Credential Phishing Prevention Overview
Understanding credential phishing prevention is key for managing security policies effectively.
- Requires an Advanced URL Filtering license (or supported legacy license).
- Prisma Access licenses include this capability.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
Notes:
|
Phishing sites are sites that attackers disguise as legitimate websites with the intent to steal user information, especially the credentials that provide access to your network. When a phishing email enters a network, it takes just a single user to click a link and enter credentials to set a breach into motion.
You can detect and prevent in-progress phishing attacks, thereby preventing credential theft, by controlling sites to which users can submit corporate credentials based on the site’s URL category . This allows you to block users from submitting credentials to untrusted sites while allowing credential submissions to corporate and sanctioned sites.
Credential phishing prevention works by scanning username and password submissions to websites and comparing those submissions against valid corporate credentials. You can choose what websites you want to either allow or block corporate credential submissions to based on the URL category of the website.
When a user attempts to submit credentials to a site in a category you have restricted, either a block response page prevents the user from submitting credentials or a continue page warns users against submitting credentials to sites in certain URL categories, but still allows them to continue with the submission. You can customize response pages to educate users against reusing corporate credentials, even on legitimate, non-phishing sites.
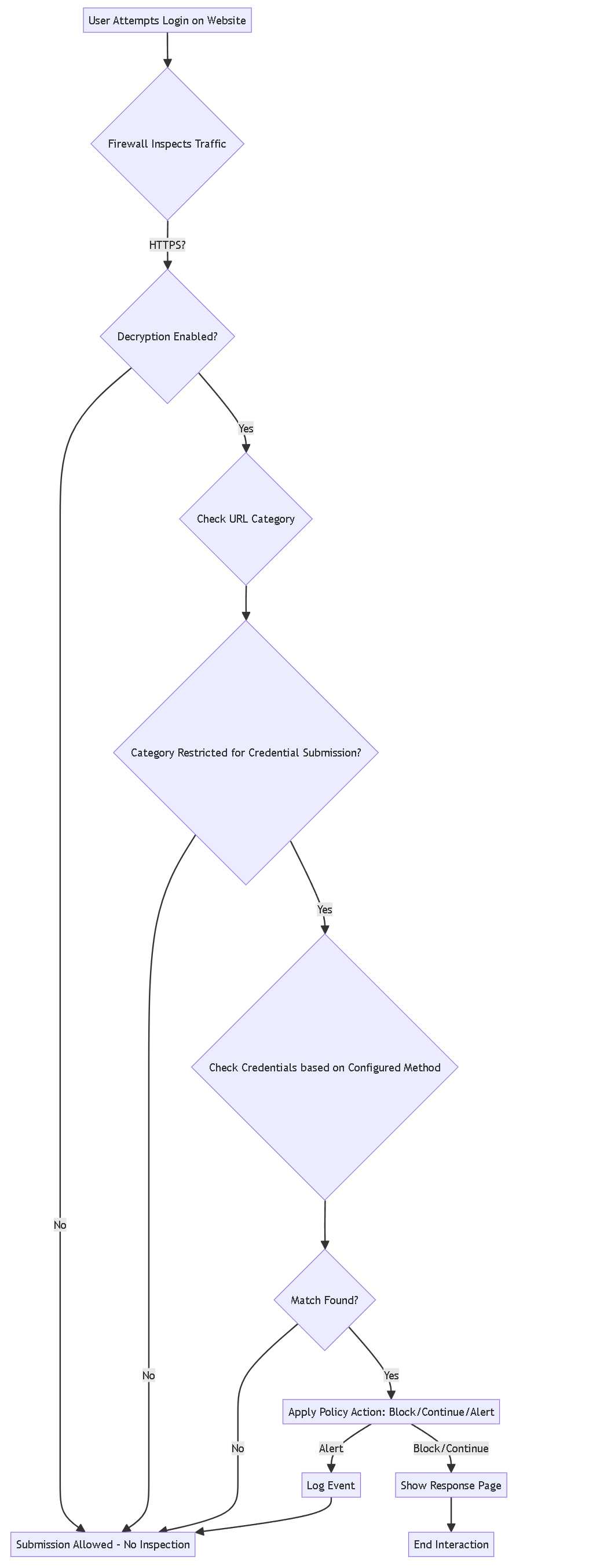
High-level flow of credential phishing prevention check.
Methods to Check for Corporate Credential Submissions
| Where can I use this? | What do I need? |
|---|---|
|
Notes:
|
Before you enable credential phishing prevention, decide which method you want to use to check if valid corporate credentials have been submitted to a web page.
| Method to Check Submitted Credentials | User-ID Configuration Requirements | How does this method detect corporate usernames and/or passwords? |
|---|---|---|
| Group Mapping | Group Mapping configuration on the firewall |
The firewall checks if the username submitted matches any valid corporate username in its user-to-group mapping table. This method only checks usernames based on LDAP group membership. Simple to configure, but prone to false positives (e.g., common usernames like 'admin'). Does not check passwords. |
| IP-User Mapping | IP address-to-username mappings via user mapping , GlobalProtect , or Authentication Policy/Portal |
The firewall checks if the username submitted maps to the IP address of the known logged-in user. Effective for detecting corporate username submissions tied to the session's source IP, but does not detect corporate password submission . |
|
Domain Credential Filter
Prisma Access doesn't support this method. |
|
Checks if the submitted username AND password match the user’s corporate credentials.
This is the most comprehensive method but requires specific infrastructure (Windows User-ID Agent on RODC). |
Configure Credential Detection with the Windows User-ID Agent
(Required for Domain Credential Filter Method)
| Where can I use this? | What do I need? |
|---|---|
|
Note: Legacy URL filtering licenses are discontinued, but active legacy licenses are still supported. |
Domain Credential Filter detection enables the firewall to detect passwords submitted to web pages. This method requires the Windows User-ID agent and the User-ID credential service (an add-on) installed on a read-only domain controller (RODC) .
An RODC maintains a read-only copy of an Active Directory database. Installing the User-ID agent on an RODC is useful because:
- Direct access to the writable domain controller directory is not required.
- You can target credential detection for a limited set of users defined in the RODC's Password Replication Policy (PRP).
- The main AD database remains secure on the writable domain controller.
Bloom Filter Process:
- The User-ID credential service runs on the RODC.
- It scans the directory for usernames and password hashes of users defined in the RODC Password Replication Policy (PRP).
- It deconstructs this data into a secure bit mask called a bloom filter .
- The User-ID credential service forwards the bloom filter to the Windows User-ID agent (also on the RODC).
- The firewall retrieves the latest bloom filter from this User-ID agent periodically.
- When the firewall detects a credential submission to a restricted site, it checks the submitted username/password hash against the bloom filter.
The User-ID agent never stores or exposes password hashes directly, nor does it forward them to the firewall. Once hashes are in the bloom filter, they cannot be recovered.
Configuration Steps Summary:
-
Install and Configure User-ID Agent on RODC:
- Refer to the Compatibility Matrix for supported OS versions.
- Install both the User-ID Agent (`UaInstall-x.x.x-x.msi`) and the User-ID Agent Credential Service (`UaCredInstall64-x.x.x-x.msi`). Download from Palo Alto Networks Support Portal .
- Use a service account with privileges to read AD via LDAP and be a member of the local administrator group on the RODC. Ensure it can log on as the local system account. See Create a Dedicated Service Account .
- Review RODC Administration Best Practices .
-
Enable Information Sharing in User-ID Agent:
- Launch the User-ID Agent on the RODC server.
- Go to Setup , edit the Setup section.
- Select the Credentials tab (visible only if the Credential Service is installed).
- Check Import from User-ID Credential Agent .
- Click OK, Save, and Commit the agent configuration.
-
Configure RODC Password Replication Policy (PRP):
- Define the group(s) of users for credential detection.
- Add these groups to the Allowed RODC Password Replication Group .
- Ensure these groups are not also in the Denied RODC Password Replication Group .
- Proceed to Firewall Configuration: Continue to the next section to configure the firewall settings.
Set Up Credential Phishing Prevention (Firewall Configuration)
| Where can I use this? | What do I need? |
|---|---|
|
Notes:
|
After deciding which user credential detection method to use and (if applicable) configuring the Windows User-ID agent , follow these steps on the firewall (PAN-OS/Panorama or Strata Cloud Manager).
sAMAccountName
attribute. Credential phishing prevention does not support alternate attributes for the primary username check.
Firewall Configuration Steps (PAN-OS / Panorama Example):
-
Enable User-ID:
Ensure User-ID is enabled and configured according to the chosen detection method:
- Group Mapping: Requires mapping users to groups .
- IP User Mapping: Requires mapping IP addresses to users (via Agent, Agentless, GlobalProtect, Auth Policy, etc.).
- Domain Credential Filter: Requires Windows User-ID Agent connection (configured on RODC) AND mapping IP addresses to users .
-
Configure URL Filtering Profile:
-
Go to
Objects > Security Profiles > URL Filtering. Add or modify a profile. -
(Best Practice) Block Dangerous Categories:
Under the
Categoriestab, setSite Accessto block for categories like:malware,phishing,dynamic-dns,unknown,command-and-control,extremism,copyright-infringement,proxy-avoidance-and-anonymizers,newly-registered-domain,grayware, andparked. -
Enable User Credential Detection:
-
Select the
Settingstab (or similar location depending on PAN-OS version/management interface). Find theUser Credential Detectionsection. -
Choose the desired
Mode
(detection method):
-
IP User Mapping -
Domain Credential Filter(Requires configuring the User-ID Agent connection underDevice > User Identification > User-ID Agentsand selecting it here). -
Group Mapping(Requires selecting the relevant Group Mapping profile).
Remember the requirements and limitations of each mode! -
-
Set the
Valid Username Detected Log Severity(default is medium).
-
Select the
-
Configure Actions for Allowed Categories:
-
Go back to the
Categoriestab. -
For each category where
Site Accessis set toalloworalert, choose an action forUser Credential Submission:-
alert: Log the submission but allow it. -
allow: (Default) Allow submission without specific logging beyond normal traffic logs. -
block: Prevent submission and display the anti-phishing block page. (Recommended for untrusted/risky categories like Social Networking, Webmail, etc.) -
continue: Display the anti-phishing continue page; user must click 'Continue' to submit. Logs the event.
Apply stricter actions (
blockorcontinue) to categories where users should generally not be entering corporate credentials. -
-
Go back to the
-
Click
OKto save the URL Filtering profile.
Note on Trusted Sites: The firewall maintains a list of "trusted" sites (updated via content updates) where credential checks are skipped for performance, even if checks are enabled for the category. Palo Alto Networks has not observed malicious activity on these sites. -
Go to
-
Create/Modify Decryption Policy:
Credential detection requires visibility into the HTTP POST data containing the username/password. Therefore, you must decrypt HTTPS traffic for the sites you want to monitor. Create a Decryption policy rule targeting the relevant source/destination zones, users, and services, setting the action to
Decrypt. -
Apply Profile to Security Policy:
-
Go to
Policies > Security. Add or modify a rule that allows the relevant web traffic (e.g., outbound web access). -
On the
Actionstab:-
Ensure
ActionisAllow. -
Set
Profile TypetoProfiles. -
In the
URL Filteringdropdown, select the profile you configured.
-
Ensure
-
Click
OKto save the rule.
-
Go to
- Commit Configuration: Commit the changes to the firewall/Panorama.
Monitor and Validate Credential Submissions
After configuration, monitor logs and use CLI commands to verify functionality.
Monitoring Logs:
-
ACC (Application Command Center):
Check widgets like
Hosts Visiting Malicious URLsfor context on phishing/malware site visits. -
URL Filtering Logs (
Monitor > Logs > URL Filtering):- Look for the Credential Detected column (add it if not visible). A 'Yes' indicates a potential corporate credential submission was detected in the HTTP POST based on the configured method.
- Log entry details will also show "Credential Detected: yes".
-
Filter by Action:
credential-phishing(for block/continue actions) or check logs where Action isalertorallowbut Credential Detected is 'Yes'.
Validation and Troubleshooting (CLI):
-
General Credential Filter Statistics:
> show user credential-filter statisticsOutput varies by detection method. For Domain Credential Filter, shows connected User-ID agents providing bloom filters and credential counts.
-
Group Mapping Statistics (Group Mapping method only):
> show user group-mapping statisticsShows profiles using Group Mapping detection and usernames detected during submissions.
-
User-ID Agent State (Especially for Domain Credential Filter):
> show user user-id-agent state allCheck the status of connected Windows User-ID agents. For agents providing bloom filters, look for bloom filter counts (updates received, failures, time since last update).
-
Windows User-ID Agent Logs (Domain Credential Filter method only):
On the Windows server hosting the User-ID agent, check the agent's logs (
Monitoring > Logsin the agent GUI). Look for messages related to BF (bloom filter) pushes to the firewall.
Credential Phishing Prevention Quiz
Test your understanding of the concepts covered.