🔍 OSPF Neighbor Adjacency Deep Dive on Palo Alto Networks
1. Establishing Neighborship: The Requirements
Before OSPF routers can become fully adjacent and exchange routing information, they must first become neighbors. This requires several parameters, advertised in OSPF Hello packets, to match exactly between the interfaces on the same network segment:
- Area ID: Interfaces must belong to the same OSPF Area ID.
- Area Type: Both interfaces must agree on the Area Type flags (e.g., both Normal, both Stub, both NSSA). This includes the NSSA flag for Type 7 LSAs.
- Hello and Dead Intervals: The frequency of Hello packets and the time before declaring a neighbor down must match. Defaults on PAN-OS (and Cisco) are typically 10 seconds (Hello) and 40 seconds (Dead) for broadcast/point-to-point networks.
- Authentication: If authentication is enabled, the Authentication Type (None, Simple Password, MD5/SHA) and the corresponding Key/Password must match. Configured via Auth Profiles on Palo Alto firewalls.
- Subnet Mask: While OSPF can sometimes form adjacencies with mismatched masks on broadcast segments (leading to routing issues), it's a strict requirement for point-to-point links and best practice to match everywhere.
- MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit): While not checked in the Hello packet, the MTU is checked during the ExStart/Exchange phase. A mismatch will prevent the adjacency from reaching Full state.
Gotcha: Basic Layer 1/2/3 connectivity must exist first! Ensure interfaces are up, IP addresses are configured correctly on the same subnet, and firewalls/ACLs aren't blocking OSPF traffic (IP protocol 89, multicast addresses 224.0.0.5/224.0.0.6).
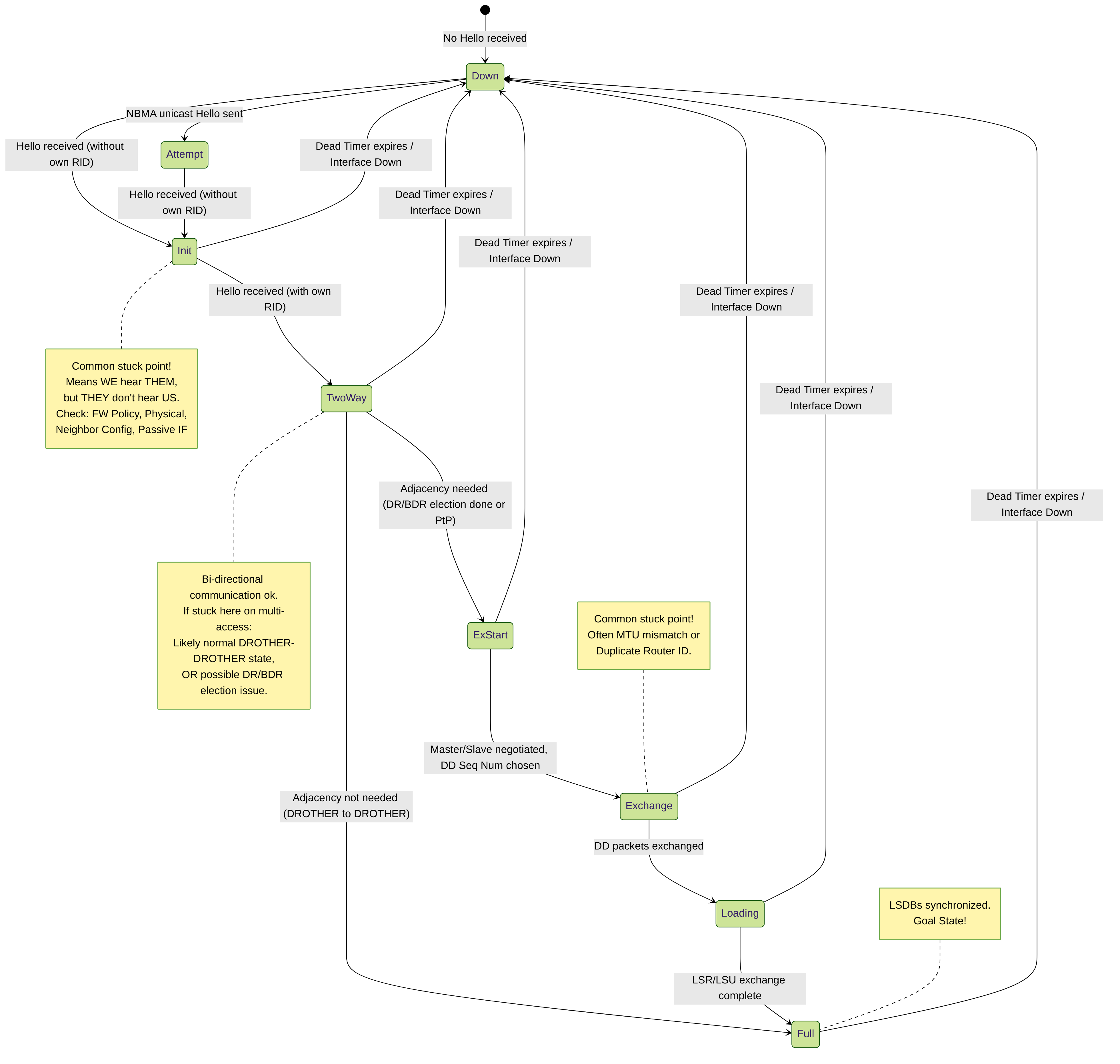
2. OSPF Neighbor States Explained (with Gotchas)
OSPF neighbors progress through distinct states. Understanding these states is key to troubleshooting.
-
Down:
The initial state. No valid OSPF Hellos have been seen from the neighbor within the Dead Interval.
Gotcha: If a neighbor flaps up and down, check for unstable links, high packet loss, or intermittent firewall blocking. - Attempt: Only used for manually configured neighbors on Non-Broadcast Multi-Access (NBMA) networks. Not common with typical Ethernet deployments on Palo Alto.
-
Init:
A Hello packet has been received from the neighbor, but it *doesn't* list the local router's Router ID (RID) in its "Active Neighbors" field.
Gotcha: This is a very common "stuck" state. It means communication is likely **unidirectional**. The local router hears the neighbor's Hellos, but the neighbor isn't hearing (or processing) the local router's Hellos. Check:- Firewall policies blocking *outgoing* Hellos from the local firewall or *incoming* Hellos on the neighbor.
- Physical layer issues (bad cable, duplex mismatch).
- Basic IP connectivity *from* the neighbor *to* the local router's OSPF interface IP.
- Ensure the neighbor interface isn't configured as passive.
- Check for mismatched Hello parameters (Area ID, Timers, Auth, Subnet, Area Type).
-
2-Way:
Bidirectional communication is confirmed. Each router sees its *own* RID in the neighbor's received Hello packet. On multi-access networks (like Ethernet), the DR/BDR election process occurs now.
Gotcha:- On multi-access networks, routers that are neither DR nor BDR (DROthers) will form a full adjacency ONLY with the DR and BDR. Their neighbor state with other DROthers will **remain in 2-Way**, which is normal.
- If a router *should* be forming a full adjacency (e.g., on a point-to-point link, or between DR/BDR/DROTHER) but is stuck in 2-Way, it might indicate issues with the DR/BDR election process (e.g., priority conflicts, inconsistent network type views) or potentially mismatched parameters preventing the move to ExStart.
-
ExStart:
First step in database synchronization. Routers negotiate a master/slave relationship (based on highest RID) and agree on the initial Database Descriptor (DBD) sequence number.
Gotcha: If stuck here, the most common cause is an **MTU mismatch** between the neighbor interfaces. OSPF checks the MTU listed in the DBD packet against the interface's configured MTU. Duplicate Router IDs can also sometimes manifest here. -
Exchange:
Routers exchange DBD packets, which contain summaries (headers) of the LSAs in their LSDBs. Routers compare received DBDs with their own LSDB to determine which LSAs they need to request.
Gotcha: Also commonly stuck due to **MTU mismatches** (as larger packets might be involved). Duplicate RIDs, corrupted packets, or issues within the LSA database itself can also cause problems here. -
Loading:
Routers send Link State Request (LSR) packets asking for the full details of LSAs identified as missing or outdated during the Exchange state. Neighbors respond with Link State Update (LSU) packets containing the requested LSAs. Link State Acknowledgement (LSAck) packets confirm receipt.
Gotcha: Getting stuck here usually implies issues transferring the full LSA information. This could be due to packet corruption, resource exhaustion on a router, inconsistent LSA information between neighbors, or potentially subtle MTU issues causing problems with larger LSU packets. - Full: Success! The LSDBs are synchronized between the two routers, and they are fully adjacent. They can now route traffic based on the shared understanding of the network topology.
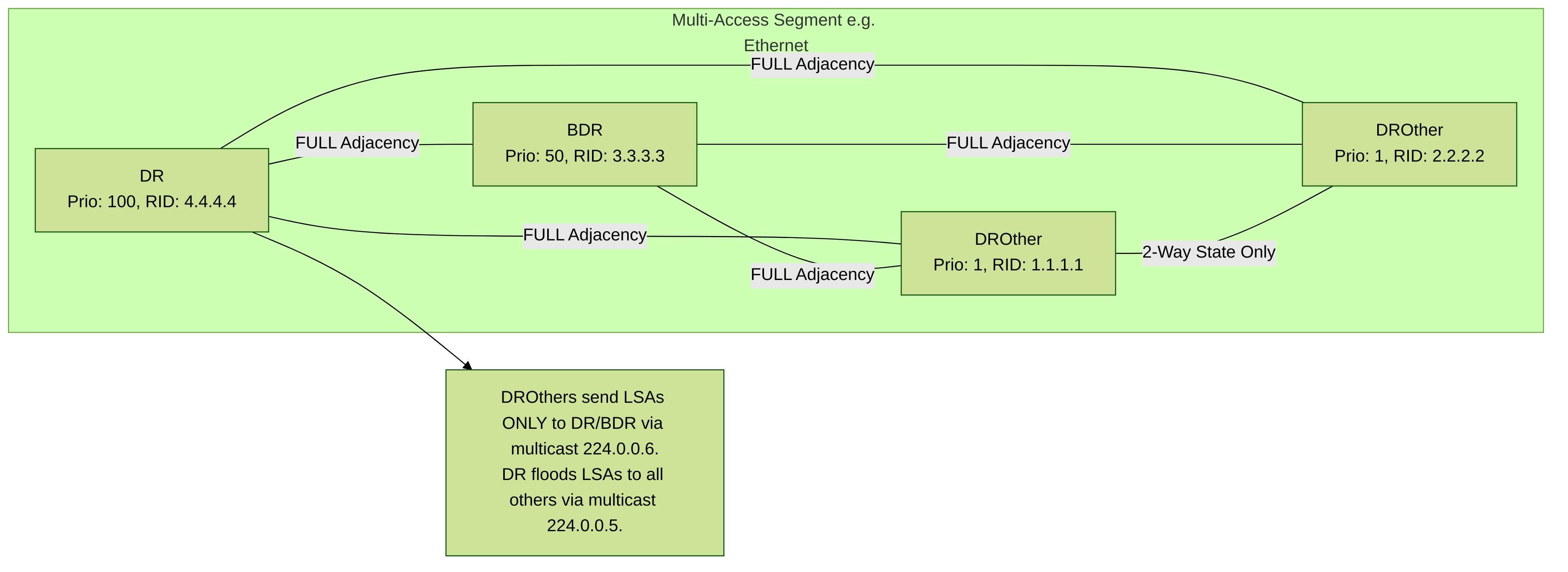
3. Designated Router (DR) and Backup Designated Router (BDR) Deep Dive
On multi-access segments (like Ethernet, default for Palo Alto interfaces), OSPF elects a DR and BDR to optimize LSA flooding. Instead of every router forming full adjacencies with every other router (N*(N-1)/2 adjacencies), all routers (DROthers) form full adjacencies only with the DR and BDR.
-
Election Process:
-
Routers with interface OSPF
Priority > 0 participate. Priority 0 means ineligible. - Highest Priority wins DR. Second highest wins BDR.
-
If priorities tie, the router with the
Highest Router ID wins the tied position (DR or BDR).
-
Routers with interface OSPF
- Timing: Election happens during the 2-Way state after Hellos are exchanged bidirectionally.
- Non-Preemptive: Once elected, a DR/BDR retains its role even if a new router comes online later with a higher priority/RID, unless the current DR/BDR fails or OSPF is restarted.
- Palo Alto Config: Priority is set per-interface under Network > Virtual Routers > [VR Name] > OSPF > Area > [Area ID] > Interface > [Interface Name] > Priority . Default is 1.
- Purpose: Reduces LSA flooding traffic and the number of adjacencies. DROthers send updates to the DR/BDR (using multicast 224.0.0.6), and the DR then floods the update to all other routers on the segment (using multicast 224.0.0.5).
- Gotcha: If you have inconsistent views of who the DR/BDR is, or if the election keeps flapping, check for unstable interfaces, duplicate RIDs, or potential issues causing routers to miss Hellos during the election window. Ensure all routers agree on the OSPF network type for the segment (should be Broadcast by default on Ethernet).
4. Troubleshooting OSPF Adjacency on Palo Alto Networks
When OSPF adjacency fails or gets stuck, systematically check the potential causes based on the state:
- Check Basic Connectivity: Can the firewall ping the neighbor's OSPF interface IP? Is the interface physically up and configured correctly ( Network > Interfaces )?
- Check Firewall Policy/ACLs: Is there a Security Policy unintentionally blocking IP protocol 89? (Less common if traffic originates from the firewall itself, but possible). Check external devices for ACLs.
-
Verify OSPF Configuration on PAN-OS:
- Is OSPF enabled on the Virtual Router ( Network > Virtual Routers > [VR Name] > OSPF > Enable )?
- Is the correct interface added to the correct OSPF Area with the correct type ( Network > Virtual Routers > [VR Name] > OSPF > Area > Interface )?
- Is the interface accidentally set to Passive ( ... > OSPF > Area > Interface > Passive )?
- Do the parameters (Hello/Dead Interval, Priority, Auth Profile) match the neighbor exactly ( ... > OSPF > Area > Interface )?
- Is the MTU setting correct ( Network > Interfaces > [Interface Name] > Advanced > MTU )?
-
Use CLI Verification Commands:
-
show routing protocol ospf neighbor: Check the current state. Look for neighbors stuck in Init, ExStart, Exchange etc. -
show routing protocol ospf interface: Verify configured timers, cost, priority, type, state, and detected DR/BDR on the segment. -
show routing protocol ospf summary: Verify the Router ID and basic OSPF process status. -
show counter global filter delta yes packet-filter yes | match ospf: Check if OSPF packets are being processed or dropped by hardware/software.
-
-
Check Logs and Debugs (Use cautiously):
-
less mp-log routed.log: Look for specific error messages related to neighbor state transitions or parameter mismatches. -
debug routing ospf component event level dump: See real-time neighbor state changes and potential reasons. -
debug routing ospf component packet level dump: See Hello/DBD packet details (can reveal parameter mismatches). -
Remember to turn off debugs:
debug routing ospf off
-
- Check Runtime Stats in WebUI: Network > Virtual Routers > [VR Name] > More Runtime Stats provides a GUI overview of neighbors, interface states etc.
-
Stuck in
Init : Usually unidirectional communication or basic parameter mismatch (check firewalls, physical links, Area ID, Auth, Timers). -
Stuck in
ExStart/Exchange : Very often MTU mismatch, or duplicate Router ID. -
Stuck in
2-Way : Normal for DROTHERs on multi-access; otherwise, check DR/BDR election or parameters.
5. PCNSE Exam Focus & Quiz
For the PCNSE exam, expect questions related to:
- Identifying required parameters for OSPF adjacency.
- Troubleshooting neighbor states (especially Init, 2-Way, ExStart/Exchange).
- Understanding the DR/BDR election process and purpose.
-
Knowing key Palo Alto Networks CLI commands for verification (
show routing protocol ospf neighbor,show routing protocol ospf interface). - Locating OSPF configuration elements in the PAN-OS WebUI (Virtual Router settings).
- Understanding common reasons for adjacency failures (MTU, Auth, Timers, Area ID, etc.).