributed. - Click Add Subinterface .
-
Interface Name / Tag:
20(becomesethernet1/2.20). - Interface Type: Layer3.
-
Config Tab:
Assign to Virtual Router (e.g.,
defaultorVR-FINANCE). Assign to Security Zone (e.g.,TO-SHAREDGW). -
IPv4 Tab:
IP Address:
10.254.254.2, Netmask:255.255.255.252(or/30). - Click OK .
-
Navigate to
Network > Interfaces > Ethernet
. Select
-
Internal LAN Interface (ethernet1/3):
-
Navigate to
Network > Interfaces > Ethernet
. Select
ethernet1/3. - Interface Type: Layer3.
-
Config Tab:
Assign to Virtual Router (e.g.,
defaultorVR-FINANCE). Assign to Security Zone (e.g.,FINANCE-LAN). -
IPv4 Tab:
IP Address:
192.168.20.1/24. - Click OK .
-
Navigate to
Network > Interfaces > Ethernet
. Select
4.4. Configure Network Interfaces - CLI
First, ensure you are in the correct VSYS context or specify VSYS for interface assignment. Interface assignment to a VSYS is a global configuration, not per-VSYS context.
configure // Global: Assign physical interfaces to VSYS set network interface ethernet ethernet1/1 vsys vsys1 set network interface ethernet ethernet1/3 vsys vsys2 // Note: ethernet1/2 (parent for subinterfaces) is not directly assigned to a VSYS // Switch to vsys1 context for its interface configurations set system setting session-TARGET vsys1 // Configure vsys1 interfaces set network interface ethernet ethernet1/1 layer3 ipset network interface ethernet ethernet1/1 layer3 interface-management-profile set network virtual-router default interface ethernet1/1 set zone UNTRUST network layer3 ethernet1/1 set network interface ethernet ethernet1/2.10 layer3 ip 10.254.254.1/30 set network interface ethernet ethernet1/2.10 layer3 interface-management-profile set network virtual-router default interface ethernet1/2.10 // Assuming 'default' VR in vsys1 set zone INTERNAL-SHARED network layer3 ethernet1/2.10 // Switch to vsys2 context for its interface configurations set system setting session-TARGET vsys2 // Configure vsys2 interfaces set network interface ethernet ethernet1/2.20 layer3 ip 10.254.254.2/30 set network interface ethernet ethernet1/2.20 layer3 interface-management-profile set network virtual-router default interface ethernet1/2.20 // Assuming 'default' VR in vsys2 set zone TO-SHAREDGW network layer3 ethernet1/2.20 set network interface ethernet ethernet1/3 layer3 ip 192.168.20.1/24 set network interface ethernet ethernet1/3 layer3 interface-management-profile set network virtual-router default interface ethernet1/3 set zone FINANCE-LAN network layer3 ethernet1/3 // Return to global or default vsys context if needed set system setting session-TARGET none exit

Figure 2: Logical inter-VSYS connectivity showing interfaces, zones, and virtual routers. Traffic from FINANCE-LAN routes via VR-FINANCE to eth1/2.20, then to eth1/2.10 in VR-SHARED, and finally out via eth1/1.
4.5. Configure Virtual Routers and Static Routes - GUI
4.5.1. In
vsys1
(Shared Gateway VSYS)
Switch context to
vsys1
.
-
Navigate to
Network > Virtual Routers
. Select your VR (e.g.,
defaultorVR-SHARED). -
Go to
Static Routes > IPv4
. Click
Add
.
-
Name:
Default-Route-INET -
Destination:
0.0.0.0/0 -
Interface:
ethernet1/1(your external interface) -
Next Hop:
IP Address (
Noneif interface handles gateway (like PPPoE). - Click OK .
-
Name:
-
Add a static route back to
vsys2's internal network:-
Name:
Route-To-FINANCE-LAN -
Destination:
192.168.20.0/24(vsys2's internal network) -
Interface:
ethernet1/2.10(vsys1's interface connecting tovsys2) -
Next Hop:
IP Address (
10.254.254.2- IP ofethernet1/2.20invsys2) - Click OK .
-
Name:
4.5.2. In
vsys2
(Tenant VSYS)
Switch context to
vsys2
.
-
Navigate to
Network > Virtual Routers
. Select your VR (e.g.,
defaultorVR-FINANCE). -
Go to
Static Routes > IPv4
. Click
Add
.
-
Name:
Default-Route-To-SharedGW -
Destination:
0.0.0.0/0 -
Interface:
ethernet1/2.20(vsys2's interface connecting tovsys1) -
Next Hop:
IP Address (
10.254.254.1- IP ofethernet1/2.10invsys1) - Click OK .
-
Name:
4.6. Configure Virtual Routers and Static Routes - CLI
configure // Switch to vsys1 context set system setting session-TARGET vsys1 set network virtual-router default routing-table ip static-route Default-Route-INET destination 0.0.0.0/0 nexthop ip-addressinterface ethernet1/1 set network virtual-router default routing-table ip static-route Route-To-FINANCE-LAN destination 192.168.20.0/24 nexthop ip-address 10.254.254.2 interface ethernet1/2.10 // Switch to vsys2 context set system setting session-TARGET vsys2 set network virtual-router default routing-table ip static-route Default-Route-To-SharedGW destination 0.0.0.0/0 nexthop ip-address 10.254.254.1 interface ethernet1/2.20 // Return to global context set system setting session-TARGET none exit
4.7. Configure Security Policies - GUI
4.7.1. In
vsys2
(Tenant VSYS)
Switch context to
vsys2
.
- Navigate to Policies > Security . Click Add .
-
Name:
Allow-Finance-To-Internet -
Source Tab:
-
Source Zone:
Add
FINANCE-LAN. -
Source Address:
any(or specific subnets withinFINANCE-LAN).
-
Source Zone:
Add
-
Destination Tab:
-
Destination Zone:
Add
TO-SHAREDGW. -
Destination Address:
any.
-
Destination Zone:
Add
-
Application Tab:
any(or specific applications likessl,web-browsing). -
Service/URL Category Tab:
application-default. -
Actions Tab:
-
Action:
Allow. - Optionally, assign Security Profiles (Antivirus, Anti-Spyware, etc.). For a Shared Gateway setup, these profiles are often more effectively applied in the Shared Gateway VSYS for centralized control over internet traffic.
-
Action:
- Click OK .
4.7.2. In
vsys1
(Shared Gateway VSYS)
Switch context to
vsys1
.
- Navigate to Policies > Security . Click Add .
-
Name:
Allow-Tenants-To-Internet -
Source Tab:
-
Source Zone:
Add
INTERNAL-SHARED. -
Source Address:
any(or specifically192.168.20.0/24if you want to be granular about which tenant networks are allowed).
-
Source Zone:
Add
-
Destination Tab:
-
Destination Zone:
Add
UNTRUST. -
Destination Address:
any.
-
Destination Zone:
Add
-
Application Tab:
any(or be more specific). -
Service/URL Category Tab:
application-default. -
Actions Tab:
-
Action:
Allow. - Profile Setting: Assign relevant Security Profiles (Antivirus, Anti-Spyware, URL Filtering, WildFire Analysis, etc.) to inspect traffic to/from the internet.
-
Action:
- Click OK .
4.8. Configure Security Policies - CLI
configure // Switch to vsys2 context set system setting session-TARGET vsys2 set vsys vsys2 rulebase security rules Allow-Finance-To-Internet from FINANCE-LAN to TO-SHAREDGW source any destination any application any service application-default action allow // Switch to vsys1 context set system setting session-TARGET vsys1 set vsys vsys1 rulebase security rules Allow-Tenants-To-Internet from INTERNAL-SHARED to UNTRUST source any destination any application any service application-default action allow profile-setting group// Example // Return to global context set system setting session-TARGET none exit
4.9. Configure NAT Policy (Source NAT) in
vsys1
- GUI
Typically, outbound Source NAT is performed in the Shared Gateway VSYS (
vsys1
) to translate private IP addresses from tenant networks to the public IP address of the Shared Gateway's external interface.
Switch context to
vsys1
.
- Navigate to Policies > NAT . Click Add .
-
General Tab:
-
Name:
SNAT-Tenants-To-Internet
-
Name:
-
Original Packet Tab:
-
Source Zone:
Add
INTERNAL-SHARED. -
Destination Zone:
Add
UNTRUST. -
Destination Interface:
Any(or specificallyethernet1/1). -
Source Address:
any(or list all tenant internal subnets, e.g.,192.168.20.0/24). This is important for matching correctly. -
Destination Address:
any.
-
Source Zone:
Add
-
Translated Packet Tab:
-
Source Address Translation:
-
Translation Type:
Dynamic IP And Port. -
Address Type:
Interface Address. -
Interface:
ethernet1/1(the external interface). - IP Address: Select the specific IP if the interface has multiple, or leave as is if single.
-
Translation Type:
-
Source Address Translation:
- Click OK .
4.10. Configure NAT Policy (Source NAT) in
vsys1
- CLI
configure // Switch to vsys1 context set system setting session-TARGET vsys1 set vsys vsys1 rulebase nat rules SNAT-Tenants-To-Internet from INTERNAL-SHARED to UNTRUST source [ 192.168.20.0/24 ] destination any service any source-translation dynamic-ip-and-port interface-address interface ethernet1/1 // Return to global context set system setting session-TARGET none exit
Note: In the CLI `source` field for NAT, list the actual original source IPs/subnets from the tenant networks.
4.11. Commit Changes
After all configurations, commit the changes to the firewall.
GUI: Click Commit at the top right, then Commit again.
CLI:
commit
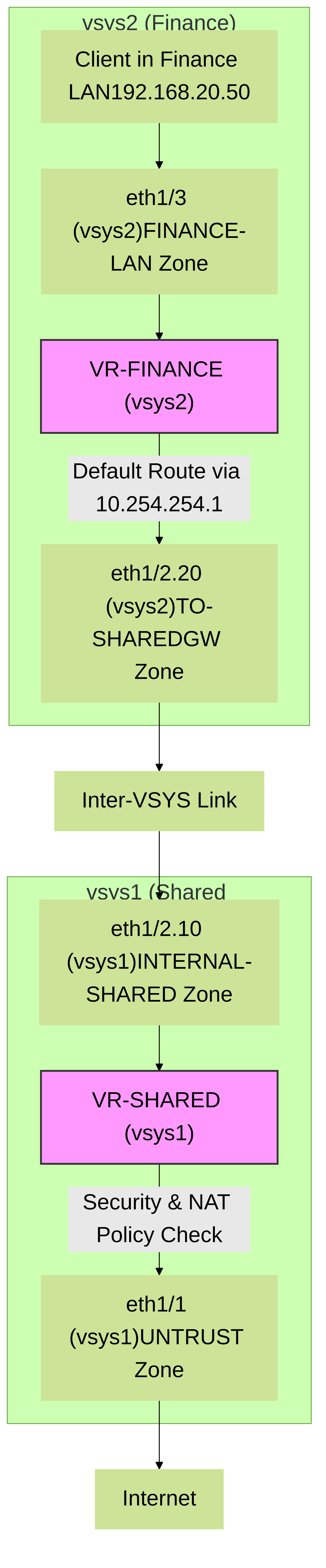
Figure 3: Simplified packet flow from a client in a tenant VSYS (vsys2) to the Internet via the Shared Gateway VSYS (vsys1). This illustrates routing hops and zone transitions.
5. Verification and Troubleshooting
5.1. GUI Verification
- Interface Status: Navigate to Network > Interfaces (within each VSYS context) to check if interfaces are up and have correct IP addresses.
- Routing Table: Navigate to Network > Virtual Routers > More Runtime Stats (select VR, then click link) to view the routing table within each VSYS. Verify default routes and routes to other VSYSs.
- Traffic Logs: Navigate to Monitor > Traffic (within each VSYS context). Filter for relevant source/destination IPs to see if traffic is hitting the correct policies and if NAT is being applied.
- Session Browser: Check active sessions.
5.2. CLI Verification and Troubleshooting
Use these commands after setting the correct VSYS context with `set system setting session-TARGET
-
show system info: Verify multi-VSYS mode is active. -
show vsys all: List all configured VSYSs and their IDs. -
show interface all: (Per VSYS) Displays status of all interfaces in the current VSYS. -
show routing route: (Per VSYS) Displays the routing table for the default VR or specified VR. -
show session all filter source <ip> destination <ip>: Check for active sessions.-
show session id <session_id>: For detailed session information, including NAT translation.
-
-
test routing fib-lookup virtual-router <vr_name> ip <destination_ip>: (Per VSYS) Simulates a FIB lookup to see which interface traffic would egress. -
show counter global filter packet-filter yes delta yes source <ip> destination <ip>: (Use with caution, can be verbose) Advanced packet diagnostics. -
debug dataplane packet-diag set filter match source <source_ip> destination <destination_ip> -
debug dataplane packet-diag set filter on -
show counter global filter aspect flow packet-filter yes debug yes delta yes(to view filtered packets). Remember to turn off debug after use: `debug dataplane packet-diag set filter off`.
6. Palo Alto Networks Best Practices for Shared Gateway
-
Dedicated Virtual Router:
Consider using dedicated virtual routers within each VSYS (e.g.,
VR-SHAREDinvsys1,VR-FINANCEinvsys2) rather than the default VR for better isolation and clarity, especially in complex setups. - Clear Naming Conventions: Use consistent and descriptive names for VSYSs, zones, interfaces, policies, and routes.
- Zone Protection Profiles: Apply Zone Protection Profiles to inter-VSYS link zones and external zones for enhanced security.
- Logging: Ensure comprehensive logging is enabled for traffic passing through the Shared Gateway VSYS. Forward logs to Panorama or a SIEM for centralized analysis.
- Panorama Management: For environments with multiple VSYSs, Palo Alto Networks Panorama is highly recommended for centralized management, policy deployment, and reporting. Panorama simplifies managing configurations across VSYSs and firewalls.
- Resource Monitoring: Regularly monitor CPU, memory, and session utilization on the firewall, particularly for the Shared Gateway VSYS, to ensure adequate resources.
- Security Profiles: Apply comprehensive security profiles (Threat Prevention, URL Filtering, WildFire, etc.) on the security policy in the Shared Gateway VSYS that allows traffic to the internet. This centralizes threat prevention for all shared traffic.
- Least Privilege Access: When defining security policies, adhere to the principle of least privilege. Only allow necessary applications and services between zones and VSYSs.
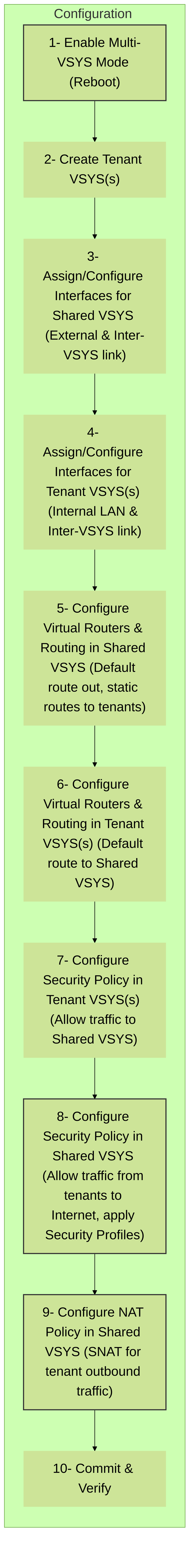
Figure 4: Palo Alto Networks Shared Gateway Configuration Workflow. This outlines the general sequence of steps for setting up the environment.
By following these guidelines and steps, you can effectively implement a Shared Gateway solution using Palo Alto Networks multi-VSYS capabilities, providing secure and efficient shared internet access for multiple logical firewall instances.