Deep Dive: Customizing Service Routes in Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS
1. Understanding Service Routes in PAN-OS
In Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS, **Service Routes** are a critical configuration element that dictates which interface and source IP address the firewall uses for its self-generated (outbound) traffic to various essential services. By default, most of these services leverage the firewall's dedicated **Management (MGT) interface**. However, network architects and security administrators often need to customize these routes for enhanced security, network segmentation, compliance, or to utilize specific network paths with better performance or reachability.
Services that utilize service routes include, but are not limited to:
- DNS (Domain Name System) Resolution: For resolving FQDNs for PAN-OS updates, WildFire, URL filtering, etc.
- NTP (Network Time Protocol): For synchronizing the firewall's clock, essential for accurate logging and certificate validation.
- Syslog: For sending logs to external Syslog servers or SIEMs.
- Palo Alto Networks Updates: Downloading new versions of PAN-OS, application signatures (App-ID), threat signatures (Threat Prevention), antivirus signatures, and WildFire updates.
- WildFire Cloud Submissions & Lookups: Sending unknown files for analysis and retrieving verdicts from the Palo Alto Networks WildFire cloud.
- Cortex Data Lake (CDL): Streaming logs to the Palo Alto Networks cloud-based logging service.
- Panorama Communication: Traffic between the firewall and its Panorama management server, including configuration pushes, log forwarding (if not using dedicated log collectors), and heartbeats, if not using the MGT interface.
- User-ID Agent Communication: When the firewall initiates connections to Windows-based User-ID agents or the PAN-OS Integrated User-ID Agent queries domain controllers.
- External Dynamic Lists (EDLs): Fetching updates for IP address lists, URL lists, or domain lists from external web servers.
- VM Information Sources (Dynamic Address Groups): Connecting to VMware vCenter, NSX, AWS, Azure, GCP, etc., to learn VM attributes for tagging.
- SNMP Traps: Sourcing SNMP trap notifications.
- Email Alerts: Sourcing email notifications sent by the firewall.
- GlobalProtect Services: Fetching CRLs for certificate validation related to GlobalProtect.
The primary reason for customizing service routes is to redirect this traffic from the typically out-of-band MGT interface to an **in-band data interface** (e.g., Ethernet1/1, ae1). This might be necessary if the MGT network is isolated and doesn't have reachability to required external services, or if security policies dictate that such traffic must traverse a data path for inspection and logging.
2. Configuring Service Routes: Global and Per-VSYS
Service routes can be configured globally for the firewall or on a per-Virtual System (VSYS) basis in multi-VSYS environments.
A. Global Service Route Configuration
Global service routes apply to all services unless overridden by a VSYS-specific configuration.
- Navigate to Device > Setup > Services .
- Click the Service Route Configuration link (or gear icon in some PAN-OS versions) to open the settings.
- By default, "Customize" is usually unchecked, meaning services use the Management Interface. To change this, check Customize for the desired service(s).
-
For each service you wish to customize:
- Service: Select the specific Palo Alto Networks service (e.g., DNS, NTP, Palo Alto Networks Updates).
-
Source Address:
-
Interface:
Choose the desired data interface (e.g.,
ethernet1/1,ae1.100,tunnel.1,loopback.1). PAN-OS will use an IP address configured on this interface. If multiple IPs exist, it typically uses the primary or lowest numbered IP. - IP Address: In some specific cases, you might be able to specify a source IP. However, "Interface" is the common choice.
-
Interface:
Choose the desired data interface (e.g.,
- Click OK to save the changes. A commit is required for changes to take effect.
B. Custom Service Routes in Multi-VSYS Environments (Expanding on base HTML)
In environments with multiple virtual systems (VSYS), each VSYS can have its own service route configurations, providing granular control for different tenants or departments. This is particularly useful for Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) or large enterprises.
To customize service routes for a specific VSYS:
- Navigate to Device > Setup > Services .
- Select the Virtual Systems tab.
- Choose the desired VSYS from the list and click its name or the Service Route Configuration button/link associated with it.
- In the dialog that appears, select Customize . If this is unchecked, the VSYS inherits the global service route settings.
- Configure the source interface and address for each service as needed, similar to global configuration. The interfaces available will be those assigned to that specific VSYS.
Inheritance Model: If a VSYS does not have a specific service route configured (i.e., "Customize" is unchecked at the VSYS level for services), it inherits the global service route settings for those services. If the global settings are also default (not customized), then the MGT interface is used.
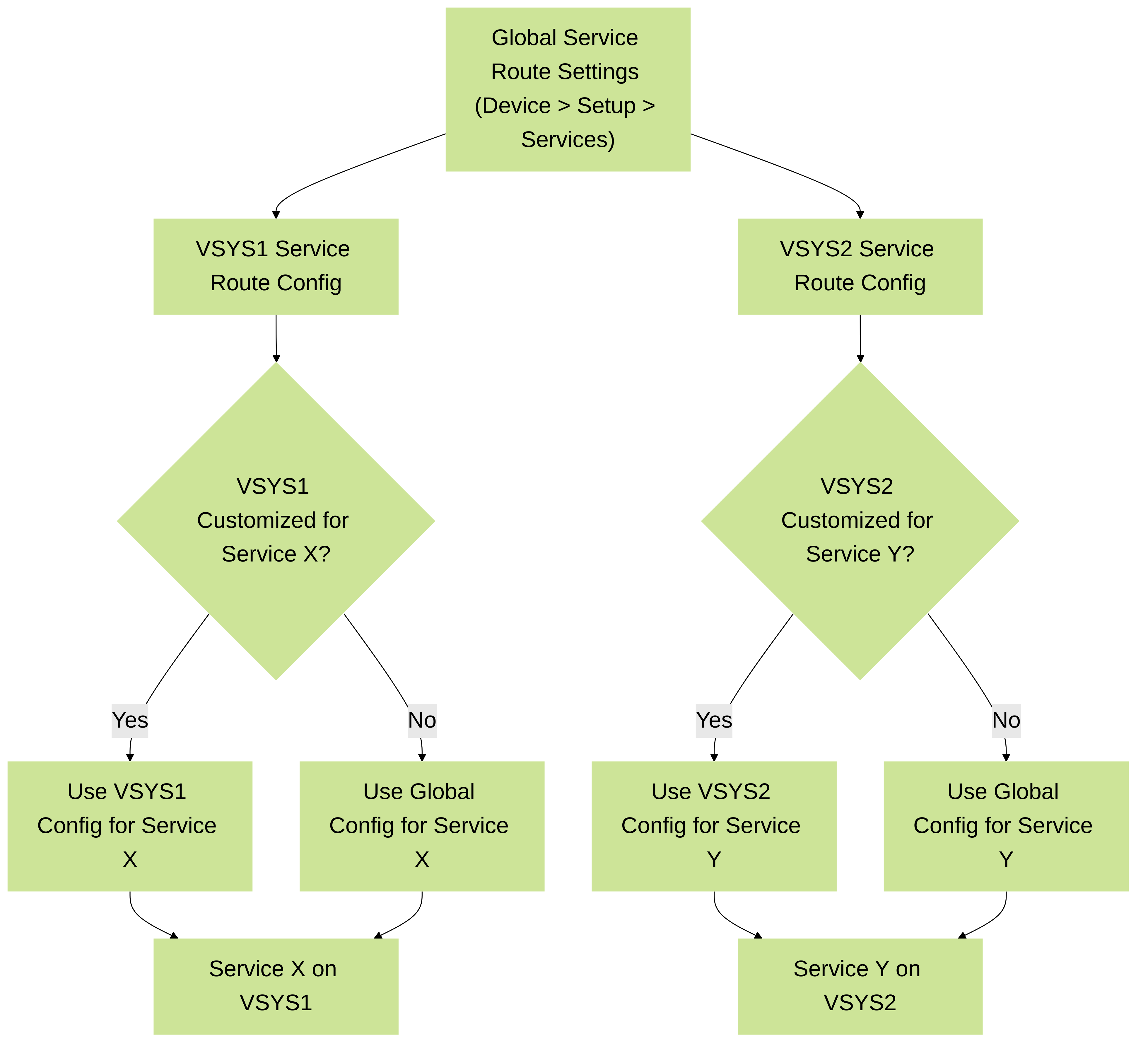
Palo Alto Networks Service Route Inheritance Model: Illustrates how a VSYS either uses its own customized service route or inherits the global configuration.
3. Critical Considerations When Using Data Interfaces for Service Routes
When configuring service routes to use data interfaces instead of the management interface, careful planning is essential. Failure to address these considerations can lead to service disruptions.
-
Routing and Reachability:
- The selected data interface must belong to a **Virtual Router (VR)** that has a valid route to the destination IP address(es) of the service. This could be a default route, a static route, or a route learned via a dynamic routing protocol (OSPF, BGP, RIP).
-
Verify routing using CLI commands like `test routing fib-lookup virtual-router
ip `. - If the MGT interface is in a separate VR (common practice), it won't provide routing for data plane interfaces.
-
Security Policies:
- Traffic originating from the firewall via a data interface for these services is subject to **Security Policy lookup**.
- You must create policies to explicitly allow this traffic. The source zone will be the zone to which the chosen data interface is assigned. The destination zone will typically be your "untrust" or internet-facing zone.
-
Required policy components:
- Source Zone: Zone of the service route interface.
- Source Address: IP of the service route interface (or `any`).
- Destination Zone: Zone leading to the service (e.g., `untrust`).
- Destination Address: FQDNs or IP addresses of the Palo Alto Networks services (e.g., `updates.paloaltonetworks.com`, specific IPs for regional WildFire clouds). Palo Alto Networks provides lists of required FQDNs/IPs .
- Application: Use specific Palo Alto Networks application IDs like `paloalto-updates`, `paloalto-wildfire-cloud`, `paloalto-dns-security`, `paloalto-cortex-data-lake`. For others like DNS or NTP, use `dns`, `ntp`. For general web-based services, `ssl` and `web-browsing` might be needed as dependencies.
- Service: `application-default` is recommended. Alternatively, specific ports (e.g., TCP/443 for most cloud services, UDP/53 for DNS, UDP/123 for NTP, TCP/UDP 514 for Syslog).
- Action: `Allow`.
- Logging: Enable logging for troubleshooting.
-
MTU Settings:
- Be cautious with Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) settings on the chosen data interface.
- Services like WildFire sample uploads can be sensitive to MTU mismatches or jumbo frames. If the interface MTU is set too high (e.g., 9000 bytes for jumbo frames) and path MTU discovery (PMTUD) isn't functioning correctly end-to-end, packets might be dropped or fragmented in a way that causes issues for the receiving Palo Alto Networks service.
- It's generally recommended to set the MTU on the service route interface to 1500 bytes or less or ensure PMTUD works flawlessly. For Palo Alto Networks cloud services, they expect standard MTU sizes.
-
SSL/TLS Decryption:
- DO NOT apply SSL Forward Proxy decryption to traffic destined for Palo Alto Networks services (e.g., WildFire, PAN-OS Updates, Cortex Data Lake, Panorama communications).
- These services often use certificate pinning or mutual authentication. Decrypting and re-encrypting this traffic with the firewall's certificate will break the trust chain and cause the services to fail.
- Create explicit No Decryption policies for the FQDNs/IPs associated with these Palo Alto Networks services.
-
Source IP Address Selection:
- When you select an "Interface" as the source in the service route configuration, PAN-OS will choose an IP address from that interface. If the interface has multiple IP addresses (e.g., secondary IPs on a Layer 3 interface, or multiple IPs on subinterfaces sharing a physical port), PAN-OS typically uses the numerically lowest IP address on the physical interface or the primary IP address if explicitly configured.
- For precise control, consider using a dedicated Loopback interface with a single IP address for critical services and then select this Loopback interface in the service route. Ensure this Loopback interface's IP is routable and included in relevant security policies and NAT (if needed).
-
NAT (Network Address Translation):
- If the IP address of the chosen data interface is a private IP (RFC 1918) and the service it needs to reach is on the public internet, a Source NAT (SNAT) policy will be required.
- The service route determines the source interface and IP, but NAT policies handle the translation if needed. Ensure the SNAT policy correctly translates the firewall's service traffic to a routable public IP.
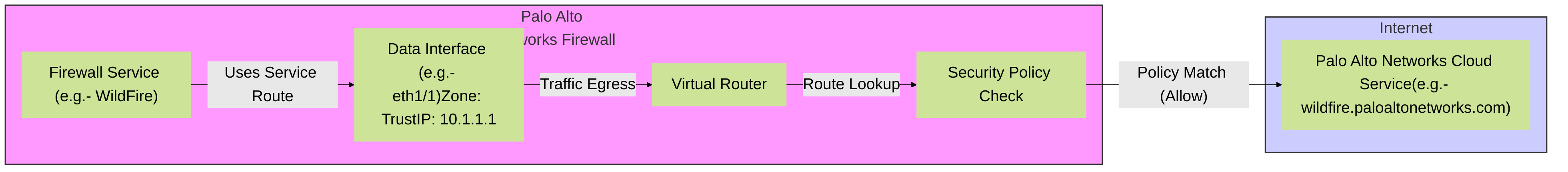
Palo Alto Networks Traffic Flow for a Service Route using a Data Interface: Illustrates how firewall-initiated traffic egresses a data interface, undergoes routing and security policy checks before reaching the external service.
4. Service-Specific Considerations for Custom Routes
Different Palo Alto Networks services have nuances when customizing their service routes:
| Service | PAN-OS Application ID(s) | Common Ports | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| DNS |
dns
|
UDP/53, TCP/53 | Firewall needs to resolve FQDNs for many other services. Ensure DNS servers are reachable via the chosen route. If using DNS Proxy, this setting dictates the source for proxied queries. |
| NTP |
ntp
|
UDP/123 | Essential for time-sensitive operations, logs, certificates. |
| Syslog |
syslog
|
UDP/514, TCP/514, TCP/6514 (secure syslog) | Ensure reachability to SIEM/Syslog server. Each Syslog Server Profile can use the default or a custom service route. |
| Palo Alto Networks Updates (Software, Content) |
paloalto-updates
,
ssl
,
web-browsing
|
TCP/443 |
Critical for security posture. Requires access to
updates.paloaltonetworks.com
and CDNs. MTU and SSL Decryption (No Decrypt) are key.
|
| WildFire |
paloalto-wildfire-cloud
,
ssl
,
web-browsing
|
TCP/443 |
Requires access to regional WildFire clouds (e.g.,
wildfire.paloaltonetworks.com
,
eu.wildfire.paloaltonetworks.com
). MTU and SSL Decryption (No Decrypt) are critical. Ensure correct regional cloud is selected.
|
| Cortex Data Lake |
paloalto-cortex-data-lake
,
ssl
|
TCP/443, TCP/3978 (older logging service port, less common now for CDL) | For log streaming. Requires access to regional CDL endpoints. SSL Decryption (No Decrypt) is critical. |
| Panorama |
panorama
,
ssl
|
TCP/3978 (for device-to-Panorama), TCP/443 (for GUI access if relevant) | Ensure firewall can reach Panorama IP/FQDN. Important for management and log collection. |
| External Dynamic Lists (EDL) |
ssl
,
web-browsing
|
TCP/443 (HTTPS), TCP/80 (HTTP) | Firewall fetches EDL source files. Ensure reachability to the web server hosting the EDL. |
| VM Information Sources (e.g., vCenter, AWS) |
ssl
, (service specific e.g.
vmware-vim
for vCenter)
|
TCP/443 (typically) | For Dynamic Address Groups. Requires network access to the management plane of these platforms. |
paloalto-wildfire-cloud
,
paloalto-updates
). This is essential for writing correct security policies when service routes use data interfaces.
5. Panorama and Service Routes
When managing firewalls with Panorama, service route configurations can be pushed using Templates or Template Stacks.
-
Templates:
You can define service route configurations within a Template in Panorama (
Panorama > Templates >).> Device > Setup > Services - Template Stacks: These templates can then be applied to Device Groups. Firewalls in those Device Groups will inherit the service route settings.
- Overrides: It's possible to override template settings locally on the firewall, but this is generally discouraged for consistency. If local overrides are necessary, ensure they are well-documented.
- VSYS on Panorama: If configuring for specific VSYS, you'd typically select the VSYS context within the template or when targeting specific devices.
Using Panorama ensures consistent service route configurations across multiple firewalls, reducing manual effort and potential misconfigurations.
6. Troubleshooting Custom Service Routes
When services fail after customizing service routes, follow a systematic troubleshooting approach:
A. Verification Commands (PAN-OS CLI)
-
show service-route config service <service_name>: Displays the configured service route for a specific service (e.g.,dns,wildfire).admin@PA-VM> show service-route config service wildfire Service Source Address Source If/Zone --------------------------------------------------- wildfire interface ethernet1/2
-
show service-route effective-config service <service_name>: Crucial for VSYS environments. Shows the actual service route in effect, considering global and VSYS-specific settings.admin@PA-VM(vsys1)> show service-route effective-config service ntp Service Source Address Source If/Zone --------------------------------------------------- ntp interface ethernet1/3
-
show routing route: Displays the firewall's routing table. Verify a route exists for the service destination via the chosen VR. -
test routing fib-lookup virtual-router <vr_name> ip <destination_ip>: Checks the Forwarding Information Base (FIB) for a specific destination IP through a specified VR. This confirms egress interface.admin@PA-VM> test routing fib-lookup virtual-router default ip 8.8.8.8 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- runtime route lookup -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- virtual-router: default destination: 8.8.8.8 result: interface ethernet1/1, nexthop 192.168.1.254 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
ping source <source_ip_on_data_interface> host <destination_ip>: Tests basic IP connectivity from the chosen source interface/IP. (Ensure correct VR context if needed: `ping vrsource host `). -
show session all filter source <chosen_source_ip> destination <service_destination_ip> destination-port <service_port>: Checks for active sessions related to the service. Look for session state and any deny actions.
B. Logs and Packet Captures
- Traffic Logs: Filter by the source IP of the service route interface and the destination IP/port of the service. Look for `allow` or `deny` actions. Check if the correct application is identified.
-
System Logs:
(
Monitor > Logs > System) Often provide high-level error messages for service failures (e.g., "WildFire registration error," "Failed to download updates"). -
Packet Captures (PCAPs):
- Configure on the chosen data interface.
- Filter for traffic to/from the service destination IPs/ports.
- Helps verify if traffic is leaving the interface, if replies are received, or if TCP handshakes are failing.
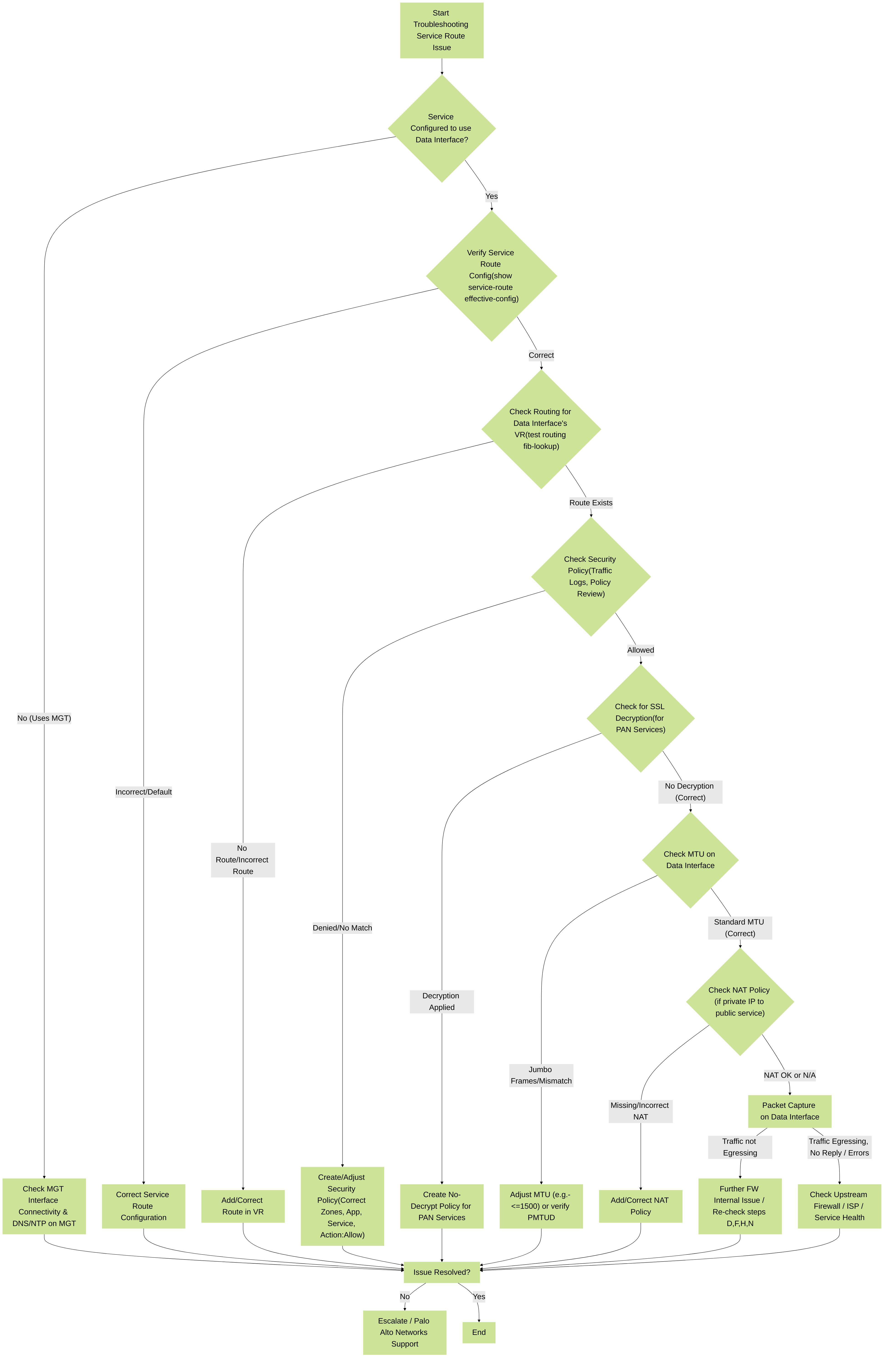
Palo Alto Networks Service Route Troubleshooting Flowchart: A decision tree to help diagnose issues when services routed via data interfaces fail.
C. Common Pitfalls Checklist
- Missing/Incorrect Security Policy: Most common issue. Ensure source/destination zones, addresses, application, service, and action are correct.
- No Route to Destination: The VR for the data interface must have a path.
- NAT Misconfiguration: If private IPs from data interface need to reach public services.
- SSL Decryption Applied to PAN-OS Services: Create No-Decrypt rules.
- MTU Issues: Especially for WildFire and updates.
- Incorrect Source Interface/IP Selected: Double-check service route configuration.
- DNS Resolution Failure: If the firewall itself cannot resolve service FQDNs using its configured DNS service route.
- Upstream Device Blocking: Check intermediate firewalls or routers.
- Service FQDNs/IPs Changed: Palo Alto Networks services might update their backend infrastructure IPs. Use FQDN objects in policies where possible.
- Commit Not Performed: Changes are not active until committed.
7. Best Practices for Custom Service Routes
- Principle of Least Necessity: Use the MGT interface for management-plane services by default. Only customize service routes to data interfaces if there's a clear architectural, security, or connectivity requirement.
- Dedicated Interfaces: If using data interfaces, consider using dedicated Layer 3 interfaces or subinterfaces for critical services like Panorama connectivity or updates, rather than heavily utilized user traffic interfaces. Loopback interfaces are also a good option for a stable source IP.
- Robust Routing: Ensure the routing to service destinations via the chosen data interface is stable and resilient.
- Explicit Security Policies: Always create specific, explicit security policies. Use FQDN objects for Palo Alto Networks services and appropriate App-IDs. Avoid overly broad `any/any/any` rules.
- Regular Review: Periodically review service route configurations, especially after network changes or PAN-OS upgrades. Check Palo Alto Networks documentation for any changes to required FQDNs/IPs for their services.
- Documentation: Document your service route strategy, including which services use which interfaces and the rationale.
- Testing: After any change to service routes, routing, or security policies, thoroughly test the affected services (e.g., force an update check, test WildFire upload, verify Panorama connection).
- Monitor Services: Implement monitoring for critical services that rely on custom routes to detect failures proactively.
- Consistent Configuration with Panorama: For multi-firewall deployments, use Panorama Templates and Template Stacks to maintain consistent service route configurations.
8. Summary of Key Palo Alto Networks Terminology
- Service Route: A PAN-OS setting that determines the source interface and IP address the firewall uses for its outbound communications to specific services.
- Management (MGT) Interface: A dedicated out-of-band interface on Palo Alto Networks firewalls primarily used for device management, and by default, for many system services.
- Data Interface: An in-band interface (e.g., ethernet1/1, ae1) that processes network traffic according to security policies. Can be used as a source for service routes.
- Virtual System (VSYS): A segmentation feature on Palo Alto Networks firewalls that allows a single physical device to act as multiple independent logical firewalls. Each VSYS can have its own service routes.
- Virtual Router (VR): A logical router instance within PAN-OS. Each data interface is assigned to a VR, which maintains its own routing table. Essential for service route path determination.
- Panorama: Palo Alto Networks centralized network security management solution. Used to manage firewalls, including pushing service route configurations via templates.
- App-ID: Palo Alto Networks patented traffic classification technology that identifies applications regardless of port, protocol, encryption (SSL/TLS), or evasive tactics. Used in security policies for service traffic.
- WildFire: Palo Alto Networks cloud-based malware analysis service. Uses service routes for sample submission and verdict retrieval.
- Cortex Data Lake (CDL): Palo Alto Networks cloud-based logging service. Uses service routes for log streaming.