Palo Alto Networks: URL Filtering vs. Advanced URL Filtering
Controlling web access is a fundamental aspect of network security. Palo Alto Networks offers two primary subscription services for this purpose: the standard URL Filtering subscription and the premium Advanced URL Filtering (Adv. URL) subscription. Both aim to protect users and networks from web-based threats and enforce acceptable use policies, but they employ different technologies and address different types of risks.
This article, based on Palo Alto Networks documentation and related web searches, compares and contrasts these two subscriptions, highlighting their features, key differences, and aspects crucial for the PCNSE certification.
Understanding when and why to use each subscription is vital for designing effective web security policies with Palo Alto Networks NGFWs.
URL Filtering (Standard): The Foundation of Web Control
The standard URL Filtering subscription provides foundational web security and content control capabilities. Its core component is PAN-DB , Palo Alto Networks' proprietary URL database, which contains millions of URLs categorized into various groups (e.g., Malware, Phishing, Gambling, Social Networking).
Key features of the standard URL Filtering subscription include:
- PAN-DB Cloud Database: Provides access to a constantly updated cloud database of categorized URLs. The firewall regularly downloads updates for its local database copy (or uses cloud lookups depending on configuration).
- URL Category Control: Allows administrators to define actions (e.g., `allow`, `alert`, `block`, `continue`, `override`) based on URL categories.
- Custom URL Categories: Enables administrators to create their own categories containing specific URLs or URL patterns.
- Block and Allow Lists: Define specific URLs that should always be blocked or allowed, irrespective of their category.
- Safe Search Enforcement: Can enforce safe search settings for major search engines (Google, Bing, YouTube, etc.) to filter explicit content.
- HTTP Header Logging: Logs User-Agent and Referer information from HTTP requests for better visibility.
- Credential Phishing Prevention: Provides mechanisms to detect and prevent users from submitting corporate credentials to websites based on category or custom lists (requires user mapping and careful configuration).
Standard URL Filtering relies on the accuracy and timeliness of PAN-DB updates to protect against known malicious or undesirable sites.
URL Filtering: Detailed Feature Explanations
Let's examine the components of the standard URL Filtering subscription more closely:
PAN-DB and Categorization
- Mechanism: The firewall checks the requested URL against its local PAN-DB cache/database. If not found locally, it may query the PAN-DB cloud (depending on PAN-OS version and configuration).
- Categories: PAN-DB includes dozens of categories, including security-focused ones (`malware`, `phishing`, `command-and-control`) and content/policy-based ones (`gambling`, `adult`, `social-networking`).
- Updates: The firewall downloads PAN-DB updates regularly (typically multiple times per day) to stay current with known site classifications.
- Uncategorized URLs: URLs not present in PAN-DB are classified as `not-resolved` or `unknown`. Policies must define how to handle these.
URL Filtering Profile Actions
- `allow`: Permits access without interruption.
- `alert`: Permits access but generates a log entry.
- `block`: Denies access and presents a block page.
- `continue`: Presents a warning page that the user must acknowledge to proceed. Logs the event.
- `override`: Presents a page requiring a password to proceed. Logs the event. Useful for temporary exceptions.
- Actions are applied per category.
Custom URL Controls
- Custom URL Categories: Group specific URLs (e.g., internal tools, specific partner sites) for targeted policy actions.
- External Dynamic Lists (EDL): URL lists can be hosted externally and dynamically imported by the firewall, useful for integrating with third-party threat feeds.
- Block/Allow Lists: Defined directly in the URL Filtering profile, these lists take precedence over category-based actions for the specified URLs.
Safe Search Enforcement
- Mechanism: When enabled, the firewall intercepts search queries to supported engines and injects HTTP headers or modifies query parameters to enforce the strictest safe search level offered by the search engine.
- Requirement: Typically requires SSL/TLS Decryption for HTTPS search traffic.
Credential Phishing Prevention (Standard)
- User-to-Site Submission: Detects when users (identified via User-ID) attempt to submit their corporate username or password (based on group mapping) to websites belonging to specific URL categories (e.g., `phishing`, `unknown`, or even custom lists). Actions can be `alert` or `block`.
- Site-to-User Password Reuse: Can detect if a password submitted to an external site matches the user's corporate password (less common implementation due to security implications of password handling).
- Requirement: Requires User-ID configuration, group mapping, and often SSL Decryption.
Standard URL Filtering provides robust control over access to known websites but is inherently reactive to newly created malicious sites.
Advanced URL Filtering (Adv. URL): Proactive Web Threat Prevention
Advanced URL Filtering is a premium subscription designed to overcome the limitations of database-only approaches by adding real-time, inline detection capabilities for web-based threats .
Key Enhancements Introduced by Advanced URL Filtering:
- Inline Deep Learning / Machine Learning: Analyzes web page content, structure, and code (e.g., JavaScript) in real-time as the user accesses the site.
- Zero-Day Web Threat Detection: Identifies and blocks malicious URLs and web content (like phishing pages, malware distribution sites, web-based exploits) *before* they are classified in PAN-DB.
- Real-time Cloud Intelligence: Leverages Palo Alto Networks' cloud infrastructure for instant analysis of uncategorized or suspicious URLs and for continuous updates to ML models.
- Detection of Evasive Threats: Designed to catch short-lived malicious sites, sites using URL manipulation, and those hosting malicious scripts that database lookups might miss.
- Potentially Enhanced Credential Phishing Prevention: May use ML to better identify sophisticated credential theft pages beyond simple category matching.
Advanced URL Filtering shifts web security from being purely reactive based on known classifications to being proactive and predictive based on real-time analysis.
Advanced URL Filtering: Key Advanced Features
The power of Advanced URL Filtering comes from its dynamic, inline engines:
Inline Deep Learning / Machine Learning for Web Threats
- Mechanism: The firewall, assisted by cloud intelligence, analyzes various aspects of a web page request and response in real-time. This includes URL structure, HTML content, JavaScript behavior, site reputation, and more.
-
Focus:
- Zero-Day Phishing Detection: Identifies phishing pages based on page structure, form elements, and resemblance to legitimate login pages, even if the URL is brand new.
- Malicious JavaScript Detection: Detects and blocks harmful scripts (e.g., cryptojackers, exploit kits loaders, advanced skimmers) embedded in web pages inline.
- Detection of Malicious URLs: Identifies newly registered domains or URLs exhibiting characteristics commonly associated with malware distribution or C2 infrastructure.
- Benefit: Provides instant protection against web threats that haven't yet been seen or categorized by PAN-DB, significantly reducing the risk from novel attacks.
- Operation: Occurs inline as part of the firewall's single-pass architecture when the Advanced URL Filtering license is active and relevant settings are enabled in the URL Filtering profile. Requires SSL Decryption for HTTPS.
Real-time Cloud Analysis and Updates
- Mechanism: For URLs that are uncategorized or deemed suspicious by initial checks, the firewall can perform real-time lookups against Palo Alto Networks' cloud threat intelligence network. ML models used for inline analysis are also continuously updated via the cloud.
- Benefit: Provides the most current threat intelligence available, faster than traditional database download cycles. Catches threats leveraging very short-lived domains or infrastructure.
Enhanced Credential Phishing Prevention
- Potential Enhancements: Adv. URL may leverage its ML capabilities to analyze login pages more deeply, potentially identifying sophisticated phishing attempts that mimic corporate portals even if the URL category isn't explicitly 'phishing' in PAN-DB yet. (Specific implementation details may vary by PAN-OS version).
Advanced URL Filtering essentially adds an intelligent, real-time analysis layer on top of the traditional database lookup, providing a much more robust defense against modern, dynamic web threats.
Feature Comparison: URL Filtering vs. Advanced URL Filtering
This table summarizes the key capabilities and differences:
| Feature / Aspect | URL Filtering (Standard) | Advanced URL Filtering (Adv. URL) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Subscription | Foundation Subscription | Premium Subscription (Includes all Standard UF features) |
| Primary Technology | PAN-DB (Categorized URL Database) | PAN-DB + Inline ML/AI Analysis + Real-time Cloud Intelligence |
| Focus | Known Malicious/Undesirable Sites, Policy Enforcement | Known Sites + Unknown/Zero-Day Web Threats (Phishing, Malware URLs, Malicious Scripts) |
| Detection of Known Malicious URLs | Yes (via PAN-DB categories) | Yes (via PAN-DB categories) |
| Detection of Unknown/New Malicious URLs | Delayed (Requires PAN-DB update) | Yes (Real-time via Inline ML/Cloud Lookup) |
| Zero-Day Phishing Page Detection | Limited (Relies on category update) | Yes (Inline ML analysis of page content/structure) |
| Inline Malicious Script Detection | No (Relies on AV/ATP for file download, not inline script execution) | Yes (Inline ML analysis of JavaScript etc.) |
| Detection Speed (New Threats) | Reactive (Latency based on DB update cycle) | Proactive / Near Real-time |
| Credential Phishing Prevention | Yes (Category/List-based) | Yes (Category/List-based + potential ML enhancements) |
| Requires SSL Decryption (for HTTPS) | Yes (for full URL/content visibility) | Yes (Essential for inline analysis of encrypted traffic) |
| Licensing | Standard Subscription | Premium Subscription (Separate license required) |
Key Differences & PCNSE Focus
Summarizing the crucial distinctions for PCNSE preparation:
-
Primary Technology & Scope:
- Standard UF: Relies on PAN-DB (database) for known URL classifications. Primarily blocks known bad or unwanted categories.
- Advanced UF: Adds inline ML/AI and real-time cloud lookups to detect *unknown* malicious URLs, zero-day phishing sites, and malicious scripts *before* they hit a database.
-
Handling of New Threats:
- Standard UF: Reactive. Protection depends on the speed of PAN-DB updates. There's an inherent delay.
- Advanced UF: Proactive. Inline analysis provides immediate detection and prevention opportunities for novel web threats.
-
Detection Engine Location:
- Standard UF: Database lookup (local cache/DB or cloud lookup for PAN-DB).
- Advanced UF: Database lookup + Inline analysis engine (on firewall, assisted by cloud) operating in the data plane.
-
Licensing Model:
- Standard UF: A base-level subscription.
- Advanced UF: A separate, premium subscription license. Crucially, activating Adv. URL automatically includes the standard URL Filtering functionality; you don't need both licenses active.
-
Configuration:
- Both are configured within URL Filtering Security Profiles . Advanced URL Filtering simply enables additional detection mechanisms and potentially new actions/settings within that same profile type when the license is active.
-
Decryption Requirement:
- While beneficial for standard UF (to see full URLs in HTTPS), decryption is essential for Advanced URL Filtering to perform its inline content analysis (HTML, JavaScript) on HTTPS traffic. Without decryption, Adv. URL has very limited visibility into encrypted web sessions.
PCNSE Scenario Example
Scenario: An organization is highly concerned about targeted phishing attacks using newly registered domains (NRDs) that host convincing replicas of their Office 365 login page. These sites are often live for only a few hours, potentially before PAN-DB can classify them.
Solution Focus: This scenario strongly indicates the need for Advanced URL Filtering . Its inline ML engine can analyze the structure and content of the unknown webpage in real-time. It can identify characteristics of a phishing page (login forms, resemblance to known brands, suspicious scripts) and block access instantly, even if the URL itself has zero history or reputation in PAN-DB.
Configuration: Ensure the Advanced URL Filtering license is active, configure a URL Filtering profile with strict actions for malicious categories and enable the advanced detection features (often implicitly enabled by the license but verify settings), ensure SSL Decryption is applied to relevant traffic, and attach the profile to the appropriate Security Policy rules.
Choosing between standard and Advanced URL Filtering depends on the organization's risk tolerance, exposure to novel web threats, and budget. For comprehensive protection against modern, dynamic web attacks, Advanced URL Filtering offers significant advantages.
Illustrations: Simplified URL Filtering Processing Flow
This diagram illustrates the conceptual flow when a URL request is processed:
Simplified flow showing initial checks (cache, lists), PAN-DB lookup, and the branch for Advanced URL Filtering inline analysis if licensed and the URL isn't definitively classified by PAN-DB.
Illustrations: URL Lookup Sequence Example
This sequence diagram shows the lookup process for a requested URL, highlighting the Adv. URL path:
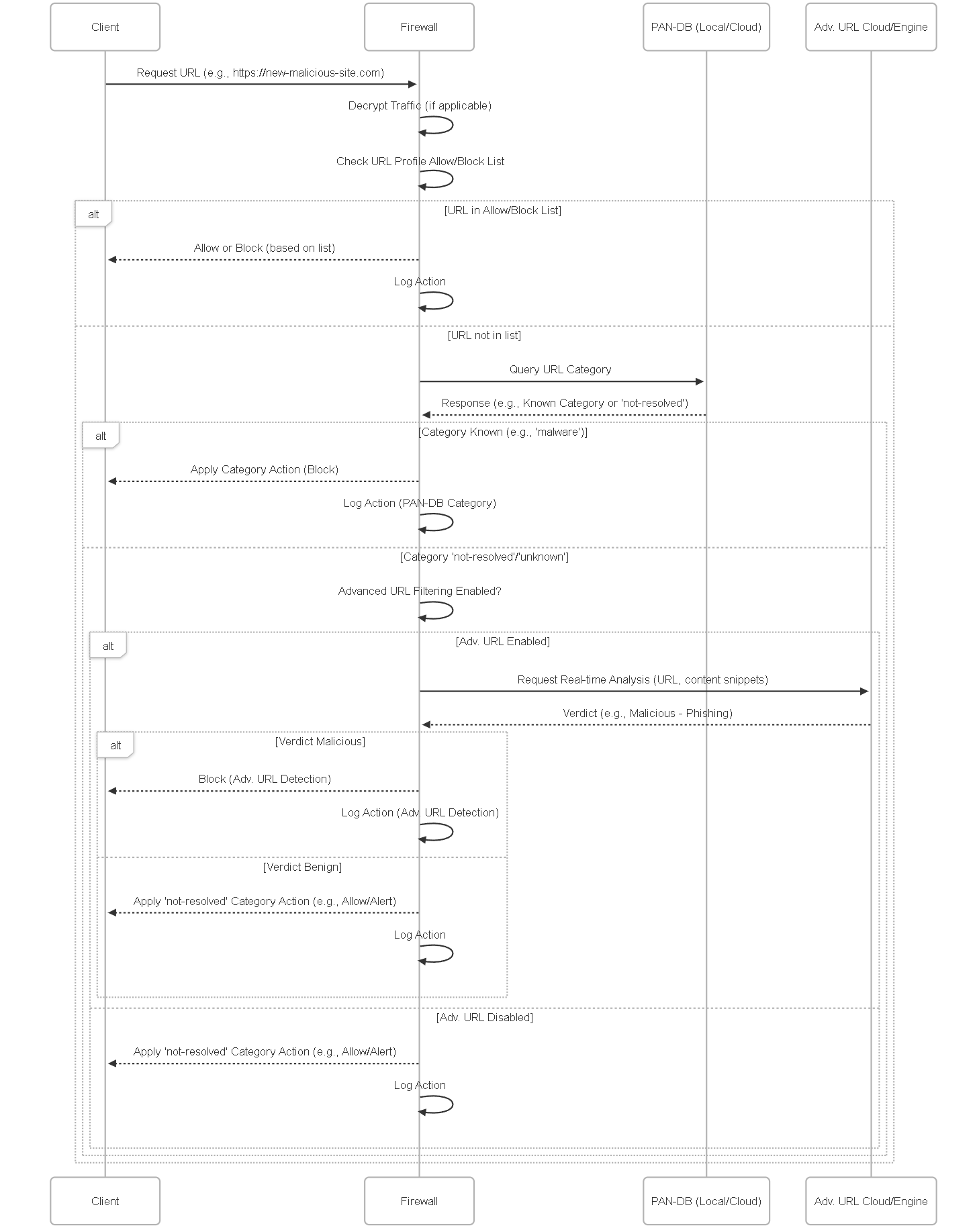
Sequence showing how Adv. URL provides a real-time analysis step for unknown URLs, potentially leading to a malicious verdict and block before PAN-DB is updated.
Illustrations: Simplified URL State Example
This state diagram illustrates the possible classification states of a URL during processing:
State diagram showing the path a URL takes. Adv. URL introduces the `Adv_URL_Analysis` state for unknown URLs, potentially leading to an `Action_Adv_Malicious` state based on real-time detection.
PCNSE Prep Quiz: URL Filtering vs. Advanced URL Filtering
Test your understanding of Palo Alto Networks URL Filtering subscriptions.