Comprehensive Guide to Multicast on Palo Alto Networks Firewalls
This guide provides a detailed overview of multicast support, configuration, and troubleshooting on Palo Alto Networks firewalls. It is intended for network engineers and administrators with a good understanding of networking concepts who may be new to Palo Alto Networks multicast specifics. PAN-OS software, which runs on Palo Alto Networks firewalls, offers robust multicast capabilities.
PCNSE Exam Relevance: Understanding multicast concepts, how Palo Alto Networks firewalls handle multicast traffic, and common troubleshooting commands are crucial for the PCNSE exam.
I. Multicast Fundamentals and Palo Alto Networks Firewall Support
Basic Multicast Concepts
- Multicast Overview: Multicast is a communication method where a single source sends data to multiple interested receivers simultaneously (one-to-many) or multiple sources send to multiple receivers (many-to-many). This is more efficient than unicast (one-to-one) for applications like video streaming, online gaming, and financial data distribution.
-
Key Multicast Addresses:
-
Class D Addresses:
IPv4 multicast addresses range from
224.0.0.0to239.255.255.255. -
Link-Local Addresses:
224.0.0.0to224.0.0.255are for local network segment use and are not routed. Examples include224.0.0.1(All Hosts),224.0.0.2(All Routers),224.0.0.5(OSPF),224.0.0.13(PIM). -
Administratively Scoped Addresses:
239.0.0.0to239.255.255.255are for private multicast domains.
-
Class D Addresses:
IPv4 multicast addresses range from
-
Core Multicast Protocols:
- IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol): Used by hosts to signal their interest in receiving multicast traffic for a particular group to their local multicast router. Palo Alto Networks firewalls support IGMPv1, IGMPv2, and IGMPv3, though newer PAN-OS versions (Advanced Routing Engine) primarily focus on IGMPv2 and IGMPv3, with IGMPv2 providing backward compatibility for IGMPv1.
- PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast): Used by routers to build multicast distribution trees and route multicast traffic between routers. PIM itself doesn't discover the network topology but relies on unicast routing protocols (hence "protocol independent").
Firewall's Role in Multicast
Palo Alto Networks firewalls primarily act as a multicast router participant when configured for multicast. This means the firewall actively engages in IGMP and PIM protocols to manage multicast groups and route multicast traffic. For multicast routing, Layer 3 interfaces (Ethernet, Aggregate Ethernet, VLAN, loopback, or tunnel) are configured within a virtual router.
-
Processing Multicast Traffic:
- Layer 3 Mode: The firewall functions as a PIM router, making forwarding decisions based on the Multicast Forwarding Information Base (MFIB). It participates in IGMP querying and PIM neighbor relationships.
- Transparent/Virtual Wire/Layer 2 Mode: In these modes, the firewall does not typically act as a multicast router. While some IGMP/PIM control plane packets might be snooped or passed, active multicast routing is a Layer 3 function. Layer 2 interfaces can be configured to support IGMP snooping in some contexts, which helps prune multicast traffic on VLANs by forwarding it only to interested ports. However, the focus of this guide is L3 multicast routing.
- Impact of Security Policies: Multicast traffic, like unicast traffic, is subject to security policy enforcement. Policies must explicitly permit multicast traffic between zones, specifying the source, destination (multicast group address), and application/service.
- NAT Considerations for Multicast: Standard NAT (Network Address Translation) as used for unicast is generally not applicable to multicast group addresses. The destination of multicast is a group, not a single translated IP. However, if the *source* of the multicast traffic needs to be NATed before it's sent to the multicast tree, source NAT policies can be applied as usual.
PCNSE Gotcha: A common oversight is forgetting to create security policies that specifically allow multicast traffic (e.g., to a multicast group address in the destination) or the PIM/IGMP control plane protocols if Zone Protection is strict or default interzone policies are deny.
Supported Multicast Protocols and Features
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) Support
- Versions Supported: PAN-OS supports IGMPv1, IGMPv2, and IGMPv3. The advanced routing engine focuses on IGMPv2 and IGMPv3, with IGMPv2 being backward-compatible with IGMPv1.
- Firewall as an IGMP Querier: The firewall can act as the IGMP querier on a segment, sending out IGMP Query messages to discover which hosts are members of which multicast groups. On a multi-access segment, an IGMP querier election takes place (typically the router with the lowest IP address if PIM is used, or configured).
- IGMP Snooping: While PAN-OS firewalls primarily operate as L3 multicast routers, IGMP snooping is a Layer 2 mechanism. If the firewall is acting as a Layer 3 gateway for VLANs where multicast receivers reside, it uses IGMP to learn about group memberships. True L2 switches in the path would perform IGMP snooping to limit multicast flooding within VLANs. For the firewall's L3 interfaces, IGMP must be enabled to process membership reports from hosts.
-
Configuration of IGMP on Interfaces:
IGMP is enabled on receiver-facing Layer 3 interfaces within a virtual router's multicast settings.
Network > Virtual Routers > (select VR) > Multicast > Interfaces > Add
You can specify IGMP version, query intervals, and max response times here.
PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast) Support
Palo Alto Networks firewalls support PIM on Layer 3 interfaces.
-
PIM Modes Supported:
- PIM-SM (Sparse Mode): This is the most commonly used mode. It's suitable for networks where receivers are sparsely distributed. It uses a Rendezvous Point (RP) to build shared trees.
- PIM-SSM (Source-Specific Multicast): Allows receivers to specify the source from which they want to receive multicast traffic (S,G) joins. This mode doesn't require an RP. Requires IGMPv3 (or IGMPv2 with SSM mapping).
- PIM-DM (Dense Mode): Assumes receivers are densely populated and initially floods traffic, then prunes back branches with no receivers. Generally less scalable than PIM-SM for larger networks. Some documentation suggests PAN-OS supports PIM-DM, while others indicate a focus on SM and SSM. Always verify with current PAN-OS release notes for definitive support.
- PIM BiDir (Bidirectional PIM): Builds bi-directional shared trees and does not use source-specific state or shortest-path trees. PAN-OS documentation typically emphasizes SM and SSM. Explicit confirmation of full BiDir PIM support and its limitations should be checked against the latest PAN-OS documentation.
-
Role as a PIM router, Rendezvous Point (RP), Bootstrap Router (BSR):
- PIM Router: Any firewall interface with PIM enabled acts as a PIM router, forming adjacencies with other PIM routers.
-
Rendezvous Point (RP):
In PIM-SM, the RP is a chosen router that acts as a meeting point for sources and receivers. The firewall can be configured as an RP, or it can learn the RP dynamically.
- Static RP: Manually configure the address of the RP. All routers in the PIM domain must have the same static RP configuration for a given group range.
- Auto-RP: A Cisco-proprietary mechanism for dynamic RP discovery. The firewall can act as a Candidate RP or Mapping Agent.
- Bootstrap Router (BSR): An IETF standard for dynamic RP discovery. The firewall can be configured as a Candidate RP and can also participate in the BSR election process or be a BSR itself.
-
Configuration of PIM:
Network > Virtual Routers > (select VR) > Multicast > PIM
Here you enable PIM. Interface-specific PIM settings (like mode, hello interval) are under:Network > Virtual Routers > (select VR) > Multicast > Interfaces > (select interface) > PIM
RP settings (static, Auto-RP, BSR) are configured under the PIM settings within the virtual router's multicast configuration. PIM Assert messages are used to elect a single forwarder on multi-access networks. PIM Join/Prune messages are fundamental to building the multicast distribution trees.
PCNSE Tip: Know how to configure static RPs and understand the concept of BSR for dynamic RP discovery. PIM-SM is a key area.
MSDP (Multicast Source Discovery Protocol)
- Support for MSDP: Yes, Palo Alto Networks firewalls support MSDP.
- Use Cases: MSDP is used to share information about active multicast sources between RPs in different PIM-SM domains. This is particularly useful for inter-domain multicast and for Anycast RP (where multiple RPs share the same IP address for redundancy). MSDP peers establish TCP connections (port 639) to exchange Source Active (SA) messages.
-
Configuration Aspects:
Network > Virtual Routers > (select VR) > Multicast > MSDP
Requires enabling MSDP globally within the virtual router, configuring peer addresses, and potentially authentication.
Virtual Router Configuration for Multicast
-
Enabling Multicast Routing:
Multicast routing must be explicitly enabled within a virtual router.
Network > Virtual Routers > (select VR) > Multicast > Enable (checkbox)
-
Interface-Level Multicast Settings:
Each Layer 3 interface participating in multicast needs to have PIM and/or IGMP enabled as required.
Network > Virtual Routers > (select VR) > Multicast > Interfaces
Here you add interfaces and configure their PIM and IGMP parameters. -
Interaction with Unicast Routing Protocols:
PIM relies on the unicast routing table to perform Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF) checks. This means the firewall must have a valid unicast route towards the source of the multicast traffic and towards the RP. If the RPF check fails, multicast traffic will be dropped.
PCNSE Gotcha: A common multicast problem is a misconfigured unicast routing table. If the firewall doesn't know how to reach the source or the RP via unicast, PIM will fail to build the tree correctly.
Multicast and Security Policies
-
Writing Security Policies:
Create security policies to permit multicast traffic between zones.
- Source Zone: The zone where the multicast traffic originates or enters the firewall.
- Destination Zone: The zone where the multicast receivers are located or where the traffic exits the firewall.
- Destination Address: Use an Address Object of type "IP Netmask" or "IP Range" to specify the multicast group address(es) (e.g., 239.1.1.1/32).
- Application/Service: Define the application (e.g., 'udp') and the specific destination port used by the multicast stream. You can create custom service objects.
Policies > Security > Add
-
Zone Protection Considerations:
Zone Protection Profiles can be configured to protect against flood attacks or reconnaissance. Ensure these profiles do not inadvertently drop legitimate multicast control plane packets like IGMP (protocol 2) or PIM (protocol IP protocol number 103). You may need to add explicit allows in the Zone Protection Profile for these protocols if you have strict "Non-IP Protocol Protection" or "Packet Based Attack Protection" settings.
Network > Zone Protection
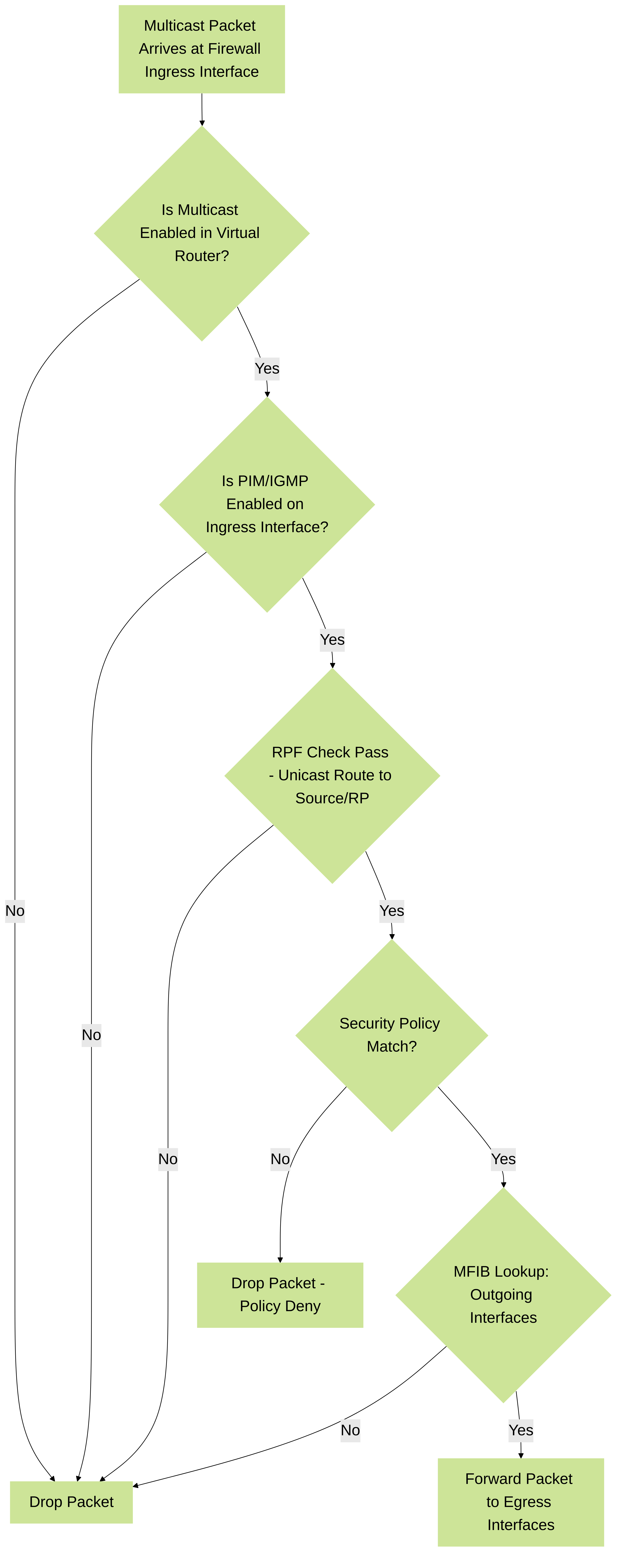
Figure 1: Simplified Multicast Traffic Flow and Decision Process on Firewall
Multicast in High Availability (HA)
Palo Alto Networks firewalls support High Availability (HA) in Active/Passive and Active/Active modes.
-
Behavior During HA Failover:
- In an Active/Passive HA pair, if the active firewall fails, the passive firewall becomes active and takes over all functions, including multicast routing.
- PIM neighbor relationships will need to be re-established with the newly active firewall. IGMP memberships might also need to be re-queried or re-reported.
- Multicast session state synchronization can vary. While general session information (like for unicast TCP/UDP) is synchronized over the HA2 (data) link in many cases, specific multicast routing protocol states (PIM join states, RP information) might not be fully synchronized and may need to be rebuilt by the newly active firewall through normal protocol operation. This can lead to a brief interruption in multicast traffic flow during failover.
- Path monitoring and link monitoring are crucial for triggering failovers.
- Synchronization of Multicast State Information: Information like the multicast routing table (MFIB) itself is generally not synchronized in real-time. The newly active firewall rebuilds this based on PIM and IGMP messages after failover.
PCNSE Tip: Understand that after an HA failover, PIM adjacencies and multicast forwarding states typically need to be re-established, which might cause a short traffic disruption.
Multicast and VPNs (Site-to-Site IPsec)
-
Strategies for Running Multicast over IPsec Tunnels:
Standard IPsec tunnels do not inherently support multicast traffic. The common method to transport multicast over an IPsec VPN is to use a
GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) tunnel over IPsec
.
- Create a GRE tunnel interface between the two sites.
- Configure PIM on these GRE tunnel interfaces.
- Create an IPsec tunnel to encrypt the GRE traffic. The GRE tunnel endpoints become the source and destination for the IPsec policy.
-
Limitations and Best Practices:
- MTU considerations are important due to the overhead of GRE and IPsec. Fragmentation might occur if not handled correctly.
- Ensure PIM is enabled on the GRE tunnel interfaces on both sides.
- Security policies must allow multicast traffic through the GRE tunnel (and the underlying IPsec traffic if policies are very specific).
- Redundancy for GRE over IPsec tunnels carrying multicast should be considered (e.g., multiple tunnels, dynamic routing over tunnels).
PCNSE Gotcha: Remember that multicast doesn't directly run over a standard IPsec tunnel. GRE encapsulation is the typical solution.
GlobalProtect and Multicast
- Support or Limitations: Multicast traffic to/from GlobalProtect clients is generally not supported directly over the GlobalProtect VPN tunnel. GlobalProtect tunnels are typically point-to-point and designed for unicast traffic. If multicast is required for remote users, alternative solutions or application-level relays might be needed. Always check the latest PAN-OS and GlobalProtect documentation for any feature enhancements in this area.
II. Multicast Troubleshooting on Palo Alto Networks Firewalls
Common Multicast Issues
- Hosts not joining multicast groups (IGMP issues).
- Multicast streams not reaching destinations (PIM routing, RPF failures, security policy blocks).
- Intermittent multicast connectivity.
- RP reachability problems (PIM-SM).
- Incorrect PIM neighbor relationships.
- Security policies blocking multicast traffic or control plane packets.
- Unicast routing issues affecting RPF checks.
Verification CLI Commands
These commands are essential for troubleshooting multicast issues from the firewall's command-line interface (CLI).
IGMP Status:
-
show routing multicast igmp interface: Displays IGMP interface status, querier information, and timers. -
show routing multicast igmp grouporshow routing multicast igmp membership: Shows active IGMP groups joined by hosts on firewall interfaces. -
show routing multicast igmp statistics: Displays IGMP message statistics.
PIM Status:
-
show routing multicast pim interface: Displays PIM status for interfaces, DR (Designated Router) information. -
show routing multicast pim neighbor: Shows PIM neighbors and their status. -
show routing multicast pim rp [rp_address: Displays information about Rendezvous Points (RPs) for PIM-SM.] [group ] -
show routing multicast pim bsr: Shows current BSR and candidate BSR information. -
show routing multicast pim assert: Displays PIM Assert election winners on interfaces. -
show routing multicast pim join-prune: Shows PIM join/prune state information (often part ofshow routing multicast pim state). -
show routing multicast pim state: Provides detailed PIM state information.
Multicast Forwarding Information Base (MFIB):
-
show routing multicast fib [group: Displays the multicast forwarding table (MFIB), showing (S,G) and (*,G) entries, incoming and outgoing interfaces, and RPF interface. This is a critical command to see how the firewall will forward multicast traffic.] [source ] [incoming-interface ]
MSDP Status (if applicable):
-
show routing multicast msdp peer: Displays MSDP peer status. -
show routing multicast msdp sa-cache: Shows the Source-Active (SA) cache learned from MSDP peers.
General Routing Commands:
-
show routing route [destination: Verifies unicast reachability to RPs and sources.] -
test routing fib-lookup virtual-router: Tests unicast FIB lookup for a specific destination, crucial for RPF checks.ip
PCNSE Tip:
Be very familiar with
show routing multicast fib
,
show routing multicast pim neighbor
, and
show routing multicast pim rp
. These are your go-to commands for most PIM-SM issues.
Packet Captures for Multicast
Packet captures are invaluable for diagnosing multicast problems.
-
How to Use:
Use the firewall's built-in packet capture capabilities (Monitor > Packet Capture or CLI
debug routing pcap ...commands). Capture on ingress and egress interfaces relevant to the multicast flow. -
Filtering:
-
IGMP:
Filter for IP protocol 2 (
ip.proto == 2). -
PIM:
Filter for IP protocol 103 (
ip.proto == 103) or destination224.0.0.13for PIM hellos. -
Multicast Data:
Filter for the specific multicast group IP address as the destination (e.g.,
ip.dst == 239.1.1.1) and the relevant UDP/TCP port.
-
IGMP:
Filter for IP protocol 2 (
-
Interpreting Capture Results:
- Check if IGMP reports from hosts are reaching the firewall.
- Verify PIM Hellos are exchanged between PIM neighbors.
- See if PIM Join/Prune messages are sent/received correctly towards the RP or source.
- Confirm if multicast data packets are arriving at the firewall and being forwarded out the correct interfaces.
- Look for RPF check failures (often indicated by traffic arriving but not being forwarded).
-
CLI Packet Capture for Control Plane:
-
debug routing pcap pim on | off | view | delete -
debug routing pcap igmp on | off | view | delete
-
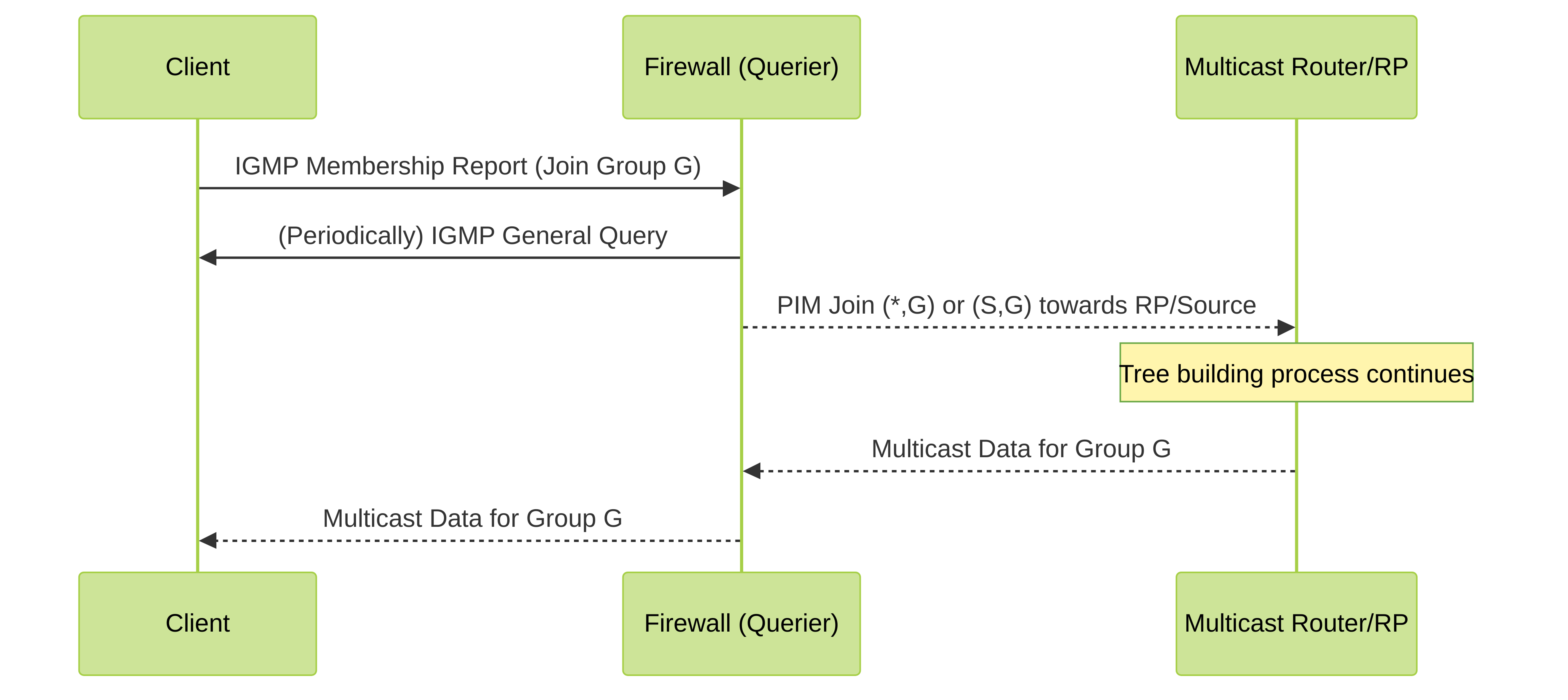
Figure 2: Simplified IGMP and PIM Join Sequence
Log Analysis
-
Traffic Logs (Monitor > Logs > Traffic):
- Look for denies for the multicast group IP address or associated ports.
- Check if traffic is hitting the correct security policy with an "allow" action.
- Filter by source IP (multicast source), destination IP (multicast group), and application/port.
- System Logs (Monitor > Logs > System): May contain general routing daemon messages or HA-related events if applicable.
-
Routing Logs:
-
Use CLI commands like
less mp-log rtm.logorless mp-log pmd.log(for PIM) andless mp-log igmpd.log(for IGMP) to view detailed routing daemon logs. Accessing and interpreting these logs often requires deeper knowledge or TAC assistance.
-
Use CLI commands like
Troubleshooting Methodology
- Verify Layer 2 Connectivity: Ensure basic network connectivity (ARP, MAC learning) on segments where sources and receivers reside.
-
Verify IGMP on Receiver Segment:
-
Is the firewall the IGMP querier? (
show routing multicast igmp interface) - Are hosts sending IGMP reports? (Packet capture)
-
Does the firewall see IGMP group memberships? (
show routing multicast igmp group)
-
Is the firewall the IGMP querier? (
-
Verify PIM Adjacencies:
-
Are PIM neighbors up? (
show routing multicast pim neighbor) - Are PIM hello intervals and other parameters compatible?
-
Are PIM neighbors up? (
-
Verify RP Configuration and Reachability (PIM-SM):
-
Is the RP configured correctly (static, BSR, Auto-RP)? (
show routing multicast pim rp) -
Can the firewall ping the RP's unicast address? (
ping ...) -
Is there a unicast route to the RP? (
show routing route)
-
Is the RP configured correctly (static, BSR, Auto-RP)? (
-
Verify Unicast Reachability to Source:
- Can the firewall ping the multicast source's unicast address?
- Is there a unicast route to the source? (This is crucial for RPF checks).
-
Check MFIB Entries:
-
Does an (S,G) or (*,G) entry exist for the desired flow? (
show routing multicast fib) - Is the incoming interface correct? Is the RPF interface correct?
- Are there outgoing interfaces listed? If not, it means no downstream receivers or joins have been pruned.
-
Does an (S,G) or (*,G) entry exist for the desired flow? (
-
Check Security Policies:
- Is there an allow policy for the multicast group address and service from the source zone to the destination zone?
- Check traffic logs for denies.
- Check Zone Protection: Ensure IGMP (protocol 2) and PIM (protocol 103) are not being dropped.
- Isolate the Problem: Work hop-by-hop from source to receiver, checking multicast state on each PIM router in the path.
Specific Scenarios
-
Troubleshooting PIM-SM:
- RP Issues: Most PIM-SM problems relate to the RP. Verify RP configuration, reachability, and that all routers agree on the RP for a given group.
- Shared Tree vs. Source Tree: Understand the transition from shared tree (*,G) to source tree (S,G). Problems can occur if the firewall doesn't switch to the SPT or if RPF checks fail for the direct source path.
-
Troubleshooting IGMP:
- Hosts not sending reports: Check host configuration, local firewall on host.
- Querier issues: Ensure a querier is active on the segment. Multiple queriers can sometimes cause issues if not resolved correctly.
-
Troubleshooting Multicast over HA or VPNs:
- HA: Expect brief reconvergence after failover. Check PIM/IGMP status on the newly active firewall.
- VPN (GRE over IPsec): Verify GRE tunnel is up. Check PIM on GRE interfaces. Ensure MTU is handled correctly. Check IPsec tunnel status. Security policies must allow traffic through the tunnel.
Debug Commands (Use with Caution)
Debug commands can provide very detailed information but can also consume significant CPU resources. Use them cautiously, preferably during a maintenance window or under the guidance of Palo Alto Networks Technical Assistance Center (TAC).
-
debug routing igmp all | detail | error | packets |(Syntax might vary per PAN-OS version) -
debug routing pim all | detail | error | packets | jp |(Syntax might vary per PAN-OS version,jpfor join/prune) -
To view the logs generated by these debugs, you might need to look at specific log files (e.g.,
mp-log pmd.log,mp-log igmpd.log) or useshow counter global filter packet-filter yes delta yesto see related counters if packet filters are set for debugging.
For PAN-OS 6.0.1 and later, the
debug routing multicast log
command syntax changed or was deprecated for some options, directly using daemon debugs (e.g.
debug routing pmd ...
) became more common. Always refer to the CLI reference guide for your specific PAN-OS version.
Common Misconfigurations
- PIM or IGMP not enabled on the correct interfaces.
- Missing or incorrect security policies for multicast traffic or control plane protocols (PIM/IGMP).
- Incorrect RP configuration (address, group range) or RP not reachable via unicast.
- Firewall not being the IGMP querier on a segment when it should be (or vice-versa if another device is intended to be querier).
-
Unicast routing problems leading to RPF check failures.
PCNSE Gotcha: RPF failure due to asymmetric routing or missing unicast routes is a very common cause of multicast not flowing.
- Zone Protection Profiles blocking PIM/IGMP.
- MTU issues, especially with multicast over GRE/IPsec tunnels.
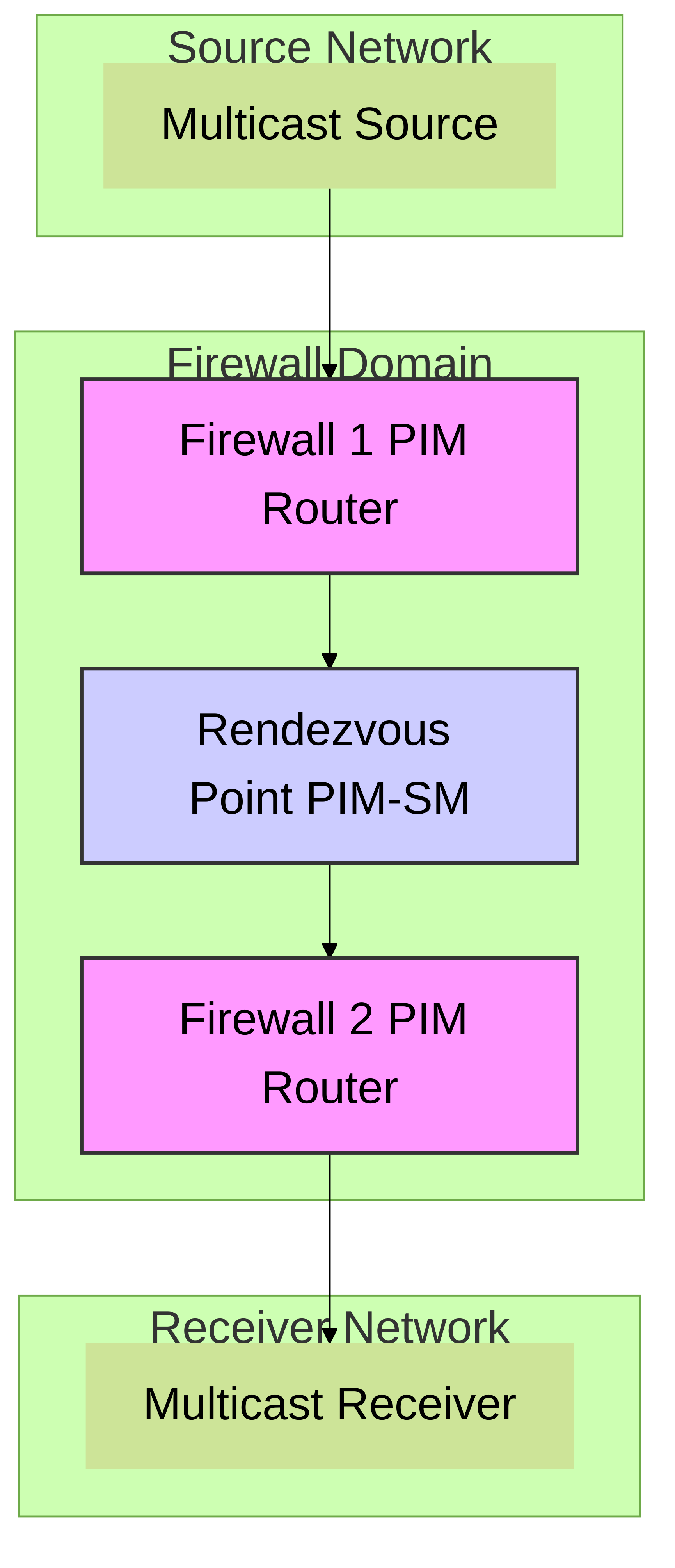
Figure 3: Simple PIM-SM Topology Example
III. Best Practices for Multicast on Palo Alto Networks Firewalls
-
Design Considerations:
- Plan your multicast domain carefully, including RP placement for PIM-SM.
- Use PIM-SSM where possible if sources are known and applications support IGMPv3, as it's more efficient and secure.
- Segment multicast traffic using separate zones if necessary for better security policy granularity.
-
Security Policy Best Practices:
- Be specific. Allow multicast only for the required groups, sources, and applications/ports.
- Use Address Objects for multicast group addresses and Service Objects for ports.
- Regularly review and audit multicast security policies.
- Ensure control plane protocols (PIM, IGMP) are permitted if necessary, especially if strict Zone Protection is in place.
-
Choosing Appropriate PIM Modes:
- PIM-SM is generally preferred for most enterprise deployments.
- Use PIM-SSM for applications like IPTV or specific content delivery from known sources.
- Avoid PIM-DM in large, sparse networks due to its flooding nature.
-
RP Placement and Redundancy (PIM-SM):
- Place RPs in a central location in the network with good connectivity.
- Implement RP redundancy using mechanisms like Anycast RP with MSDP, or BSR with multiple Candidate RPs.
-
Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Regularly monitor PIM neighbor status, RP status, and MFIB.
- Keep PAN-OS software updated to the latest recommended releases for bug fixes and feature enhancements.
- Review logs for any multicast-related issues.
PCNSE Exam Focus:
- Understand the difference between PIM-SM and PIM-SSM.
- Know that security policies apply to multicast traffic.
- Be aware of the role of the RP in PIM-SM.
-
Recognize key CLI commands for verification (
show routing multicast ...). - Understand the need for GRE over IPsec for multicast VPNs.
- RPF check failures are a classic troubleshooting scenario.