BGP Redistribution Rules to Explicitly Advertise Host Routes and Routes that Do Not Exist in Local-rib
Resolution
Overview
There are instances where the Palo Alto Networks firewall has to redistribute host routes (routes with a /32 netmask, like loopback interfaces on the firewall) and routes that are not on the local rib (Rib-in) to the peers. The redistribution profiles do not have an option to select these host routes for redistribution, or the routes that are not on the routing table
Details
The redistribution of these host routes and the nonexistent routes into BGP can be achieved using the workaround below:
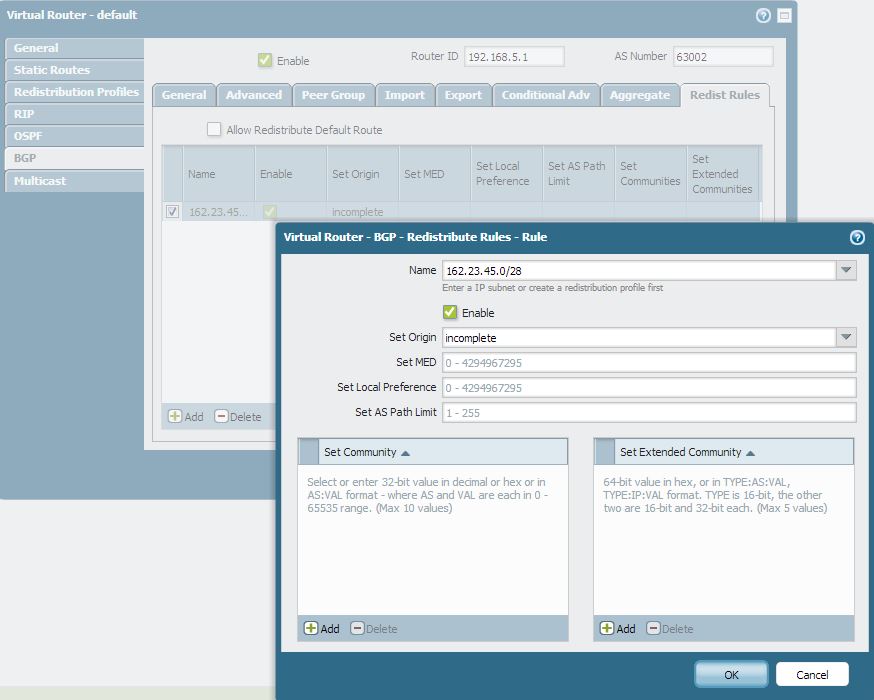
Configure a new redistribution rule under BGP by going to: Network > Virtual routers > BGP > Redistribution Rule
On the new Redistribution Rule window, configure the host route or the nonexistent networks in the “Name” field. Select the appropriate BGP attributes for these routes and check the “Enable” checkbox.
Other Important Information
This method of using the "Name" field in a BGP Redistribution Rule is a specific workaround for advertising prefixes that are not typically selectable through standard redistribution profile filters (like interface IP addresses/host routes or routes not present in the firewall's routing table).
- Use Cases: This is often used to advertise loopback interface addresses (/32 routes) used for management or BGP peering, or virtual IP addresses (VIPs) that don't exist as directly connected or static routes in the main RIB. It can also be used to selectively advertise specific subnets under controlled conditions.
- Considerations: While effective, use this method judiciously. Advertising routes that are not actually reachable through the firewall (if the route doesn't exist locally) can potentially lead to routing loops or blackholes if not carefully managed within the network topology.
- Standard Redistribution: For routes that *do* exist in the firewall's routing table (static, connected, routes learned via other protocols), using standard Redistribution Profiles with appropriate filters based on route type, tags, or access lists is the preferred and more scalable method.
- Attributes: When creating these rules, ensure you set the correct BGP attributes (like Origin, AS Path, Community, MED) as required by your network policy, just as you would for any other advertised route.