🔗 Palo Alto Networks Aggregate Interfaces and LACP Guide
📘 Overview: Link Aggregation and LACP
Aggregate interfaces, also known as Aggregate Ethernet (AE) interfaces, utilize IEEE 802.1AX Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) or static link aggregation to combine multiple physical Ethernet interfaces into a single logical interface. This bundle appears as one interface to higher-level protocols and configurations (like routing or security policies). The primary goals are to enhance bandwidth and provide link-level redundancy.
For detailed configuration steps, refer to the official documentation: Configure an Aggregate Interface Group (Palo Alto Networks Docs) .
💡 Why LACP is Important (vs. Static Aggregation)
LACP is an optional, standardized protocol (part of 802.1AX) that runs over the aggregated links. Using LACP provides several advantages over static link aggregation (where you manually configure the bundle without a negotiation protocol):
- Automatic Detection and Verification: LACP actively exchanges Link Aggregation Control Protocol Data Units (LACPDUs) between the connected devices. This allows them to automatically discover links that are part of the same bundle and verify that the other side is also configured for aggregation.
- Fault Detection: LACP can detect link failures beyond just physical link down (Layer 1). If a link is physically up but LACP PDUs are not being exchanged, LACP can identify this logical failure and remove the link from the bundle. This provides faster and more reliable failover than static aggregation, especially in complex topologies or with intermediate devices like media converters.
- Configuration Validation: LACP helps prevent misconfiguration. If the other side isn't configured for LACP or aggregation correctly, the AE bundle may not form, preventing potential bridging loops or traffic blackholes that static misconfigurations could cause.
- Standardization: Being an IEEE standard (802.1AX), LACP allows interoperability between different vendors' equipment.
While static aggregation is simpler to configure, LACP offers greater resilience and validation, making it the preferred method in most production environments.
🛡️ Role in Redundancy and High Availability (HA)
Aggregate interfaces with LACP significantly enhance redundancy and support HA deployments:
- Link Redundancy within the Bundle : If one or more physical links within the AE group fail, LACP detects the failure, removes the link(s) from the bundle, and traffic is automatically redistributed among the remaining active links. This failover within the bundle is typically very fast and transparent to higher-layer protocols.
- Increased Bandwidth : Traffic is load-balanced across the active member links, effectively increasing the total available bandwidth between the devices compared to a single link. The load-balancing algorithm determines how traffic flows are distributed.
-
HA Synchronization and Failover
: In Active/Passive HA configurations, aggregate interfaces are commonly used for data (HA3) links, facilitating session synchronization and configuration mirroring.
- HA Passive Pre-Negotiation: A critical feature for LACP in Active/Passive HA. By default, the passive firewall does not fully participate in LACP negotiation while passive. This can cause a delay during an HA failover, as the newly active firewall needs to establish the LACP bundle with the switch, which takes time (seconds).
⚙️ Supported Modes and Implications
Aggregate interfaces on Palo Alto Networks firewalls support being configured in different interface types:
- Layer 3 : The AE interface is assigned an IP address, participates in routing (static or dynamic), and belongs to a security zone. This is a very common deployment for connecting routed networks. LACP is fully supported.
-
Layer 2
: The AE interface is configured as a Layer 2 interface, typically belonging to a VLAN. This allows the firewall to perform switching functions between interfaces within the same VLAN or route traffic between VLANs. LACP *is* supported on Layer 2 AE interfaces.
Layer 2 Deployment Considerations: While supported, Layer 2 aggregate interfaces can sometimes introduce complexities. Some engineers prefer Layer 3 routed links whenever possible for better routing protocol convergence and simpler troubleshooting. If using Layer 2 AE, ensure consistent VLAN tagging configuration on both the firewall and the connected switch ports. All physical member interfaces within the AE bundle must have the same configuration (speed, duplex, VLANs).
- Virtual Wire : Interfaces act as a transparent bump-in-the-wire. Traffic passes through without MAC or IP address changes, and the firewall makes forwarding decisions based on security policy. LACP is **NOT** supported in Virtual Wire mode. You can configure static aggregation for redundancy, but you lose the active negotiation and advanced fault detection of LACP.
- HA (HA3 link) : As mentioned, AE can be used for the HA3 link in Active/Passive HA.
Regardless of the AE interface type, all physical member interfaces assigned to it must have the same characteristics, including speed, duplex, and the same interface type (Layer 2, Layer 3, etc., matching the AE bundle type).
🔢 Capacity Limits
Palo Alto Networks firewalls have limits on the number of physical interfaces that can be members of a single AE bundle and the total number of AE bundles you can create.
- Maximum Interfaces per Aggregate Bundle: Typically, a single AE group can have up to **8 physical interfaces** as members.
- Maximum Aggregate Interfaces (Bundles) per Firewall: This limit varies significantly by firewall model. Refer to the Palo Alto Networks Product Selection tool or specific model documentation for exact numbers.
- Maximum Subinterfaces on AE interfaces: While not a limit on the *bundle* itself, there are limits on the total number of VLAN tags (subinterfaces) per physical interface and per device (often 4094 per physical/AE interface, and a total limit per device).
🚧 Potential LACP Issues and Troubleshooting
While LACP provides benefits, configuration errors or physical issues can prevent the bundle from forming or cause links within the bundle to flap.
- LACP Mode Mismatch: Both sides cannot be in Passive mode. At least one side (firewall or switch) must be Active. If both are Passive, they will wait for the other to initiate negotiation and the bundle won't form.
- Speed/Duplex Mismatch on Member Links: All physical interfaces intended to be part of the same AE bundle *must* have matching speed and duplex settings with the connected device. If auto-negotiation fails or is misconfigured on one side, individual member links may fail or have errors (like CRC), preventing them from being added to the bundle.
- Physical Connectivity Issues: Faulty cables, dirty fiber connectors, or bad transceivers on individual member links will prevent that specific link from coming up, even if LACP is configured correctly.
- Switch Configuration Issues: The connected switch must also be configured for link aggregation (often called EtherChannel or Port-Channel) and LACP (if using LACP) on the corresponding ports, and those ports must be assigned to the same logical channel group.
- VLAN Tagging Mismatches (Layer 2 AE): If using Layer 2 AE with VLANs, ensure the AE interface and subinterfaces on the firewall have VLAN tagging configured correctly (native VLAN, allowed VLANs) and this matches the trunk configuration on the switch.
- Control Plane Issues: Less common, but high CPU load or issues with the firewall's control plane could potentially impact LACP PDU processing.
- Bug Affecting LACP: Rarely, specific PAN-OS versions might have bugs affecting LACP stability, particularly with certain modes like "Fast" transmission rate.
🛠️ Troubleshooting Commands
Use these CLI commands to diagnose AE and LACP issues:
-
show lacp aggregate-ethernet all: Displays the status of all LACP-enabled AE interfaces. This output is crucial as it shows the LACP state (e.g., operational, disabled), the mode (Active/Passive), transmission rate (Slow/Fast), member interfaces, and partner information (System ID, Key). Look for the state of the AE bundle and its member links. Member links should show the correct LACP state flags indicating they are bundled. -
show interface ethernet: Check the physical and logical status of individual member interfaces. Ensure the link is up, speed/duplex matches, and look at interface counters for errors (CRC, input errors). -
show interface aggregate-ethernet: Check the status and configuration of the logical AE interface. -
show system state filter sys.sX.pY.detail: Provides low-level physical interface details, useful for confirming speed/duplex negotiation and hardware status of member links. -
show log system: Filter for events related to interface status changes, LACP, or the specific AE interface. -
debug lacp state all(Use with caution): Provides detailed LACP state machine information. - Packet Capture: Capture LACP traffic (EtherType 0x8809, Slow protocols subtype 0x01 for LACPDUs) on the physical member interface to verify if LACPDUs are being sent and received correctly.
📈 Visualizing Aggregate Interfaces and LACP
🔗 Basic AE Bundle Diagram
This illustrates multiple physical interfaces bundled into one logical AE interface.
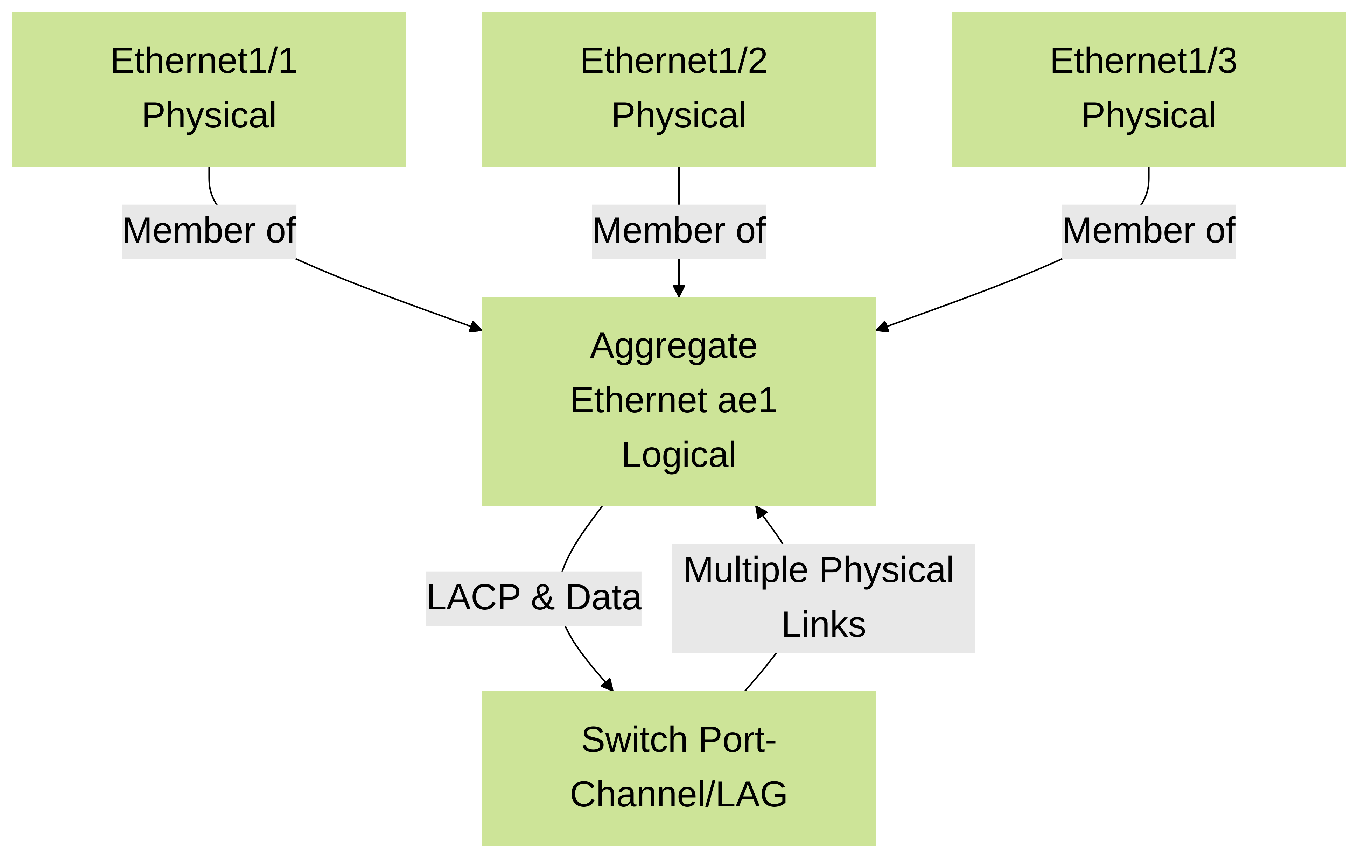
Physical Interfaces Forming an Aggregate Ethernet Bundle
🔄 HA Passive Pre-Negotiation Flow
This diagram shows how LACP pre-negotiation works in an Active/Passive HA setup for faster failover.
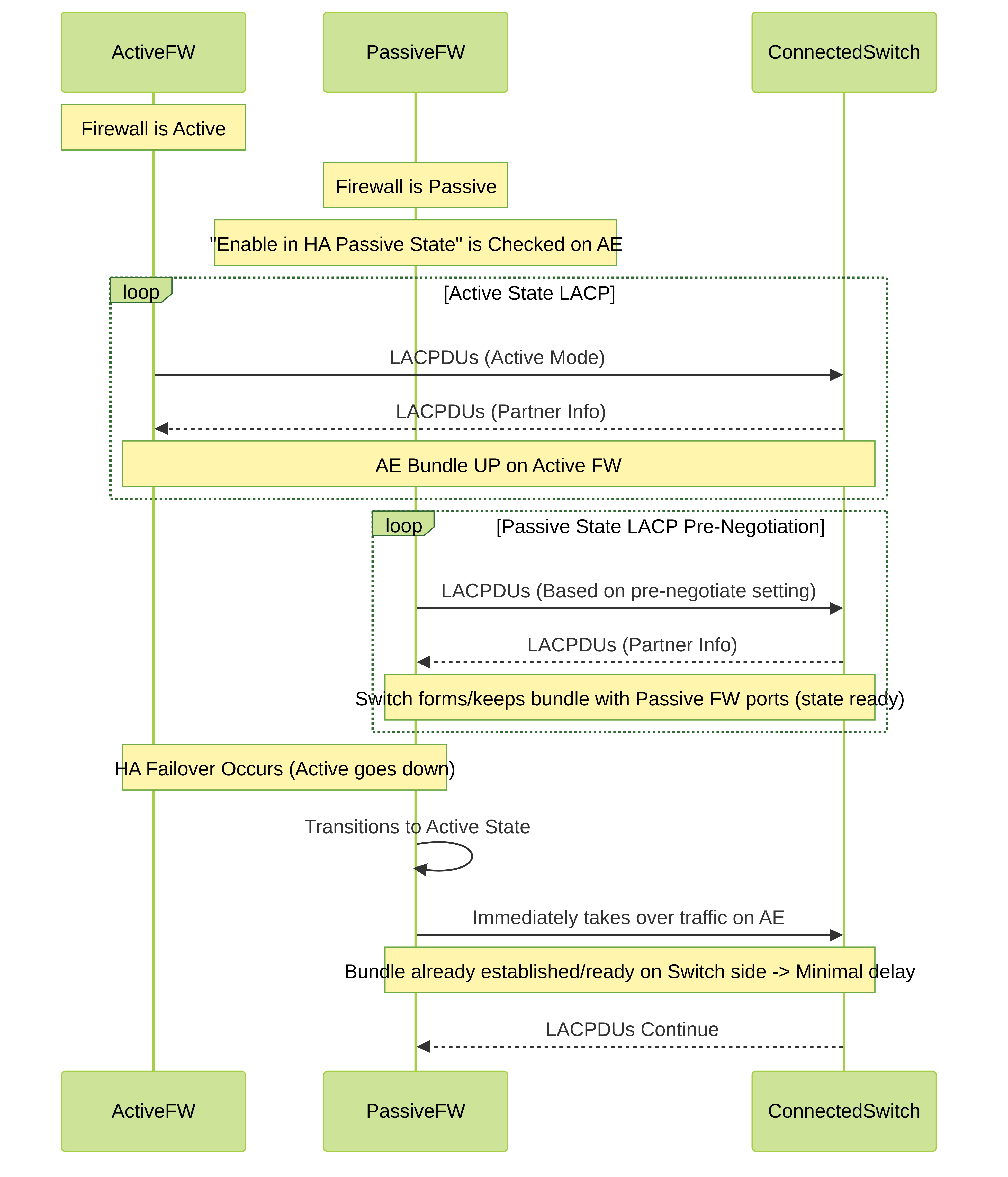
HA Active/Passive Failover with LACP Pre-Negotiation
⚠️ Troubleshooting LACP Issues Flow
A systematic approach to diagnosing problems with AE interfaces and LACP.
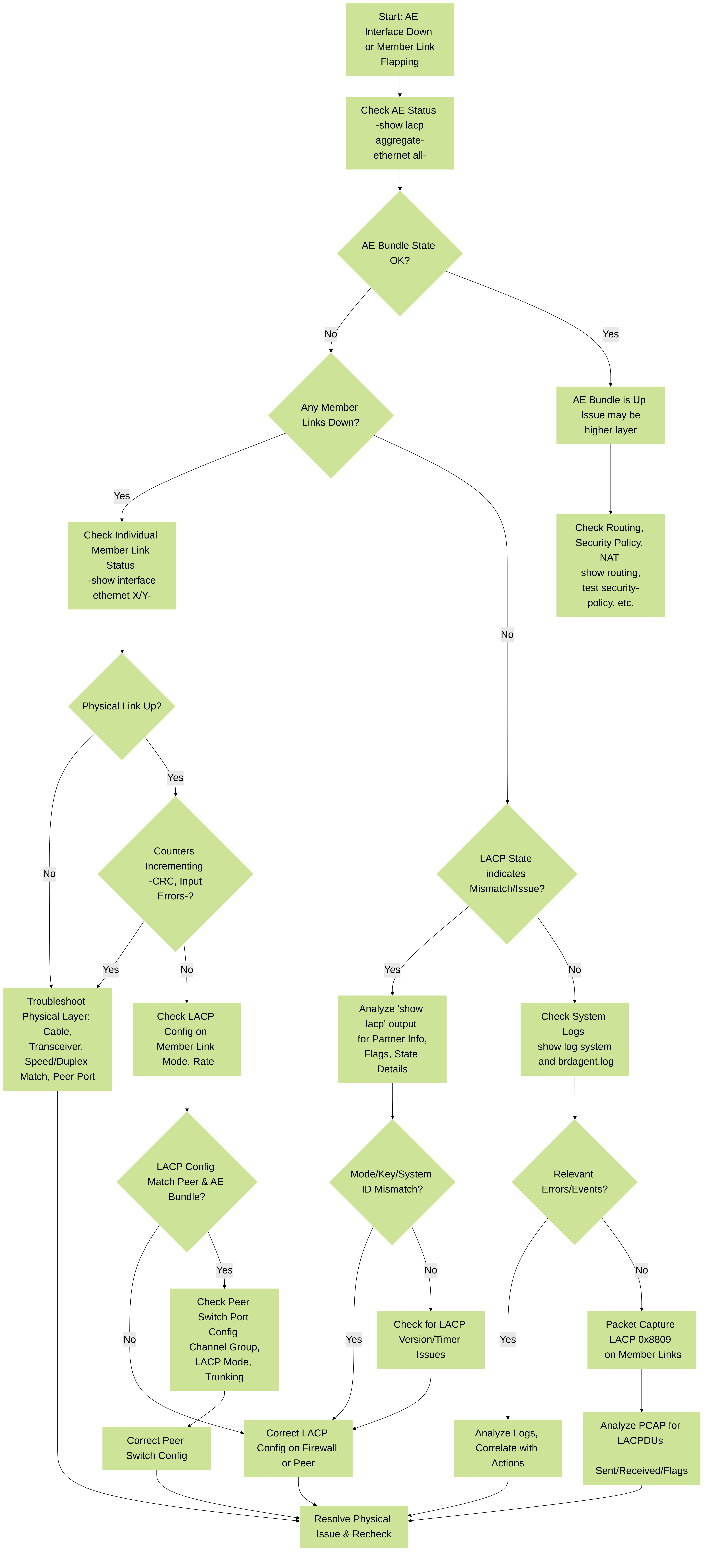
Aggregate Ethernet and LACP Troubleshooting Flowchart