🔍 Palo Alto Networks Transceiver Troubleshooting Guide
Transceivers (like SFPs, SFP+, QSFP, QSFP28, etc.) are critical components for network connectivity on Palo Alto Networks firewalls, especially for fiber optic links. Issues with transceivers can prevent links from coming up or cause intermittent connectivity problems. This guide covers common troubleshooting steps and commands. Transceiver monitoring, also known as digital optical monitoring (DOM), allows you to view diagnostics like transmitted bias current, transmitted power (Tx), received power (Rx), temperature, and voltage, which are crucial for troubleshooting optical links.
🔬 Initial Checks and CLI Commands
Start by inspecting the transceiver status and details using the CLI.
📡 Show Transceiver Details
These commands provide detailed information about the installed transceiver(s), including vendor, part number, serial number, and optical power levels.
-
Show details for a specific interface:
show transceiver-detail ethernet1/1 -
Show details for all interfaces with transceivers:
show transceiver-detail all
Key fields to examine in the output:
- Vendor Name/Part Number: Helps confirm if a supported transceiver is being used.
- Serial Number: Unique identifier for the specific module.
- Connector: (e.g., LC) Matches the cable type.
- Transceiver Type: (e.g., 1000B-SX, 10GBASE-SR, 40GBASE-SRBD) Confirms the speed and fiber type.
- Nominal Bit Rate: Expected speed.
- Link Length: For different fiber types (e.g., OM3, OM4).
- Temperature: Operating temperature.
- Voltage: Power supply voltage.
-
Tx Power (Output Power):
The power the transceiver is transmitting.
- Should be within the vendor's specified range. Low Tx power can indicate a faulty transmitter or dirty connector.
-
Rx Power (Input Power):
The power the transceiver is receiving from the peer device.
- This is critical for troubleshooting link issues. Rx power must be above the receiver sensitivity threshold of the transceiver and within the acceptable range.
- Low Rx power can indicate excessive signal loss in the cable (long distance, bad splice, dirty connectors), issues with the transmitting transceiver on the peer device, or a faulty receiver on the local transceiver.
- High Rx power can potentially damage the receiver, although less common with modern optics.
- Alarms/Warnings: Check for any flags indicating temperature, voltage, Tx power, or Rx power is outside acceptable limits.
📦 SFP Module State via System State
The `show system state` command can provide lower-level details about the physical interface and detected module.
show system state filter sys.sX.pY.phy
Replace `sX` with your slot number and `pY` with your port number (e.g., `sys.s1.p19.phy` for slot 1, port 19).
Look for:
- `media`: Should show the expected media type (e.g., SFP-Plus-Fiber). If it shows "SFP-Empty" or similar, the module is not detected.
- `sfp` block: Contains parsed information like vendor, part number, serial number, etc.
- `link-partner`: Information about the device on the other end, if the link is up.
If `show system state` shows "SFP-Empty" but you believe a module is installed, try reseating the module or restarting the device/interface.
🔗 Check Link Status
While transceiver details are important, always verify the interface's logical and physical link status.
show interface ethernet1/1
Check:
- Link state: Should be 'up'.
- State: Operational state (e.g., 'up').
- Speed/Duplex: Verify negotiated or configured speed and duplex match the peer device.
- Counters: Look for incrementing error counters (e.g., CRC errors).
📄 Review System Logs
System logs can provide crucial information about interface status changes, transceiver insertion/removal events, and hardware errors.
show log system direction equal backward
Filter logs for relevant events, such as those related to the specific interface or keywords like "transceiver," "link," or "ethernet".
tail lines 100 follow yes mp-log brdagent.log
This command provides a real-time view of logs from the board agent process, which handles hardware events like transceiver hot-plugging.
🛠️ Advanced Debugging
For deeper troubleshooting, use debug commands (use with caution in production).
debug system interface-xcvr-info ethernet1/1
This command provides low-level raw data from the transceiver's internal registers (EEPROM). Interpreting this requires knowledge of SFP/QSFP MSA standards but can be helpful for advanced issues or when working with support.
✅ Compatibility
Using officially supported transceivers is highly recommended. Unsupported transceivers may appear to work initially but can cause unpredictable issues or stop working after PAN-OS upgrades.
- Always check the official Palo Alto Networks hardware compatibility list for your specific firewall model and PAN-OS version.
- Even if a third-party transceiver is marketed as "compatible," issues can arise due to firmware differences or strict validation on the firewall.
🚶 Troubleshooting Transceiver Issues: Step-by-Step Flow
Follow this general process when troubleshooting transceiver or fiber optic link issues.
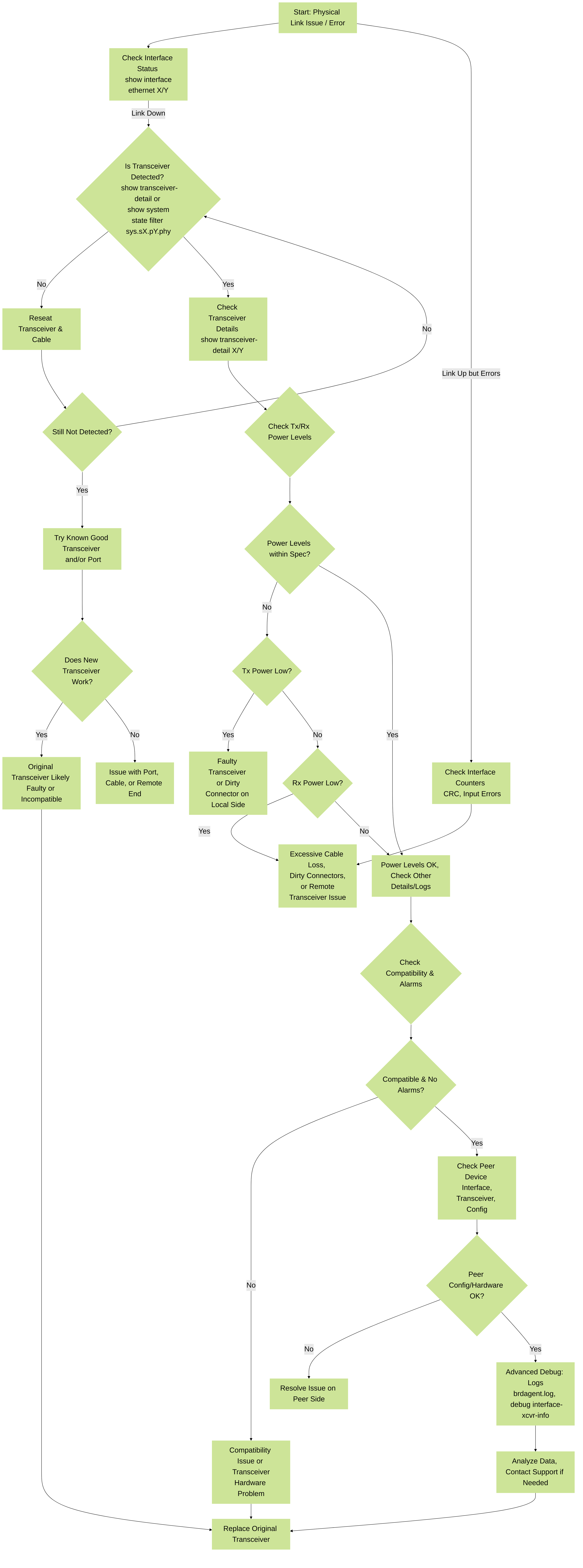
Transceiver Troubleshooting Flowchart
🔁 Debug and Log Analysis Sequence
This diagram illustrates the sequence of using key debug commands and logs.
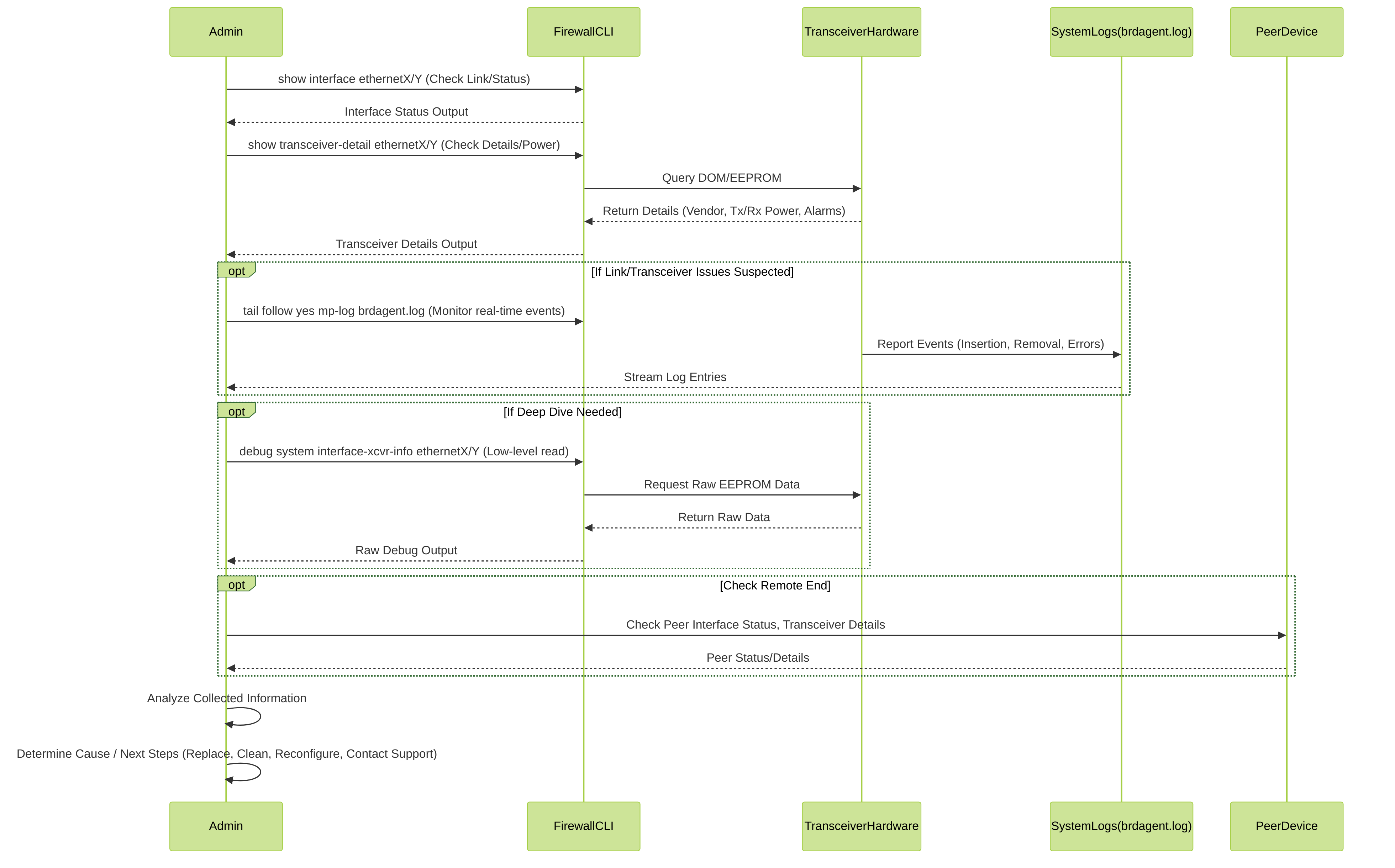
Transceiver Debug and Log Analysis Sequence