🔁 Mastering Route Redistribution in Palo Alto Networks Firewalls – PCNSE Guide
This guide expands on the fundamental concepts of route redistribution within Palo Alto Networks firewalls, a crucial topic for network engineers and those preparing for the PCNSE certification. We will delve into basic principles, advanced techniques like filtering and route manipulation, traffic engineering applications, and typical use-case scenarios.
1. What is a Redistribution Profile?
A Redistribution Profile in Palo Alto Networks firewalls defines how routes learned from one source (e.g., static, connected, OSPF, BGP) are advertised into another routing protocol. This mechanism enables seamless route sharing between different protocols within the firewall's virtual router. Without redistribution profiles, each routing protocol operates in isolation, and no route information is exchanged.
2. Supported Route Types for Redistribution
Redistribution Profiles can handle the following route types:
- Static Routes
- Connected Interfaces/Networks
- OSPF (IPv4 only for OSPFv2, OSPFv3 for IPv6)
- BGP (IPv4 and IPv6)
- RIP (IPv4 only)
- Host Routes (often managed as part of connected or static)
Configuration Path:
Network > Virtual Routers > [select your VR] > Redistribution Profiles
3. Key Configuration Elements
These elements are configured within a Redistribution Profile:
- Name: A unique identifier for the profile.
- Priority: Determines the order of evaluation when multiple profiles exist; lower values have higher precedence. This is crucial when profiles might overlap in the routes they match.
-
Action:
-
Redist: Allows redistribution of matching routes. -
No Redist: Prevents redistribution of matching routes. This can be used to create exceptions.
-
- General Filter (Source Type): Specifies the origin of routes to be redistributed (e.g., static, connected, OSPF, BGP). You can select multiple source types.
-
Destination Filter:
Optionally, you can specify exact prefixes (e.g.,
192.168.1.0/24) or use0.0.0.0/0to match any (often used for default routes). - Interface Filter: Allows filtering based on the interface through which the route was learned or is associated.
- Next-Hop Filter: Allows filtering based on the next-hop IP address of the route.
- Metric: Sets a specific metric value for the redistributed routes. This can influence path selection in the receiving protocol.
-
OSPF Specific Filters (when Source Type is OSPF):
- Path Type: Filter by Intra-Area, Inter-Area, External Type 1, or External Type 2 routes.
- Area: Filter routes originating from specific OSPF areas.
- Tag: Filter routes based on their OSPF route tag.
- BGP Specific Filters (when General Filter includes BGP): Allows for more granular control over which BGP routes are redistributed.
- Route Map (Optional but Powerful): Applies additional policies or modifications to the routes being redistributed, such as setting tags, modifying metrics, or changing other route attributes. Route maps offer fine-grained control over the redistribution process.
4. Basic Principles of Redistribution
Route redistribution is the process of taking routes learned by one routing source (like OSPF, BGP, static configurations, or directly connected networks) and advertising them into another routing protocol or process. The core principle is to enable interoperability and connectivity between disparate routing domains that might exist within a single virtual router on the Palo Alto Networks firewall.
- Control Plane Operation: Redistribution operates at the control plane level, influencing how routing information is exchanged and populated in routing tables (RIBs).
- Administrative Distance (AD) and Metric: When a route is redistributed, the receiving protocol assigns its own AD (if applicable, though AD is more about route source preference) and a new metric. The metric assigned during redistribution is critical for path selection within the receiving protocol's domain.
- Seed Metric: When redistributing into protocols like OSPF or RIP, a "seed" or default metric is often required. If not explicitly set in the redistribution profile or route map, the protocol might assign a default metric which may or may not be optimal.
- Preventing Routing Loops: This is a critical consideration. Redistributing routes without careful planning can lead to routing loops, especially in scenarios with mutual (two-way) redistribution. Techniques like route filtering, metric manipulation, and administrative distance adjustments are used to prevent loops.
- Path Selection: Redistribution influences how different parts of the network learn about available paths. The goal is to ensure optimal and loop-free routing.
5. Filtering, Route Manipulation, and Route Injection
Redistribution profiles, often in conjunction with route maps, provide powerful mechanisms for controlling the flow of routing information.
Filtering Routes
Filtering allows administrators to selectively choose which routes are redistributed. This is essential for preventing unwanted routes from entering a routing domain, conserving resources, and enhancing security.
- Source Type Filter: The most basic form, allowing redistribution only from specified sources (e.g., only static routes).
- Destination Prefix Filter: Within the redistribution profile, you can specify destination network prefixes to match specific routes. For instance, you might only want to redistribute a specific summary route or a default route.
- Route Maps: For more complex filtering, route maps can be used. Route maps can match routes based on prefix lists, access lists (less common in PA for this), route tags, and other attributes, then permit or deny their redistribution.
- "No Redist" Action: Using a redistribution profile with a higher priority and "No Redist" action can be used to explicitly block certain routes that might otherwise be allowed by a lower priority "Redist" profile.
Route Manipulation
Once routes are selected for redistribution, their attributes can often be modified to influence routing decisions in the receiving protocol's domain.
- Metric Modification: Setting a specific metric for redistributed routes is a common way to influence path preference. For example, when redistributing static routes into OSPF, you can assign a specific cost and OSPF external route type (E1 or E2).
- Setting Tags: Route tags can be applied to redistributed routes. These tags can then be used by other routers for filtering or policy decisions.
- Modifying BGP Attributes: When redistributing into BGP, attributes like Local Preference, MED (Multi-Exit Discriminator), AS-Path (prepending), and Communities can be set or modified using route maps. This gives granular control over BGP path selection.
- Changing OSPF Route Type: When redistributing into OSPF, you can typically specify whether the route should be advertised as an External Type 1 (E1) or External Type 2 (E2) route. E1 includes the internal OSPF cost to the ASBR, while E2 only considers the external cost.
Route Injection
Route injection is essentially the act of introducing routes from one source into a dynamic routing protocol. This is the primary purpose of redistribution.
- Redistributing Static Routes: Commonly, static routes (e.g., to a specific partner network or a default route to the internet) are injected into dynamic protocols like OSPF or BGP to propagate them throughout the network.
- Redistributing Connected Routes: Directly connected networks on the firewall can be injected into dynamic routing protocols, making them reachable from other parts of the network.
- Conditional Advertisement: While not direct injection, route maps can be used to inject routes only if certain conditions are met (e.g., if a particular interface is up or another route exists).
Filtering and manipulation are often configured via
Network > Virtual Routers > [select_vr] > Redistribution Profiles
and, for more advanced control,
Network > Virtual Routers > [select_vr] > Route > Route Maps
.
6. Traffic Engineering with Redistribution
Traffic engineering involves guiding network traffic along specific paths to optimize performance, manage bandwidth, or provide redundancy. Route redistribution is a key tool for achieving traffic engineering goals by influencing the routing information exchanged between protocols.
- Path Preference with Metrics: By setting different metrics for routes redistributed into a protocol from different points or sources, you can make one path appear more desirable than another. For example, a route redistributed with a lower OSPF cost will be preferred over a route with a higher cost.
- Selective Route Advertisement: By filtering which routes are redistributed, you can ensure that certain parts of the network only learn specific paths, effectively forcing traffic for those destinations through desired gateways.
- AS-Path Prepending (BGP): When redistributing routes into BGP, you can prepend AS numbers to the AS_PATH attribute. Longer AS_PATHs are less preferred by BGP, allowing you to influence inbound traffic from external BGP peers.
- Setting BGP Local Preference: When redistributing routes into your iBGP, you can set a higher Local Preference on routes learned from a preferred exit point to ensure outbound traffic uses that path.
- Community Values (BGP): Attaching specific BGP communities to redistributed routes can signal to BGP peers (internal or external) how to treat those routes (e.g., no-export, local-AS, or custom communities for specific routing policies).
- Backup Path Activation: You can redistribute routes for a backup path with a less favorable metric (e.g., higher cost in OSPF, or lower local preference/longer AS-path in BGP). If the primary path fails and its routes are withdrawn, the backup path's redistributed routes become the active path.
Careful planning is essential in traffic engineering to avoid creating suboptimal routing or routing loops. It often involves a deep understanding of how different routing protocols make their path selection decisions.
7. Redistribution Techniques
Effective redistribution relies on various techniques to ensure stability, prevent routing loops, and achieve desired routing policies.
-
One-Way vs. Two-Way (Mutual) Redistribution:
- One-Way: Routes from Protocol A are redistributed into Protocol B, but not vice-versa. This is generally safer and easier to manage.
- Two-Way (Mutual): Routes from Protocol A go to Protocol B, AND routes from Protocol B go to Protocol A. This requires extreme caution due to the high risk of routing loops. Administrative distance manipulation, route tagging, and meticulous filtering are critical in such scenarios.
-
Use of Route Maps/Policies:
Route maps (or similar policy mechanisms in other vendors) are crucial for fine-grained control. They allow:
- Matching specific routes using prefix lists.
- Setting attributes (metric, tag, BGP communities, AS-path, local preference).
- Permitting or denying redistribution on a match.
- Filtering with Prefix Lists and Filters: As detailed earlier, applying filters based on source, destination, next-hop, or interface is fundamental.
-
Metric Management:
- Seed Metric: Defining a default metric for routes being redistributed into a protocol.
- Metric Translation: If possible, translating metrics from one protocol to another in a meaningful way (often difficult due to different metric calculation methods). Palo Alto Networks typically requires setting a new metric in the redistribution profile.
- Tagging: Assigning tags to routes during redistribution. These tags can then be used in route maps or filters elsewhere in the network to identify or influence these routes.
- Administrative Distance (AD) Tuning: While not a direct redistribution technique, understanding and sometimes adjusting the AD of routing protocols can prevent a virtual router from preferring a redistributed route that has looped back over a more direct, natively learned route. However, AD is a local setting on the router and influences which route source is preferred for the RIB, not directly how routes are advertised.
- Summarization at Redistribution Points: If appropriate, summarizing routes before redistributing them can reduce the size of routing tables in the receiving domain and improve stability.
8. Typical Scenarios for Redistribution
Redistribution is utilized in various network scenarios to achieve specific connectivity or policy goals.
- Migrating Between Routing Protocols: When transitioning from an older IGP (e.g., RIP) to a more modern one (e.g., OSPF), or from one OSPF design to another, redistribution allows for phased migration by enabling communication between segments running different protocols.
-
Connecting Different Routing Domains:
- IGP to EGP (e.g., OSPF into BGP): Internal routes (OSPF) are often redistributed into BGP to be advertised to external peers (like an ISP or other autonomous systems).
- EGP to IGP (e.g., BGP into OSPF): Specific BGP routes (often a default route or summary routes from an ISP) might be redistributed into an internal OSPF domain. This must be done carefully to avoid overwhelming the IGP with too many external routes.
- Integrating Acquired Networks: When companies merge, their networks might use different routing protocols. Redistribution can provide initial connectivity before a full network integration and protocol standardization.
- Connecting to Partner Networks with Static Routes: Static routes pointing to a partner's network can be redistributed into the internal dynamic routing protocol (e.g., OSPF) to make the partner network reachable for internal users.
- Providing Controlled Internet Access: A default static route pointing to an ISP can be redistributed into an IGP, allowing internal clients to reach the internet. Filtering can ensure only the default route is advertised.
- Hub-and-Spoke Topologies: In some SD-WAN or VPN overlay designs, routes from spoke sites (learned via BGP or static) might be redistributed at the hub into a core routing protocol, or vice-versa.
- Inter-VR Routing (Logical Routers): While Palo Alto Networks firewalls can route between logical routers (formerly virtual routers) using BGP (often iBGP with loopback interfaces), redistribution is used to get routes *into* BGP from other sources within each logical router.
- Lab or Test Network Integration: Routes to isolated lab networks, often configured statically, can be selectively redistributed into the production network for controlled access.
9. Mermaid Diagram: Redistribution Example
The following diagram illustrates a common scenario where static routes and connected interfaces on a Palo Alto Networks firewall are redistributed into OSPF, and then OSPF routes (including the redistributed ones) are further redistributed into BGP.
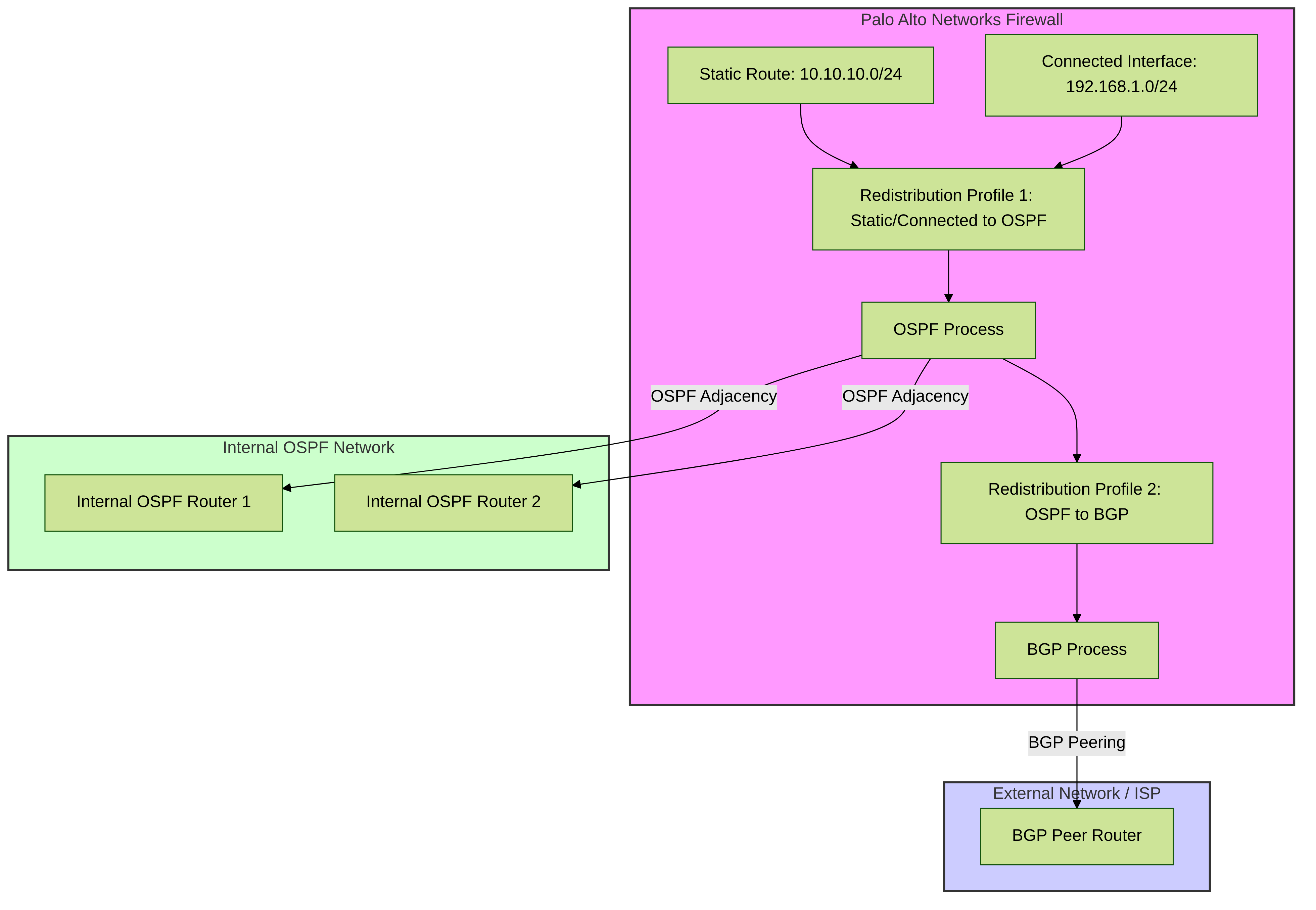
Diagram: Static/Connected routes redistributed into OSPF, and OSPF routes into BGP on a Palo Alto Networks Firewall.
In this diagram:
- A static route (e.g., for a DMZ or specific service) and a directly connected network are defined on the Palo Alto Networks firewall.
-
Redistribution Profile 1is configured to take routes from "Static" and "Connected" sources and inject them into the OSPF process running on the firewall. A metric and route type (e.g., E2) would be set here. - The OSPF process now includes these redistributed routes along with any native OSPF routes from other internal OSPF routers.
-
Redistribution Profile 2is configured to take routes from the "OSPF" source (which includes the previously redistributed static/connected routes and native OSPF routes) and inject them into the BGP process. Specific BGP attributes (like community, MED) could be set here using a route map associated with this profile. - The BGP process then advertises these routes to its BGP peer in the external network (e.g., an ISP).
10. Configuration Steps Overview
The following outlines the general steps to configure redistribution. Refer to your PAN-OS version's documentation for precise GUI navigation and CLI commands.
-
Plan Your Redistribution:
- Identify source and destination protocols.
- Determine which specific routes need to be redistributed.
- Decide on metrics, tags, and any other attribute manipulations.
- Consider potential routing loops and how to prevent them.
-
Navigate to
Network > Virtual Routersand select the desired virtual router. -
Go to the
Redistribution Profiletab and click Add to create a new profile. - Enter a unique Name for the profile.
- Set the Priority (lower value means higher priority).
-
Select the appropriate
Action
(
RedistorNo Redist). - Under the General Filter tab (or similar, depending on PAN-OS version), choose the Source Type(s) of routes to redistribute (e.g., static, connected, OSPF, BGP).
- Optionally, configure Filters for Destination, Interface, or Next-Hop to match specific routes.
- Define the Metric value to be assigned to the redistributed routes.
- For OSPF source, you might have options for Path Type, Area, and Tag filters.
-
Optionally, create and attach a
Route Map
for advanced filtering and attribute manipulation (configured under
Network > Virtual Routers > [VR] > Route > Route Maps, then applied in the Redistribution Profile). - Click OK to save the profile.
-
Apply the Redistribution Profile:
-
For redistributing
into OSPF
: Go to the OSPF configuration (
OSPF > Export Rules) and add an export rule, selecting your redistribution profile. Specify the Path Type (e.g., Type 1 or Type 2). -
For redistributing
into BGP
: Go to the BGP configuration (
BGP > Redist Rulesor similar, depending on PAN-OS version and if using Advanced Routing Engine) and apply the redistribution profile. - For redistributing into RIP : Go to RIP configuration and apply the profile under Export Rules.
-
For redistributing
into OSPF
: Go to the OSPF configuration (
- Commit the changes to the firewall.
-
Verify:
Check routing tables on the firewall and neighboring routers to ensure routes are being redistributed as expected and that there are no routing loops. Use commands like
show routing route,show routing protocol bgp rib-out, etc.
11. PCNSE Exam Considerations and Potential Questions
Redistribution is a significant topic for the PCNSE exam, testing your understanding of how Palo Alto Networks firewalls integrate into complex routing environments.
- Understanding Profile Application: Ensure that the Redistribution Profile is correctly referenced in the protocol's export or redistribution rules (e.g., OSPF Export Rules, BGP Redist Rules). A common mistake is creating the profile but not applying it.
-
Action and Source Type:
Verify that the
Action
is set to
Redistto enable redistribution and that the Source Type correctly matches the routes intended for redistribution. - Priority Impact: Understand the impact of Priority when multiple profiles could match a route – the profile with the numerically lowest priority value is processed first.
- Necessity of Profiles: Be aware that without a correctly configured and applied Redistribution Profile, routes will not be redistributed between protocols or sources.
- Filtering Logic: Know how to use filters within the profile (destination, interface, next-hop) and the purpose of "No Redist" actions.
- Metric Assignment: Understand that you need to assign a metric when redistributing, and how this metric might affect path selection in the destination protocol.
- OSPF Specifics: For OSPF, know the difference between E1 and E2 external route types and how to configure them during redistribution.
- BGP Specifics: Basic understanding of how to redistribute into BGP and where to apply these profiles (e.g., Redist Rules). Knowledge of route maps for BGP attribute manipulation is also beneficial.
-
Troubleshooting:
Be prepared for scenarios where routes are not appearing as expected in a neighboring router's routing table. This could involve checking:
- The redistribution profile itself (action, source, filters).
- The application of the profile to the correct protocol (e.g., OSPF export rules).
- Metrics assigned.
- Route maps if used.
- Neighbor adjacencies.
- Firewall's own routing table to ensure it has the route to begin with.
- Distinguishing from PBF: Understand that redistribution controls routing protocol advertisements, while Policy-Based Forwarding (PBF) overrides the routing table for specific traffic flows based on policy criteria. You can redistribute static routes, but not PBF rules.
Potential PCNSE Question Types:
-
Scenario-based:
"An administrator has configured OSPF and BGP. Routes learned via OSPF are not being advertised to BGP peers. What are two likely reasons? (Choose two.)"
- Possible answers: Missing redistribution profile, redistribution profile not applied to BGP, action in profile is "No Redist", source type in profile doesn't include OSPF.
-
Configuration Detail:
"When redistributing static routes into OSPF, which parameter in the OSPF Export Rule determines if the internal OSPF cost is added to the redistributed route's metric?"
- Answer: Path Type (External Type 1 vs. External Type 2).
-
Troubleshooting:
"A static default route 0.0.0.0/0 is configured on the firewall but is not being learned by internal OSPF routers. A redistribution profile named 'DefaultToOSPF' exists. What should be checked?"
- Answers might include: Check if 'DefaultToOSPF' profile is applied to OSPF export rules, verify 'Allow Redistribute Default Route' is enabled in OSPF if applicable, check the profile's source type includes 'static' and destination filter allows 0.0.0.0/0.
-
Concept Clarification:
"What is the primary mechanism for sharing routes learned by BGP with an OSPF domain on a Palo Alto Networks firewall?"
- Answer: Redistribution Profile.
-
Filtering:
"How can an administrator prevent a specific static route from being redistributed into OSPF while allowing all other static routes?"
- Answer: Use two redistribution profiles. One with a higher priority (lower number) set to "No Redist" for the specific static route, and another with a lower priority (higher number) set to "Redist" for all static routes.
Mastering route redistribution is key to leveraging the full routing capabilities of Palo Alto Networks firewalls and is essential for passing the PCNSE exam. Always refer to the official Palo Alto Networks documentation for the most current and detailed information.