Introduction: Modernizing Firewall Policies
This document explores the Palo Alto Networks Policy Optimizer tool, a key feature for modernizing firewall policy rules. It specifically focuses on how the tool facilitates the migration from traditional port- and protocol-based rules to the more granular and secure App-ID based approach.
Adopting App-ID provides significant security benefits by identifying applications regardless of port, protocol, or evasion tactics. However, migrating a large, existing rule base can be challenging. The Policy Optimizer aims to streamline this process, providing visibility and recommendations.
Policy Optimizer: Overview
The Policy Optimizer is a feature integrated within the Palo Alto Networks firewall management interface (both web UI and Panorama). Its primary function is to help administrators analyze existing security policy rules and identify opportunities for improvement.
Key capabilities include:
- Analyzing rule usage based on traffic logs.
- Identifying rules that can be converted from Service (port/protocol) to Application (App-ID).
- Suggesting App-IDs for existing Service-based rules.
- Highlighting unused or shadowed rules.
- Facilitating the conversion or modification of rules based on analysis.
It acts as a guide to transition towards an application-centric policy structure, aligning with the best practices of next-generation firewall security.
Migration Process: Ports/Protocols to App-ID
Migrating from traditional Service-based rules to App-ID involves several steps, primarily guided by the Policy Optimizer:
- **Traffic Logging & Analysis:** Ensure logging is enabled for relevant rules. The Policy Optimizer analyzes traffic logs to understand what applications are actually using the Service/Port.
- **Policy Optimizer Scan:** Run the Policy Optimizer scan (typically on 'Service-based' rules or 'Unused Rules'). The tool will present rules and suggest identified applications based on observed traffic.
- **Review Suggestions:** Carefully review the suggested App-IDs for each rule. Ensure the suggested applications align with the intended purpose of the rule. You might find unexpected applications using standard ports (e.g., peer-to-peer over HTTP/80).
-
**Refine Rules:** Modify the rules based on the findings.
- For rules where a single, expected App-ID is identified, convert the rule to use that specific App-ID instead of the Service.
- For rules with multiple identified applications, create new, more specific rules for critical applications and potentially leave less critical ones aggregated, or split the rule.
- Decide how to handle 'unknown-tcp', 'unknown-udp', and 'incomplete' sessions.
- **Implement Changes (Test & Commit):** Make the changes in a test environment first if possible. Otherwise, implement changes during a maintenance window. Always commit and push changes to the firewall.
- **Monitor & Iterate:** Continuously monitor the traffic matching the modified rules. Use traffic logs and the Policy Optimizer again to catch anything missed or any applications that weren't active during the initial scan period. This is an iterative process.
Policy Optimizer: Best Practices
To effectively leverage the Policy Optimizer and transition to App-ID based policies, consider the following best practices:
- **Start with High-Hit Count Rules:** Prioritize rules with the most traffic. This gives the Policy Optimizer more data to work with and addresses the busiest parts of your rulebase first.
- **Analyze One Application (or small group) at a Time:** Instead of trying to convert everything at once, focus on identifying and migrating rules for specific critical applications (e.g., SharePoint, SQL, SSH).
- **Extend Log Collection Period:** Allow logs to be collected for a sufficient period (e.g., 7-30 days, depending on the traffic cycle) before running the Policy Optimizer scan. This ensures a comprehensive view of the applications using a service.
- **Use Application Filter Objects:** Group similar applications using Application Filters. This simplifies rule management when dealing with suites of applications (e.g., 'microsoft-office-365').
- **Address Unknown/Incomplete Traffic:** Develop a strategy for traffic that the firewall cannot identify ('unknown-tcp', 'unknown-udp') or sessions that don't complete the handshake ('incomplete'). Often, a separate, restrictive rule at the bottom of the policy is used for these.
- **Document Changes:** Keep a record of which rules were converted and what App-IDs were added. This helps troubleshooting.
- **Iterate and Refine:** The network environment changes. Regularly revisit the Policy Optimizer to identify new applications using existing rules or further optimize policies.
- **Leverage the "Service" Column during analysis:** While migrating, the Policy Optimizer still shows the original Service (port/protocol) alongside the identified App-IDs. Use this to confirm the tool's suggestions make sense in the context of the original rule's intent.
Policy Optimizer: Illustrations & Diagrams
Visualizing the process and concepts can be helpful. Here are some illustrative diagrams using Mermaid syntax.
Basic Policy Optimizer Workflow
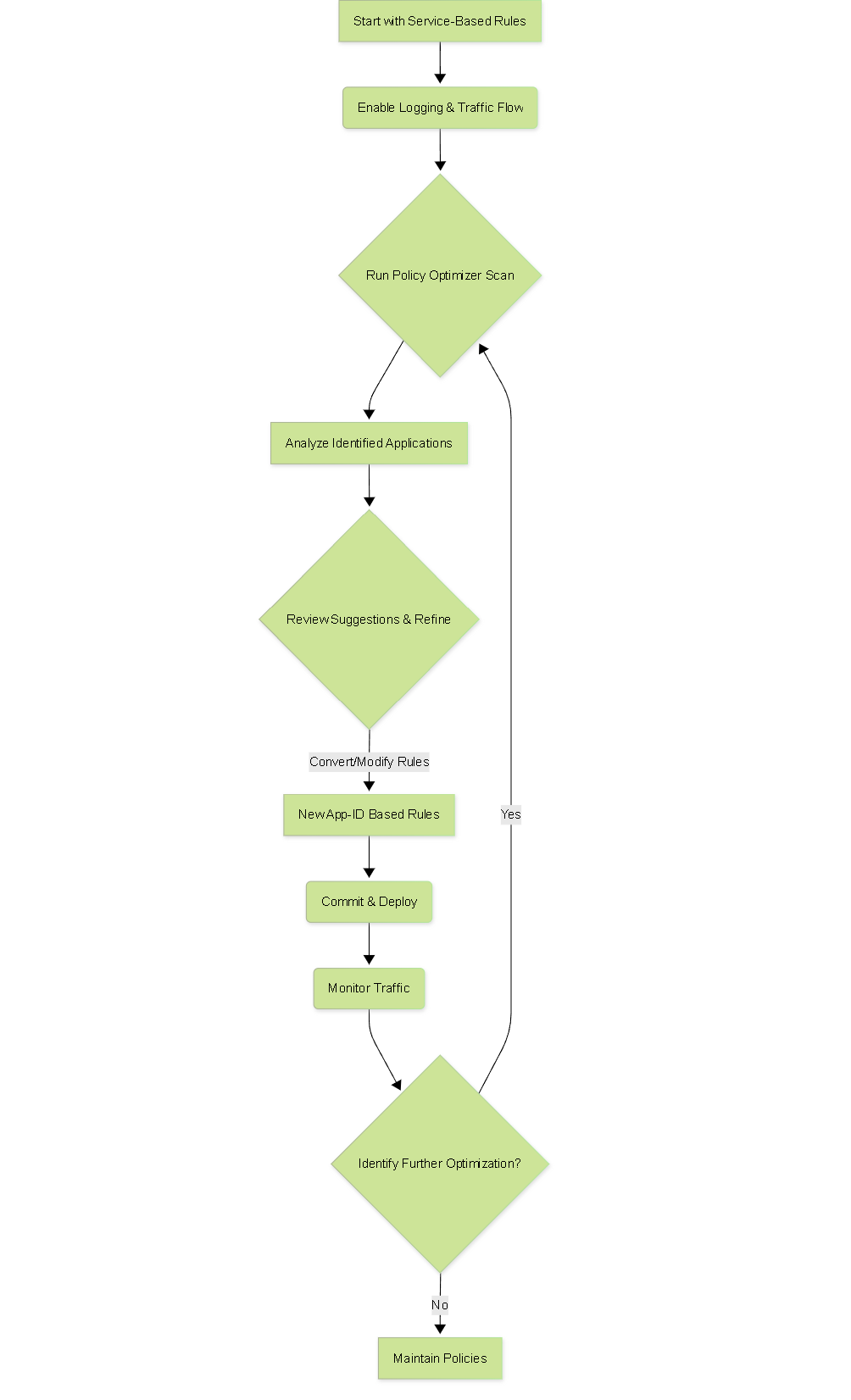
High-level workflow of using the Policy Optimizer.
Migration Decision Flow for a Single Rule
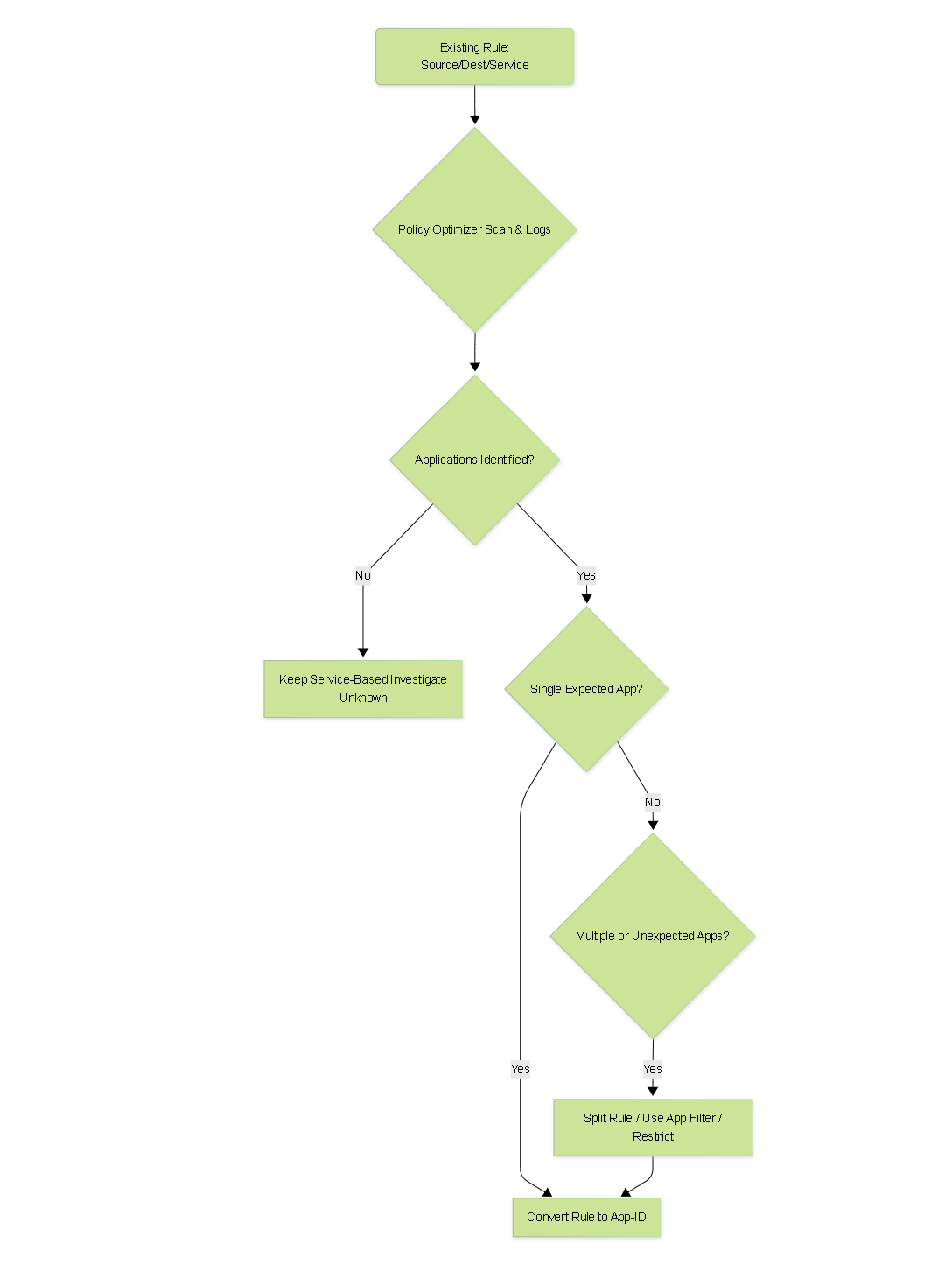
Decision process when analyzing an existing Service-based rule.
Benefits of App-ID State Machine (Conceptual)
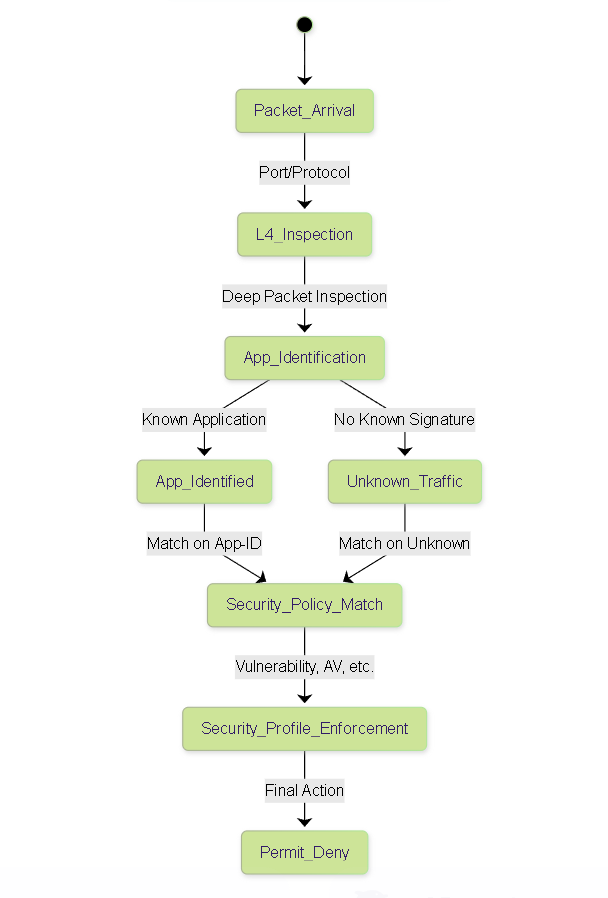
Simplified state diagram showing where App-ID fits in the packet processing flow compared to just Layer 4.
App-ID PCNSE Quiz
Test your knowledge on App-ID and related concepts commonly found in PCNSE questions. Select the best answer for each question and click "Submit Quiz" at the end.