Configure an IP Tag Cloud Connection
An IP-Tag Cloud Connection allows the Cloud Identity Engine to collect IP address-to-tag information from cloud service providers. To enforce a tag-based security policy that adapts to IP address changes, configure Dynamic Address Groups using the IP address-to-tag information.
To configure the Cloud Identity Engine to collect IP address-to-tag (also known as IP-tag) information for policy enforcement, configure a connection to your cloud service provider to synchronize the mappings. The identity management system provides the IP-tag information to the Cloud Identity Engine for processing, which then provides the information to the firewalls for policy enforcement.
To collect IP-tag information from your cloud service provider, you must grant the Cloud Identity Engine the required permissions.
- Azure — Grant the read permissions as described in the Azure Monitoring section in the VM Series documentation to the service account.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) — Grant the service account the Amazon Role Name (ARN) roles as described in the IAM Roles and Permissions for Panorama section as shown in the JSON example in the VM Series documentation . For more information on the ARN, refer to the AWS documentation .
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) — Grant the IAM roles as described in the VM Series documentation to the service account.
If you use Strata Cloud Manager , you can view your IP-tag information using the unified interface and use it to create your tag-based security policy .
For each region, you can synchronize up to 60,000 IP-tag mappings from a cloud service in a monitoring configuration at one time. The Cloud Identity Engine sync only the new or modified mappings each time. You can view up to 32,000 IP-tag mappings per page.
You can also view all IP-tag information in the Cloud Identity Engine ( User ContextMappings and tags ).
- If you have not already done so, activate User Context and use the default segment or configure a new segment to receive the mapping information.
- Select User ContextIP-Tag Collection .
- Select the Credential Configuration tab (if it does not already display).
- To Set Up a New Credential Configuration , select the cloud service provider you want to use.
- AWS
—Connect to an Amazon Web Services (AWS) instance.
- Azure
—Connect to a Microsoft Azure Active Directory instance.
- Google Cloud Platform
—Connect to a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) instance.
-
- Enter a unique and descriptive Name for the configuration.
- ( AWS only ) Configure your AWS connection.
To open your AWS administrator portal in a new window so you can create or edit any necessary ARNs, select the type of Cloud Formation Template (CFT) you want to configure and log in with your AWS credentials.
- Open CFT (Application Account Prerequisites) —Configure the Application Account prerequisites.
- Open CFT (Security Account Prerequisites) —Configure the Application Account prerequisites.
To enable monitoring using the current account, you only need to configure the application account prerequisites. If you want to use a different account, such as a service account or a cross-account role , to collect the data, you must configure the application account prerequisites, the security account prerequisites, and a role ARN for the account. For more information, refer to the Amazon documentation.
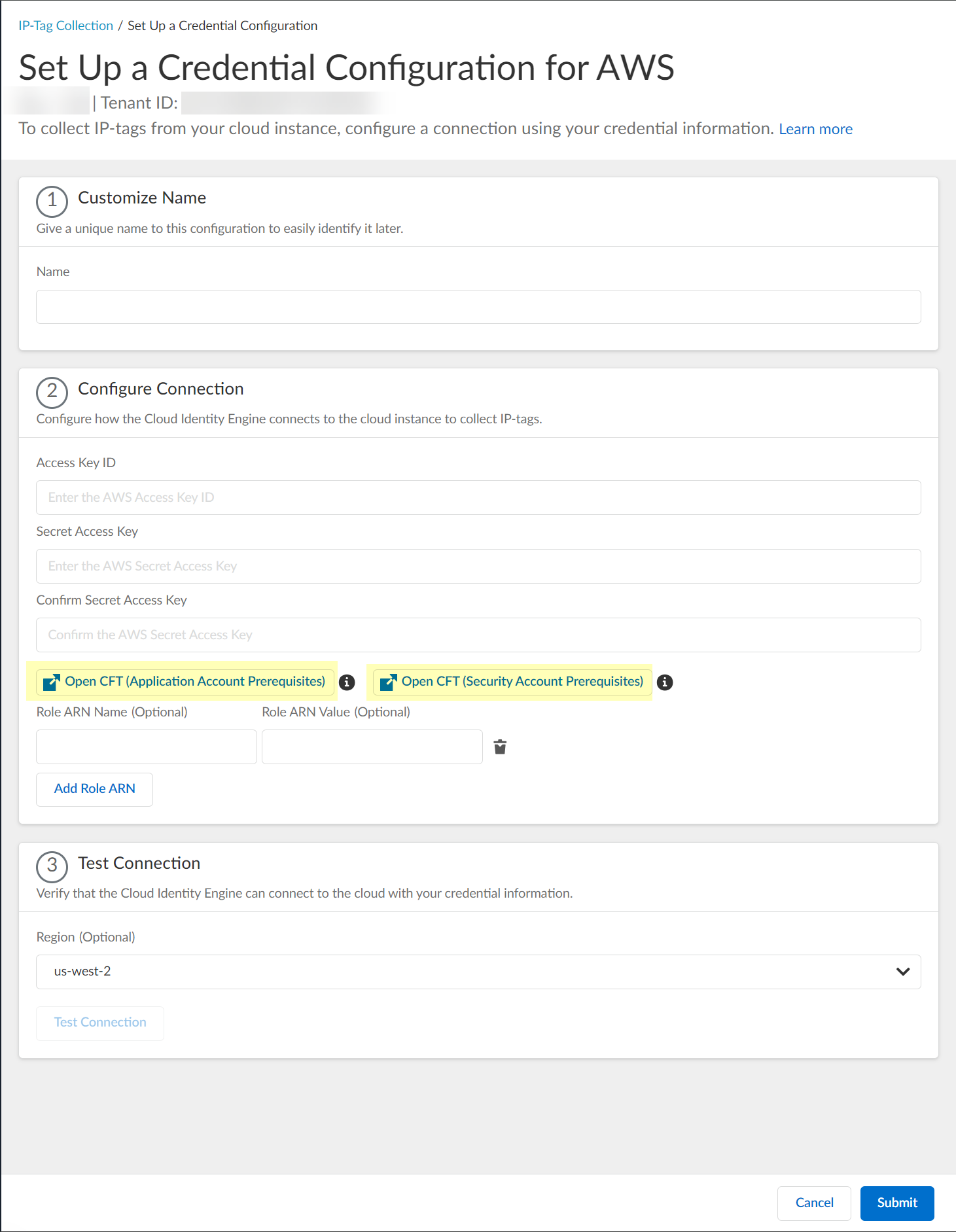
3. Enter your Access Key ID .
To learn how to obtain your access key ID and secret access key, refer to the AWS documentation.
4. Enter your Secret Access Key .
5. Reenter your secret access key to Confirm Secret Access Key .
6. (Optional) Enter a Role ARN Name and Role ARN Value .
To configure additional Role ARNs, click Add Role ARN for each Role ARN you want to include.
- ( Azure only ) Configure your Azure connection.
1. Enter your Client ID .
To learn how to obtain the client ID and client secret, refer to the Azure documentation .
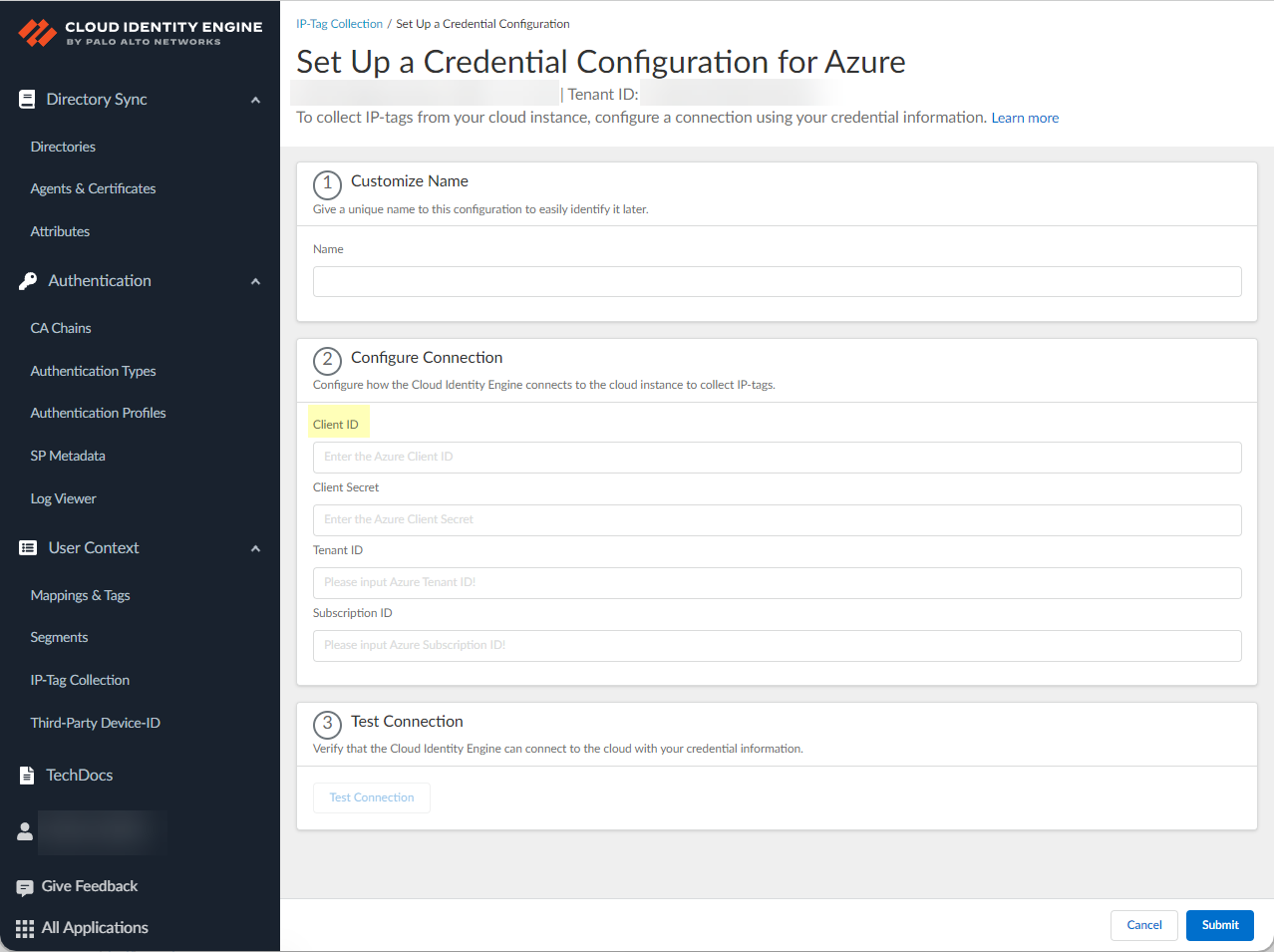
2. Enter your Client Secret .
3. Enter your Tenant ID .
To learn how to obtain the tenant ID and subscription ID, refer to the Azure documentation.
4. Enter your Subscription ID .
- ( Google Cloud Platform only ) Configure your GCP connection.
1. Create credentials for a service account in your Google Cloud console, then download and save the JSON file in a safe location.
2. Click Browse files and click Open to navigate to the JSON file or drag and drop the GCP credential JSON file.
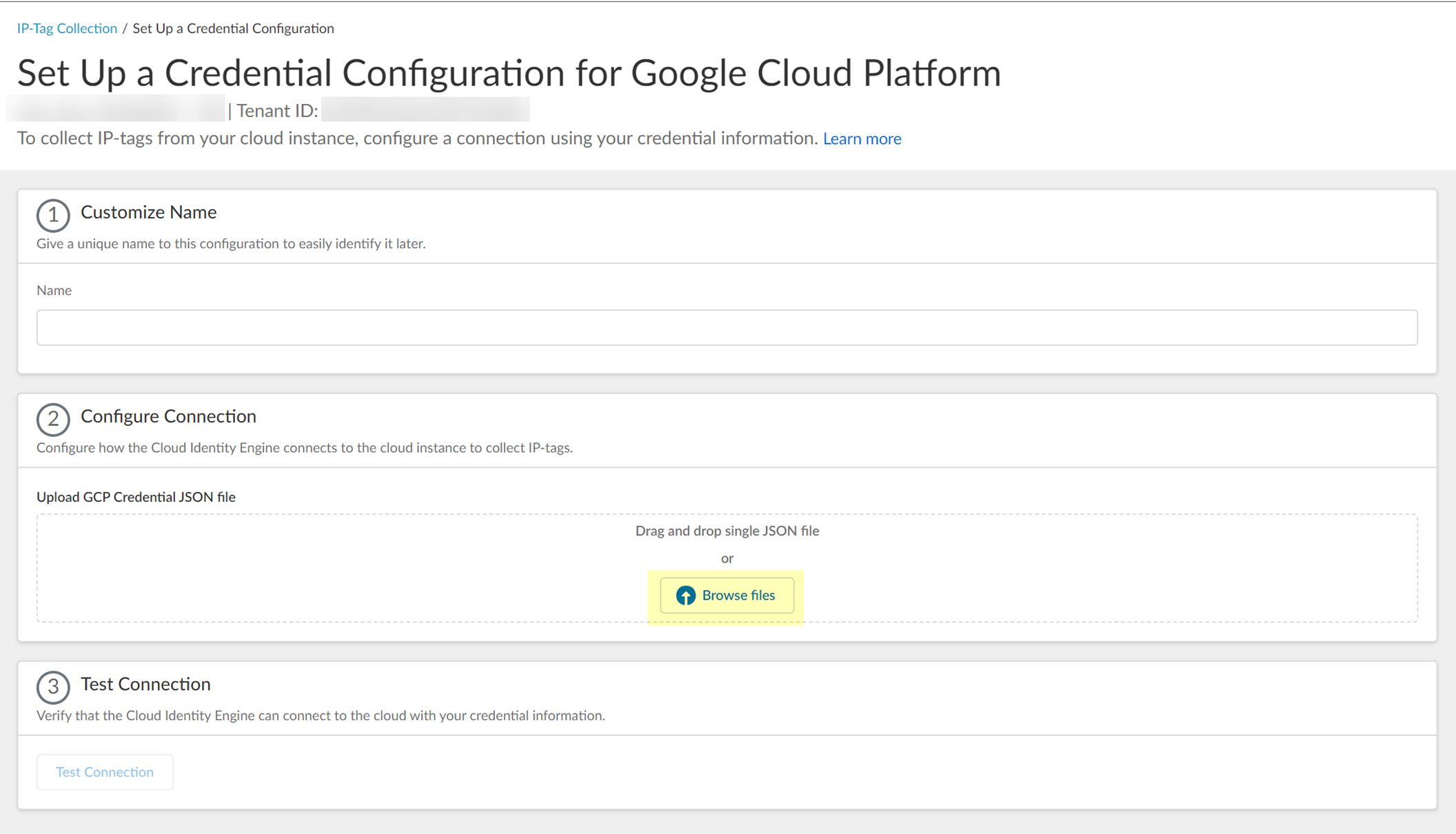
3. (Optional) Select the Region for the instance.
You can optionally Search for a region. If you don't select a region, the Cloud Identity Engine uses the us-west-2 region. You can select one region per instance.
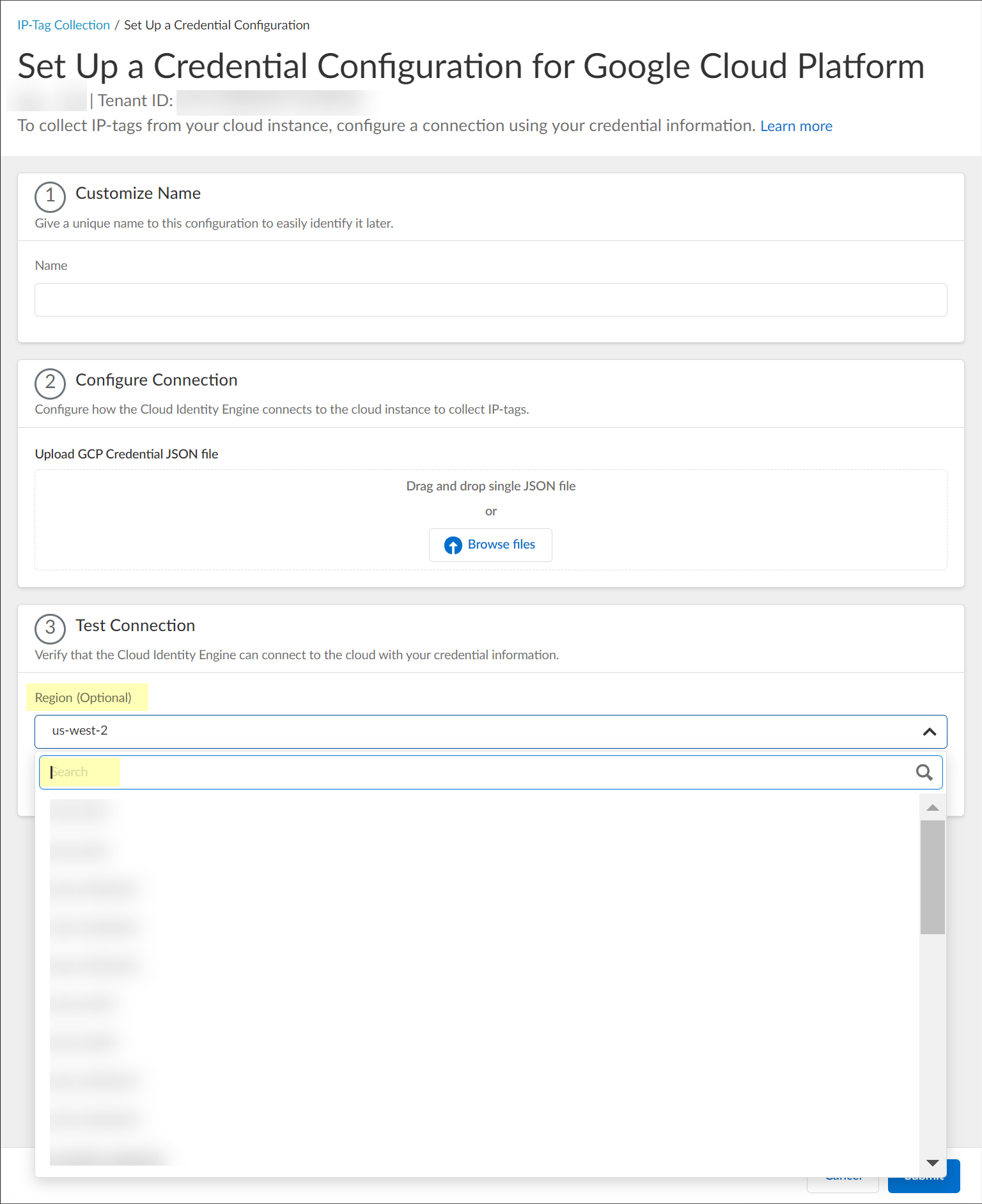
- Verify the connection by clicking the Test Connection button.
( AWS and Google Cloud Platform only ) You can optionally select the Region before testing the connection. By default, the Cloud Identity Engine selects the US West region; if this region does not allow API requests, select a region that can allow API requests.
Even if the connection test isn't successful, you can still submit your configuration; until you resolve the connectivity issues, the configuration status is Not connected . You must resolve the connection issues for the configuration to successfully retrieve the IP address-to-tag mappings.
- Submit the configuration.
To collect and view your IP-Tag mappings, you must configure a
IP-Tag monitor configuration
.
- ( Strata Cloud Manager only ) If you're using Strata Cloud Manager , view the tags that the Cloud Identity Engine shares with Strata Cloud Manager by selecting an address group then select the Tags from CIE tab when you add match criteria .
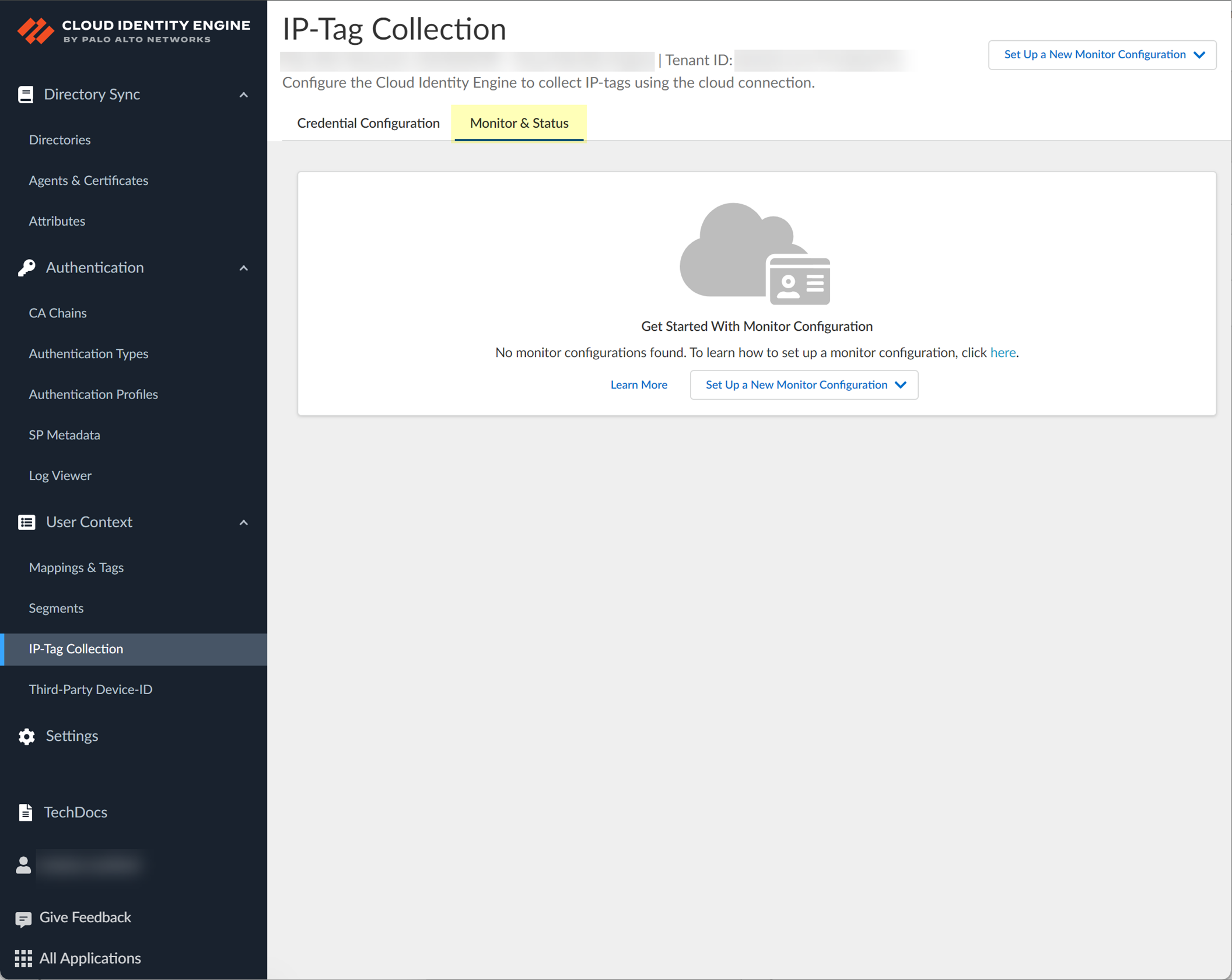
- To configure a connection to your cloud service provider for monitoring purposes (such as audits) or to share the IP address-to-tag mapping information using a segment , select the Monitor & Status tab.
There are four states for the connection to the cloud service provider:
- Connected —The Cloud Identity Engine has successfully established a connection with the cloud service provider and can collect IP-tag mapping information.
- Partially connected —The Cloud Identity Engine could successfully establish a connection to some aspects of the configuration, such as the region for AWS, but not all of them. The Cloud Identity Engine receives IP-tag mappings from connected sources; it does not receive them from unconnected sources.
- Connection pending —The Cloud Identity Engine has successfully established a connection but has not completed the sync for the IP tag mappings from one or more regions.
For more information on the connection status, select Click to see details .
- Not connected —The Cloud Identity Engine couldn’t successfully establish a connection with cloud service provider using the current configuration.
5. Set Up a New Monitor Configuration and select the monitor configuration for the cloud service provider that you configured for credential configuration in step
4
.
6. Enter a unique and descriptive Name for the configuration.
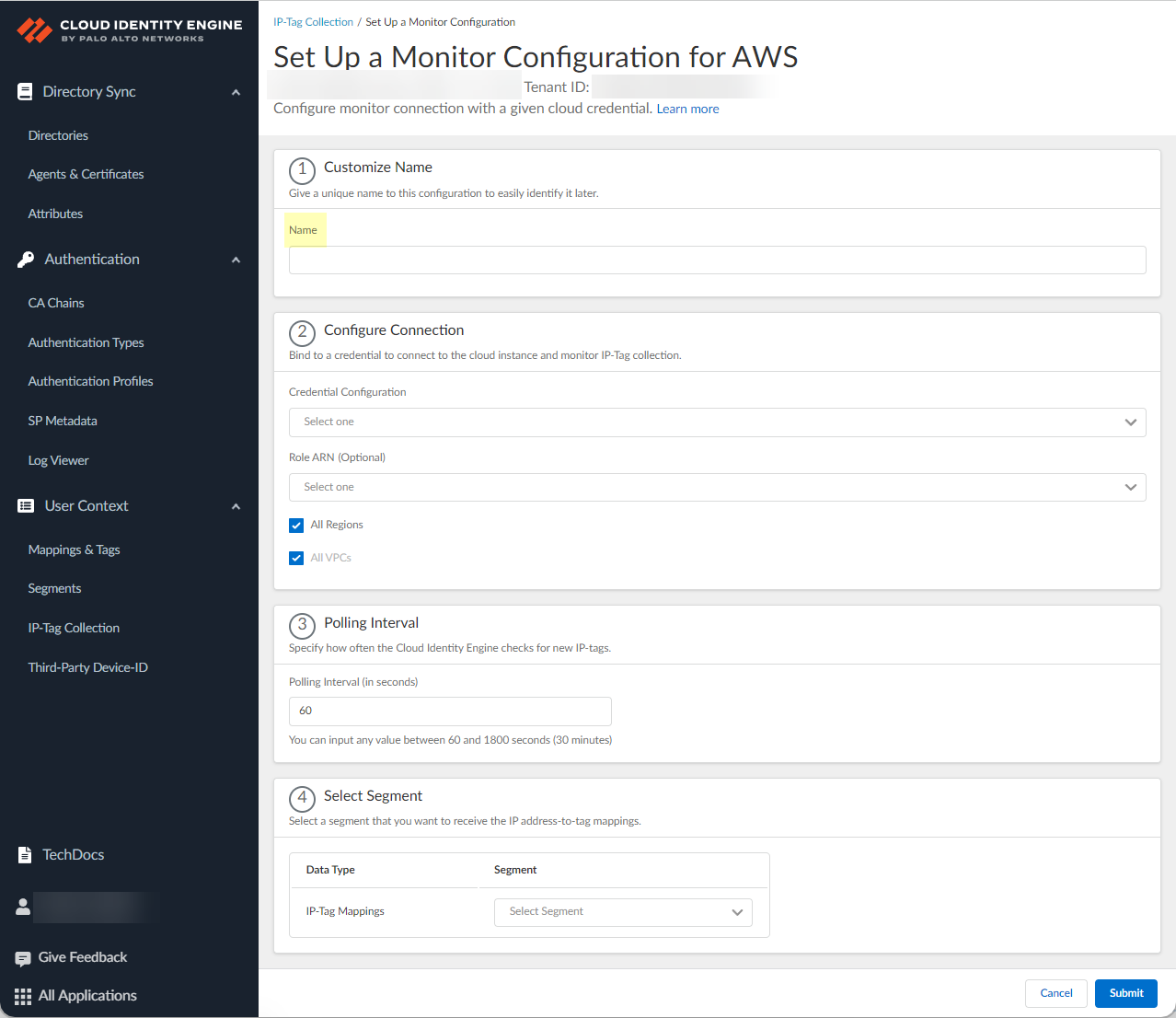
7. Select the Credential Configuration that you configured in step
4
.
8. ( AWS only ) Optionally select the Role ARN you want to use.
9. Select if you want to configure the connection for All Regions , All VPCs (AWS only) or All Project IDs (GCP only).
To select a specific region or virtual private cloud (VPC), deselect the All Regions or All VPCs check box and allow the list of regions or VPCs to populate, then select the region or VPC you want to include. To select a specific VPC, you must first select one or more regions or select all regions.
10. ( Azure only ) Select whether you want to Fetch Service Tags .
Azure Service tags simplify security for Azure virtual machines and Azure virtual networks because you can restrict network access to just the Azure services you want to use. A service tag represents a group of IP address prefixes for a particular Azure service. For example, a tag can represent all storage IP addresses.
11. Define the Polling Interval (in seconds) to specify how frequently the Cloud Identity Engine checks for new data.
The default is 60 seconds and the range is 60–1800 seconds.
12. If you want to share the mappings, select the segment you configured in step 1. Otherwise, if you want to create this configuration only for monitoring without sending mappings to any firewalls, select None .
If you need to change the segment after you submit the configuration, you must create a new configuration and select the segment you want to use.
13. Submit the configuration.
- Search and monitor your configurations in the Cloud Identity Engine.
1. Select the Monitor & Status tab.
2. Use the filters to highlight the information you want to find.
- Name —Enter the name of a configuration to filter results to this configuration.
The search query does not need to be an exact match for the name.
- Vendor —Select the vendor type of the cloud service provider to filter the results to this vendor type.
- Status — Select the status type (such as Connected or Partially Connected ) to filter the results to this status type.
- Segment — Select the Segment name to view the monitor segments that send mappings to the segment you select.
- Associated Credential — Select the name of the Associated Credential configuration to view monitor segments that use the credential configuration type you select.
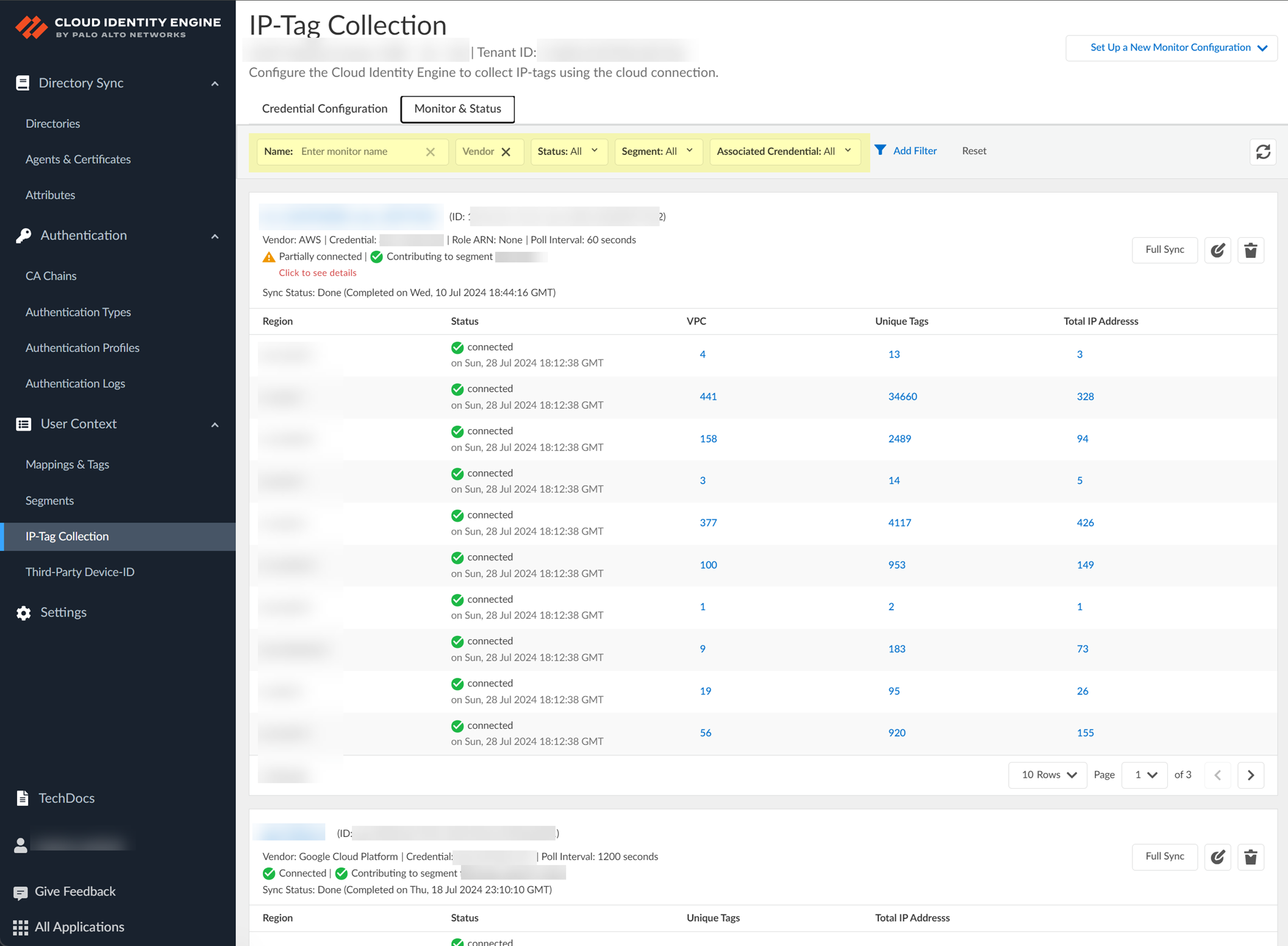
3. (Optional) To remove the filter, click Reset .
- Manage your IP-Tag Collection configuration.
1. (Optional) To sync all new IP-tag mappings and use them in the security policy immediately or to resolve any discrepancies in the IP-tag mappings, click Full Sync .
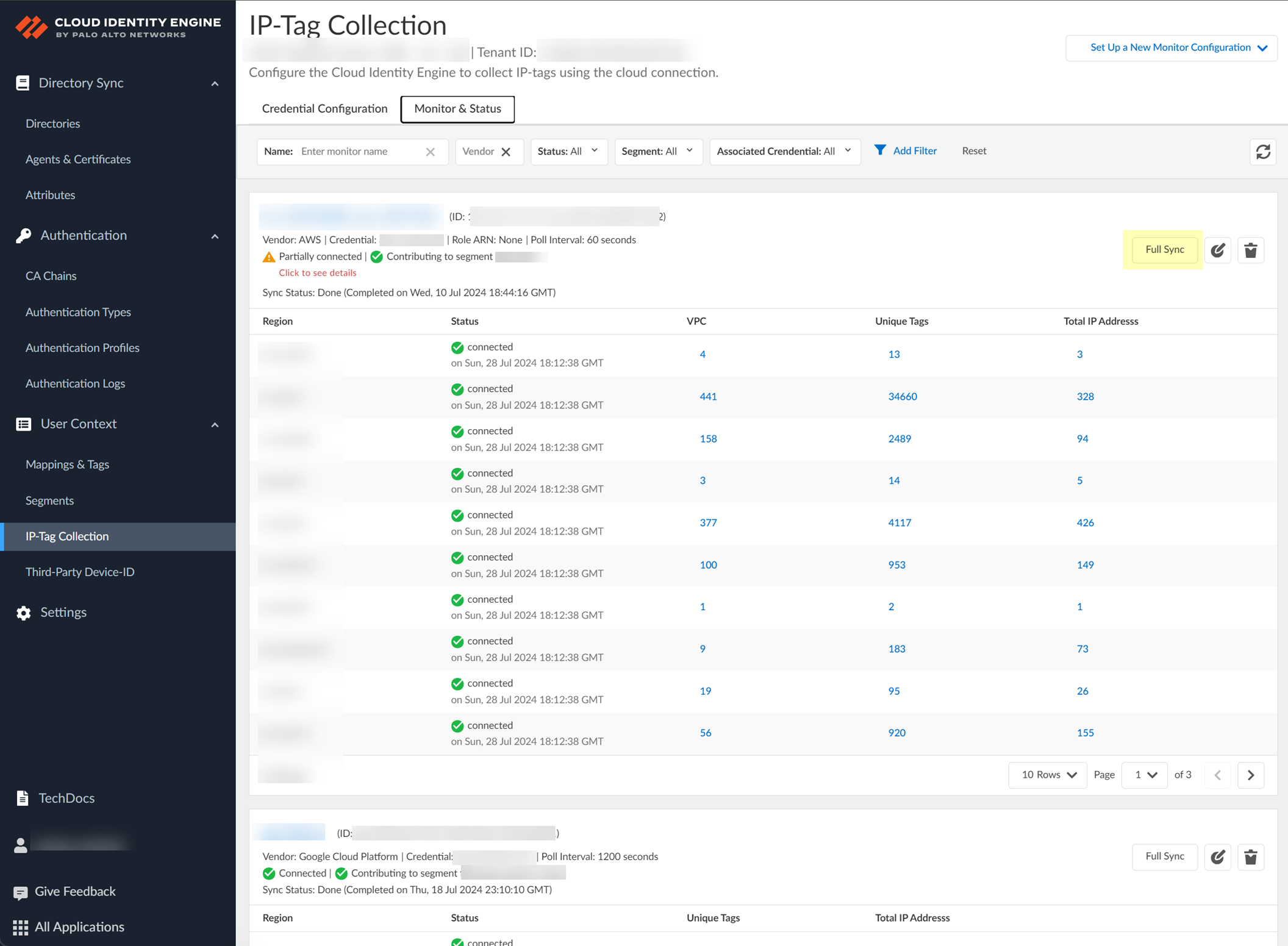
The Sync Status displays the time and date of the last sync.
2. (Optional) To change the IP-Tag Collection configuration, click Edit .
3. (Optional) To remove the IP-Tag Collection configuration, click Delete and confirm the deletion.
When you confirm the deletion, the Cloud Identity Engine removes all IP-tag mappings from the cloud service provider and from any firewalls that collect the IP-tag mappings to enforce security policy.
- View more details for a specific configuration.
1. Select the name of the configuration that you want to view from the IP-Tag Collection page.
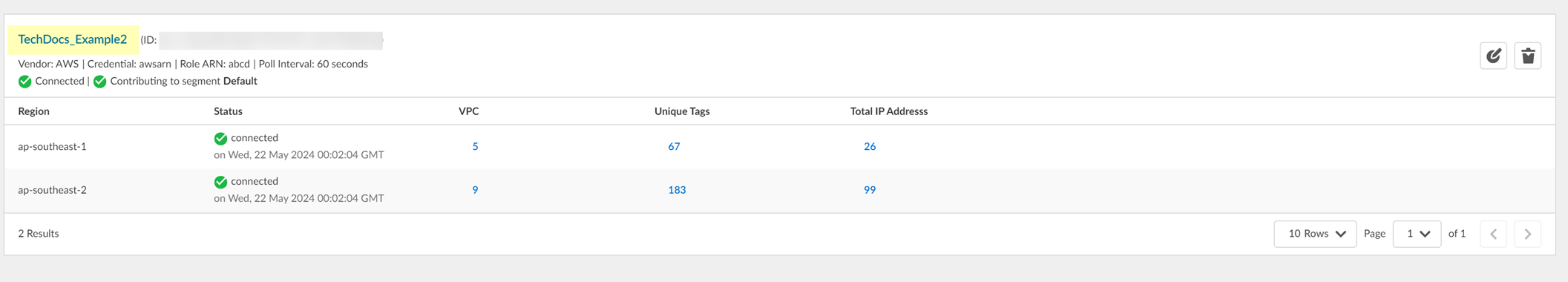
2. On the Monitor & Status page, review the Connection Details to view information such as the connection status.
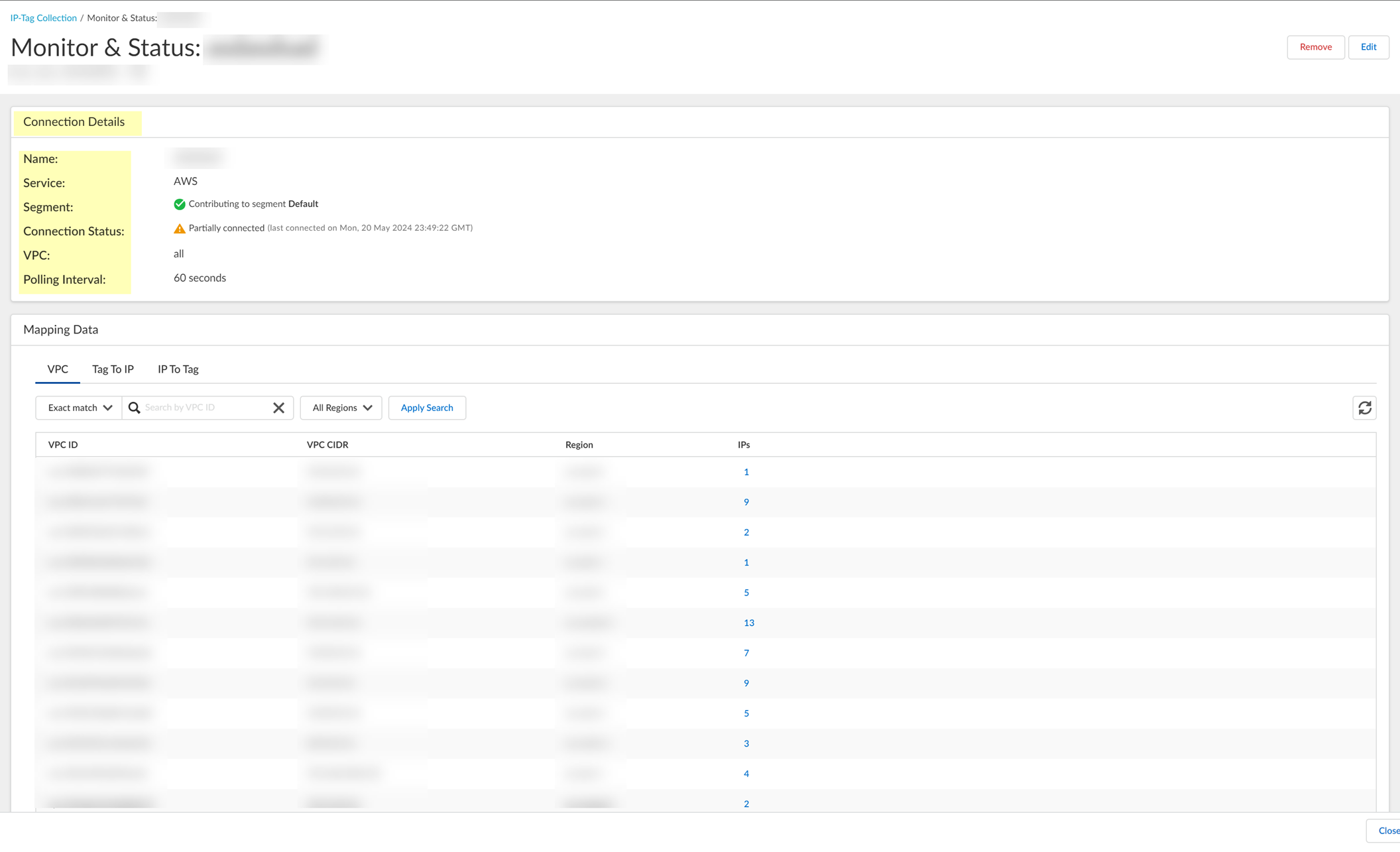
- View the IP address-to-tag mapping information.
Options vary depending on your configuration type.
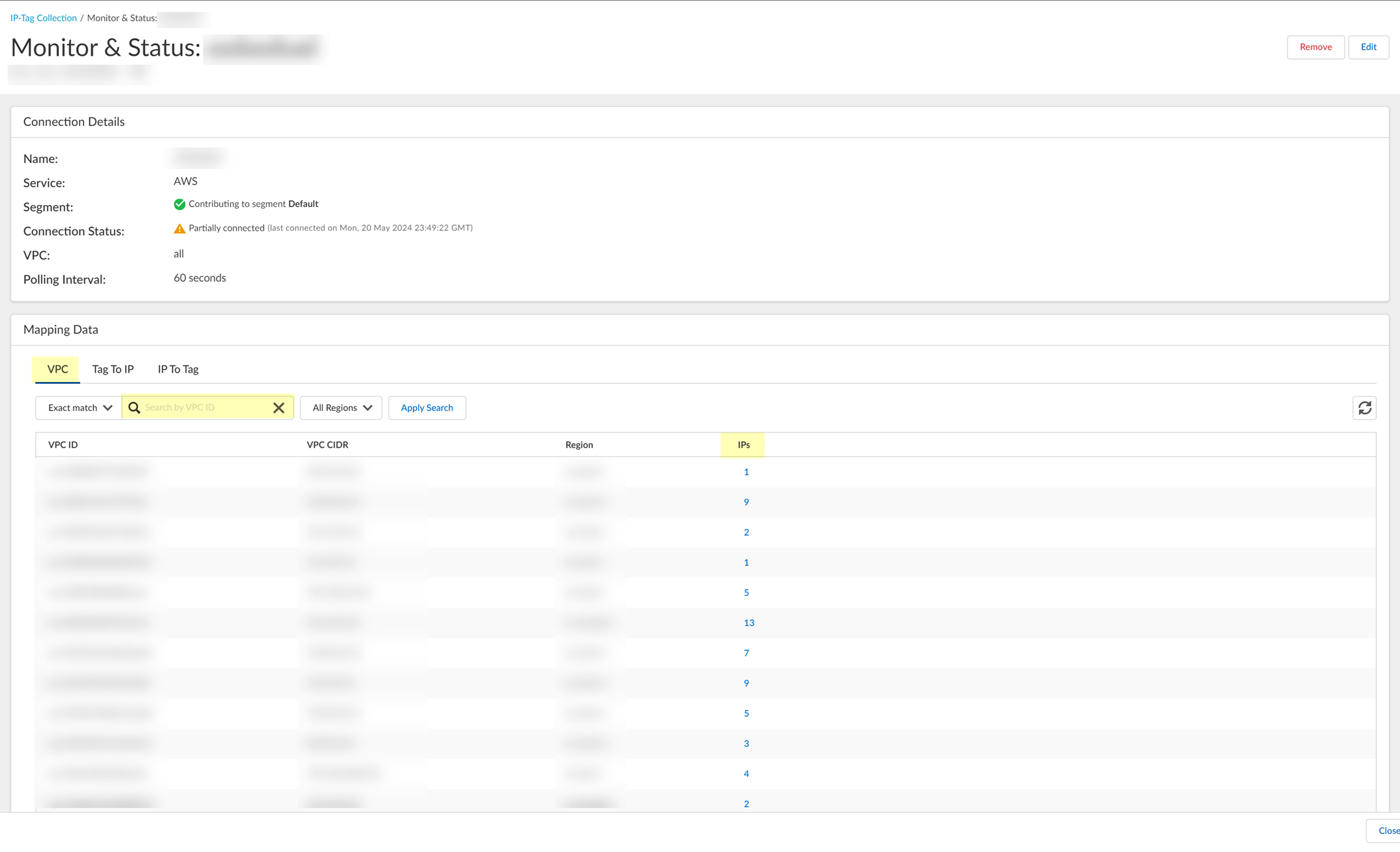
1. ( AWS only ) On the VPC tab, Search by VPC ID to view information for a specific VPC or select the number in the IPs column to view the IP addresses associated with the VPC ID in that row.
2. Select the Tag To IP tab and Search by Tag to view all IP addresses that contain the tag you specify.
You can view the results for an exact or partial match for your query. You can optionally limit the search to a specific region or select All Regions .
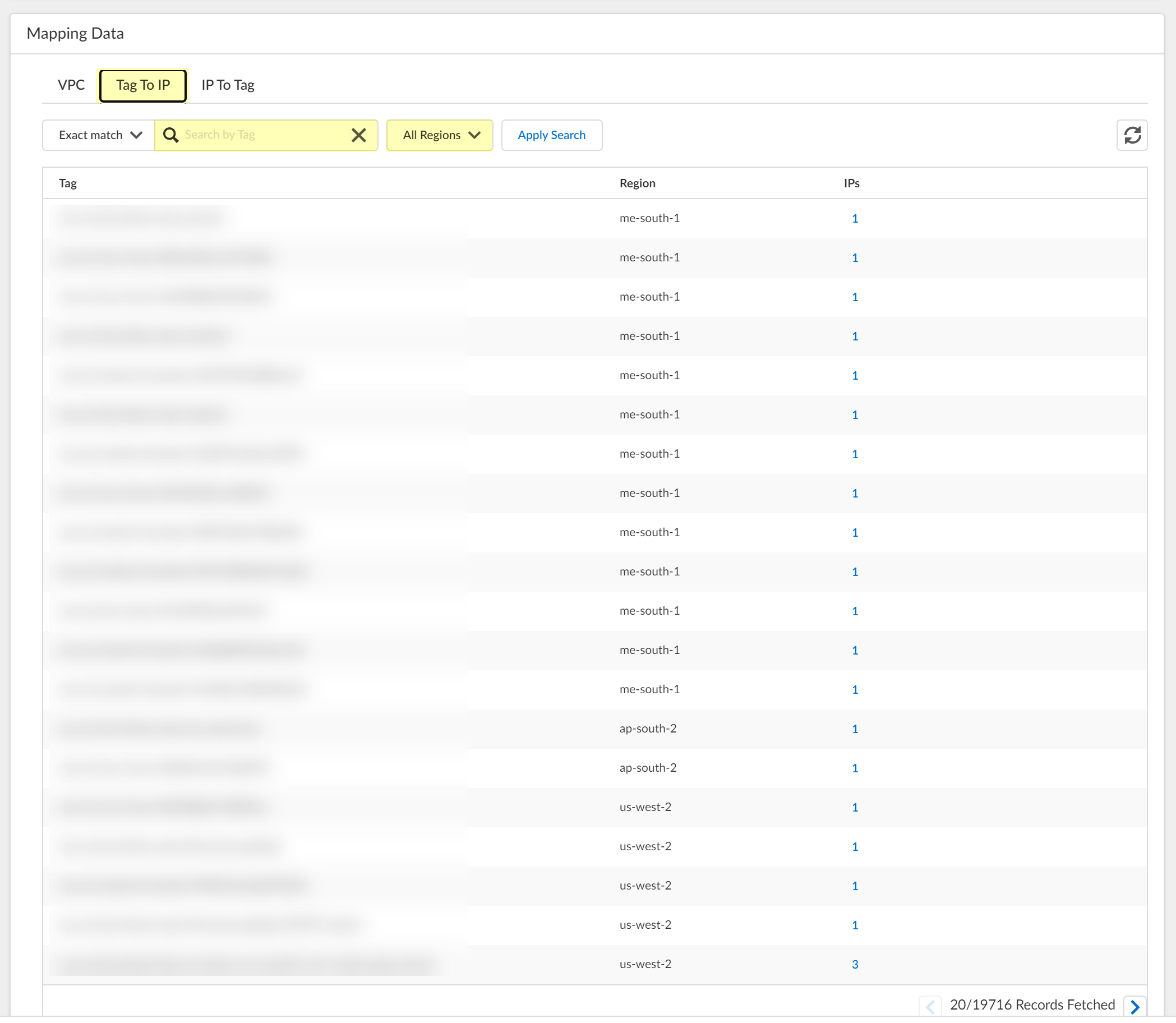
3. Select the number in the IPs column to view the IP addresses that the Cloud Identity Engine has collected for the selected Tag .
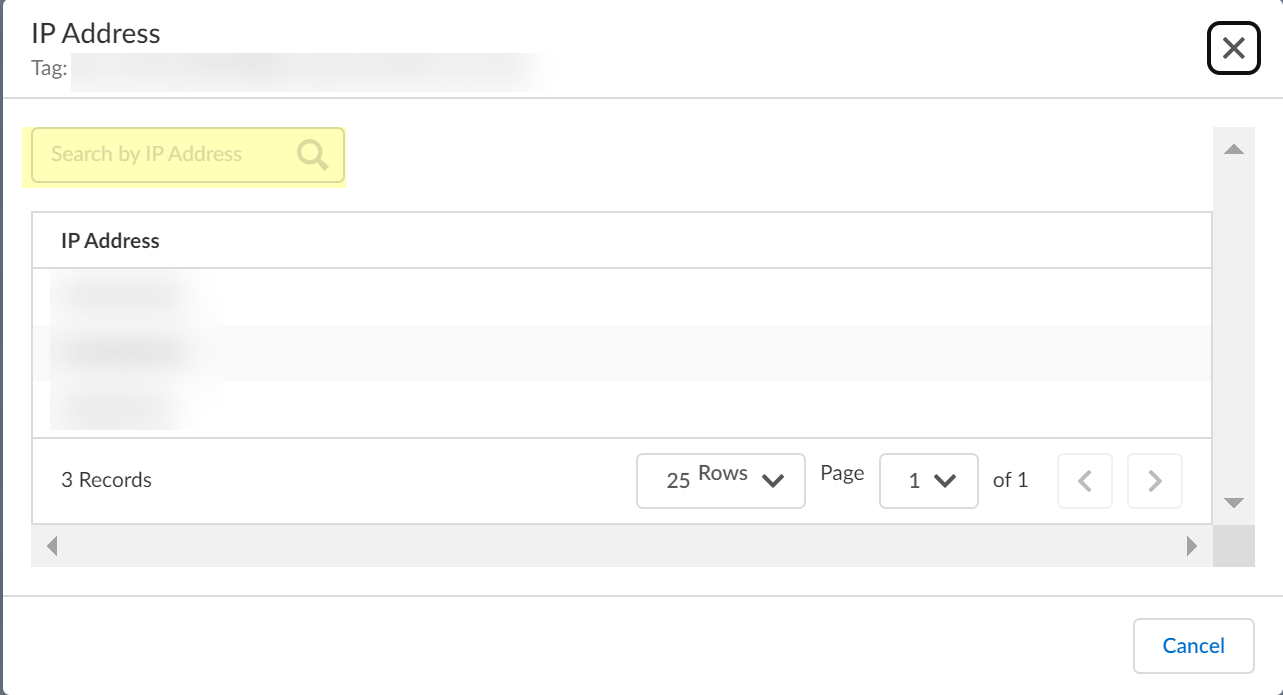
4. Search by IP Address then close the window or click Cancel after reviewing the IP addresses.
5. Select the IP To Tag tab to Search by IP Address .
For an AWS-based configuration, you can also search by VPC ID.
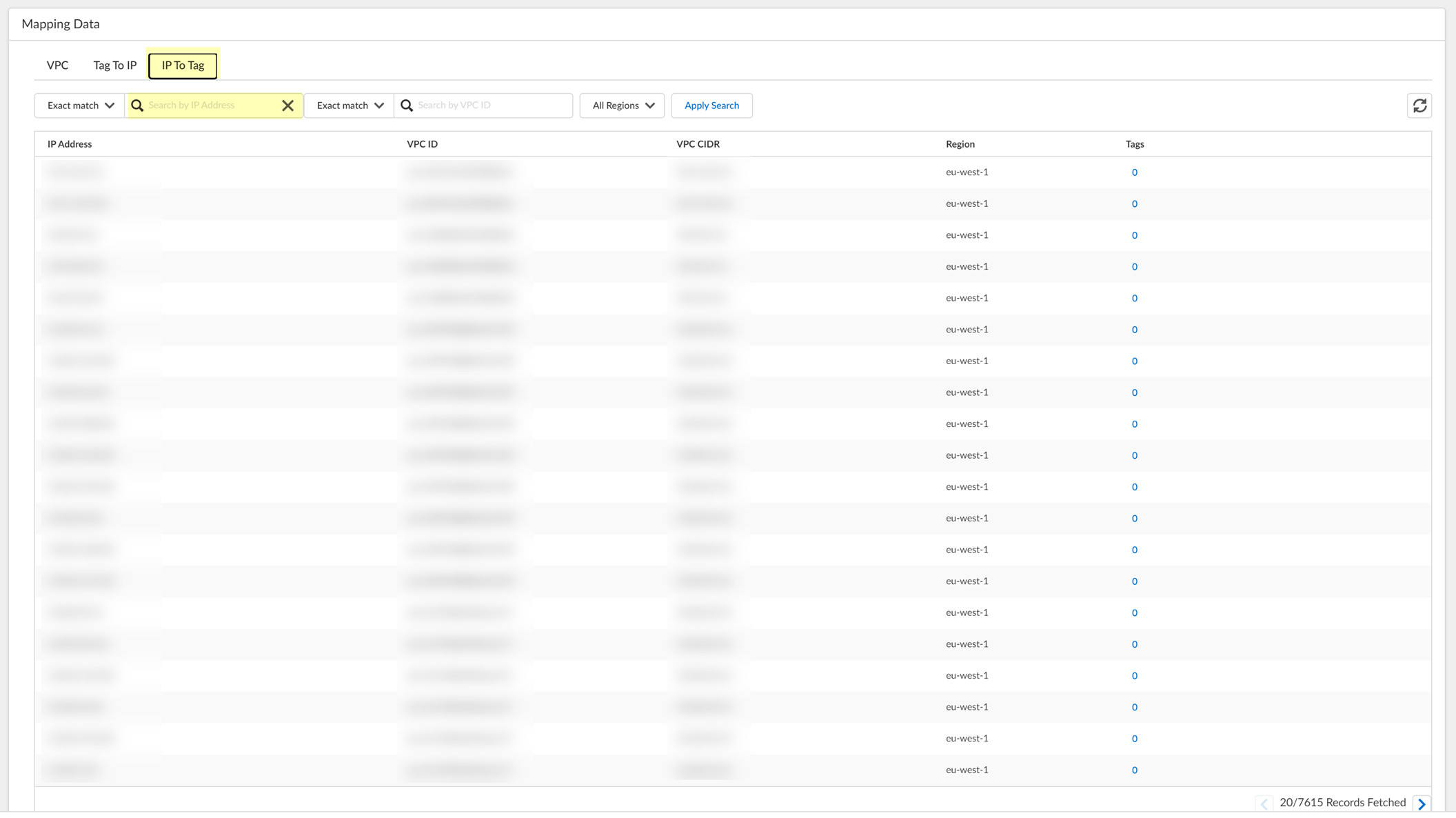
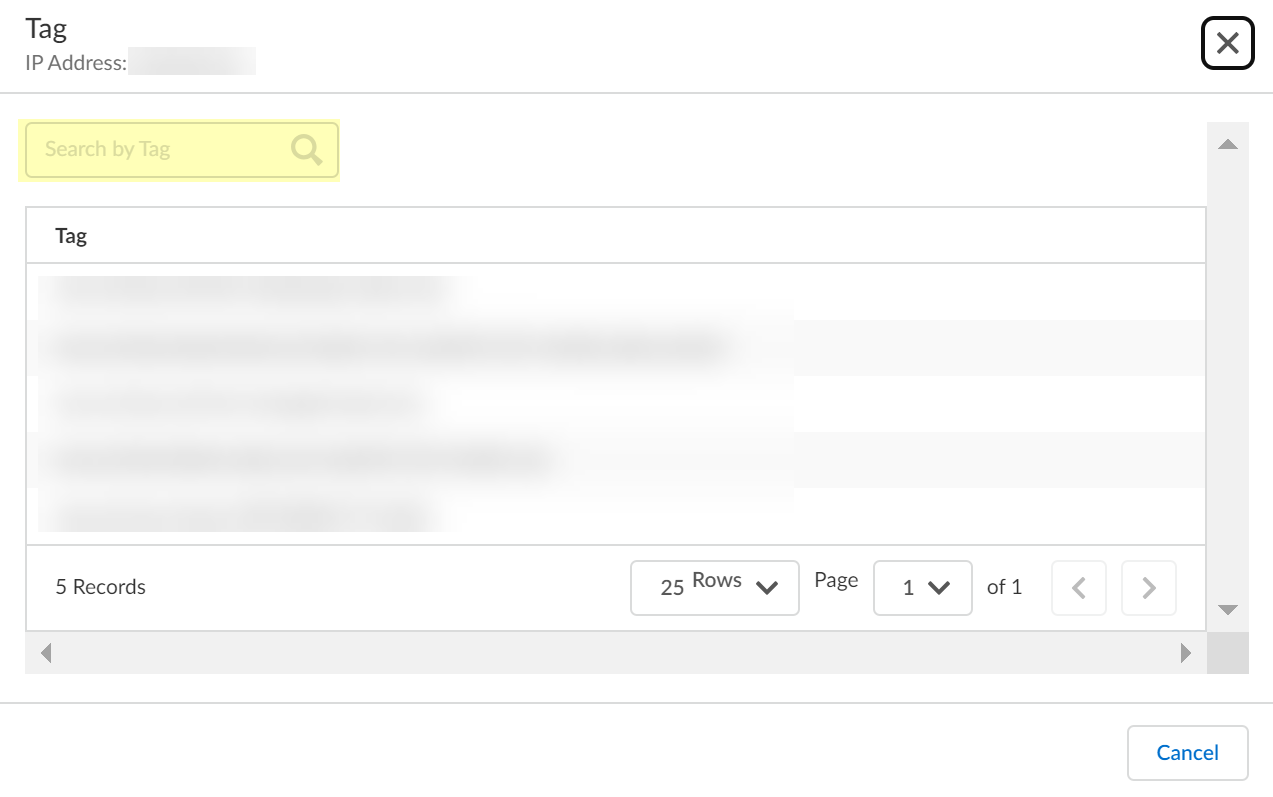
6. Click the number in the Tags column to view the tags associated with the IP Address of that row.
7. Search by Tag then close the window or click Cancel after reviewing the tags.
Configure Dynamic Privilege Access in the Cloud Identity Engine
Enabling Dynamic Privilege Access (DPA) allows you to isolate network resources so they are only accessible to users on a per-project basis.
Contact your Palo Alto Networks account representative to activate this functionality.
Complete the following steps to enable and configure DPA in the Cloud Identity Engine. For more information, refer to the Prisma Access documentation . The Prisma Access release notes have information on known issues for DPA.
Syncing new user groups for SAML applications in Azure may require up to 3 hours for the Cloud Identity Engine to complete the sync. Wait until the sync is complete before assigning projects to the new group.
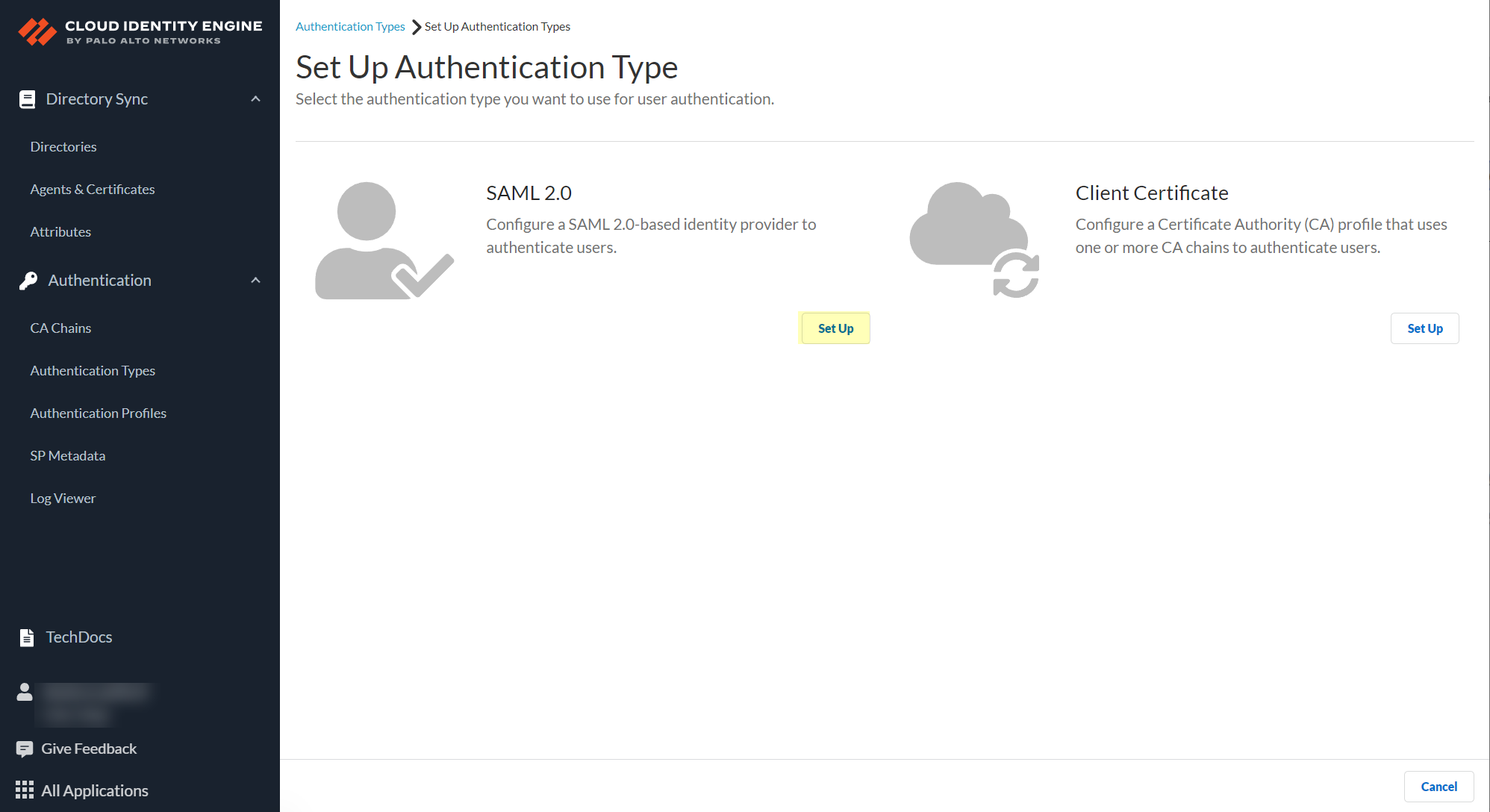
- Configure an authentication type in the Cloud Identity Engine.
The authentication type you configure in the Cloud Identity Engine is only for use with DPA authentication; don't use the same authentication type you use for DPA for another authentication type.
- In the Cloud Identity Engine, select Authentication TypesAdd New Authentication Type .
The Cloud Identity Engine supports Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) in this release. To use an existing Azure IdP configuration, select Authentication TypesActionsEdit .
- If you Set Up a new SAML 2.0 authentication type, configure Azure as the identity provider (IdP) in a new configuration.
If you edit the configuration for an existing Azure IdP authentication type, synchronize all attributes for the directory (also known as a full sync) after editing and submitting the configuration.
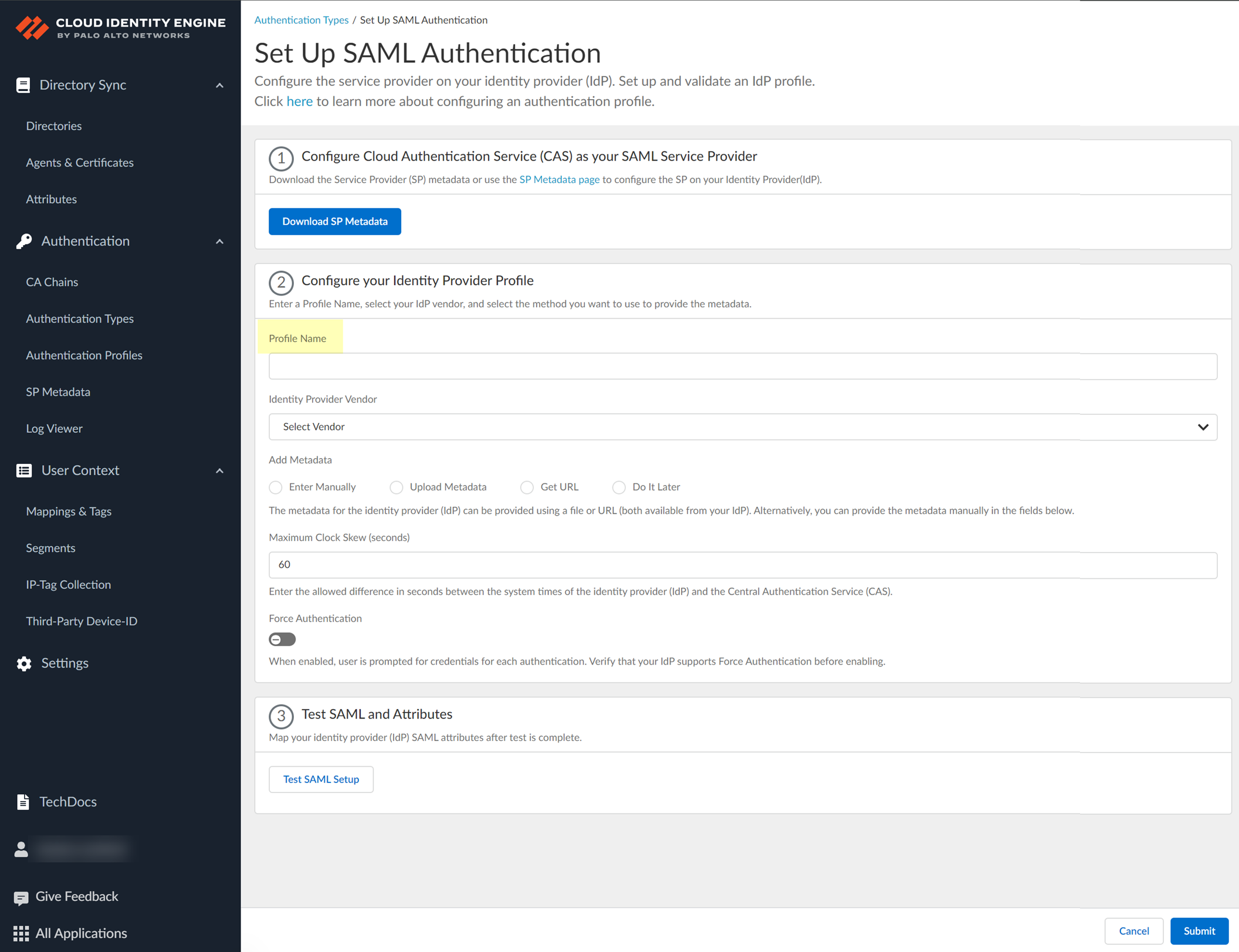
- Select Dynamic service provider metadata as the Metadata Type .
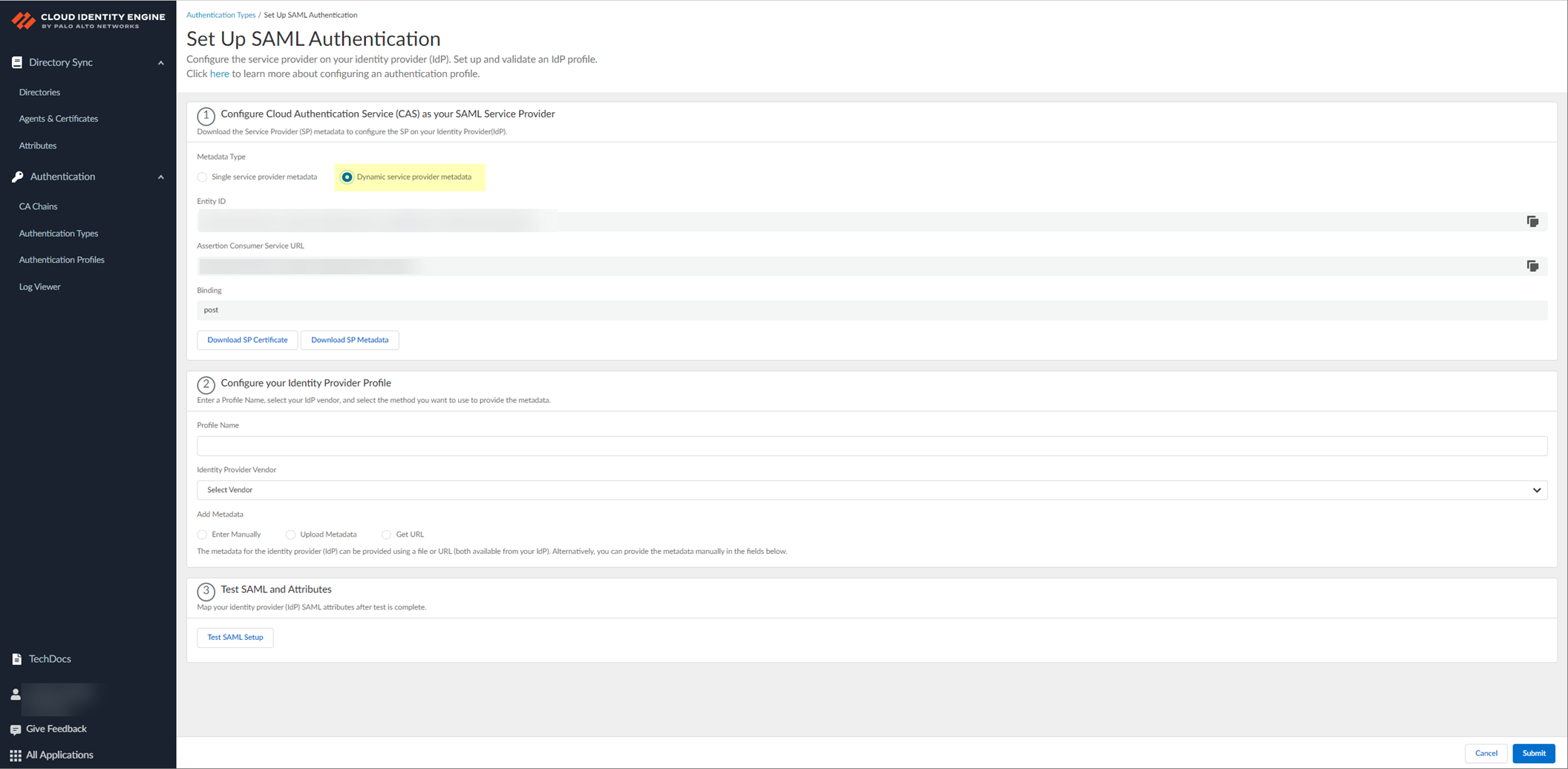
- Copy and save the information from the Cloud Identity Engine that you must configure in your identity provider.
Select one of the following methods to obtain the information you need to configure for the Cloud Identity Engine to communicate with your identity provider:
- Copy the Entity ID and the Assertion Consumer Service URL , then save them in a secure location.
Don't edit the Entity ID or use the Entity ID for other applications. You don't need to download the SP metadata if you use the Entity ID.
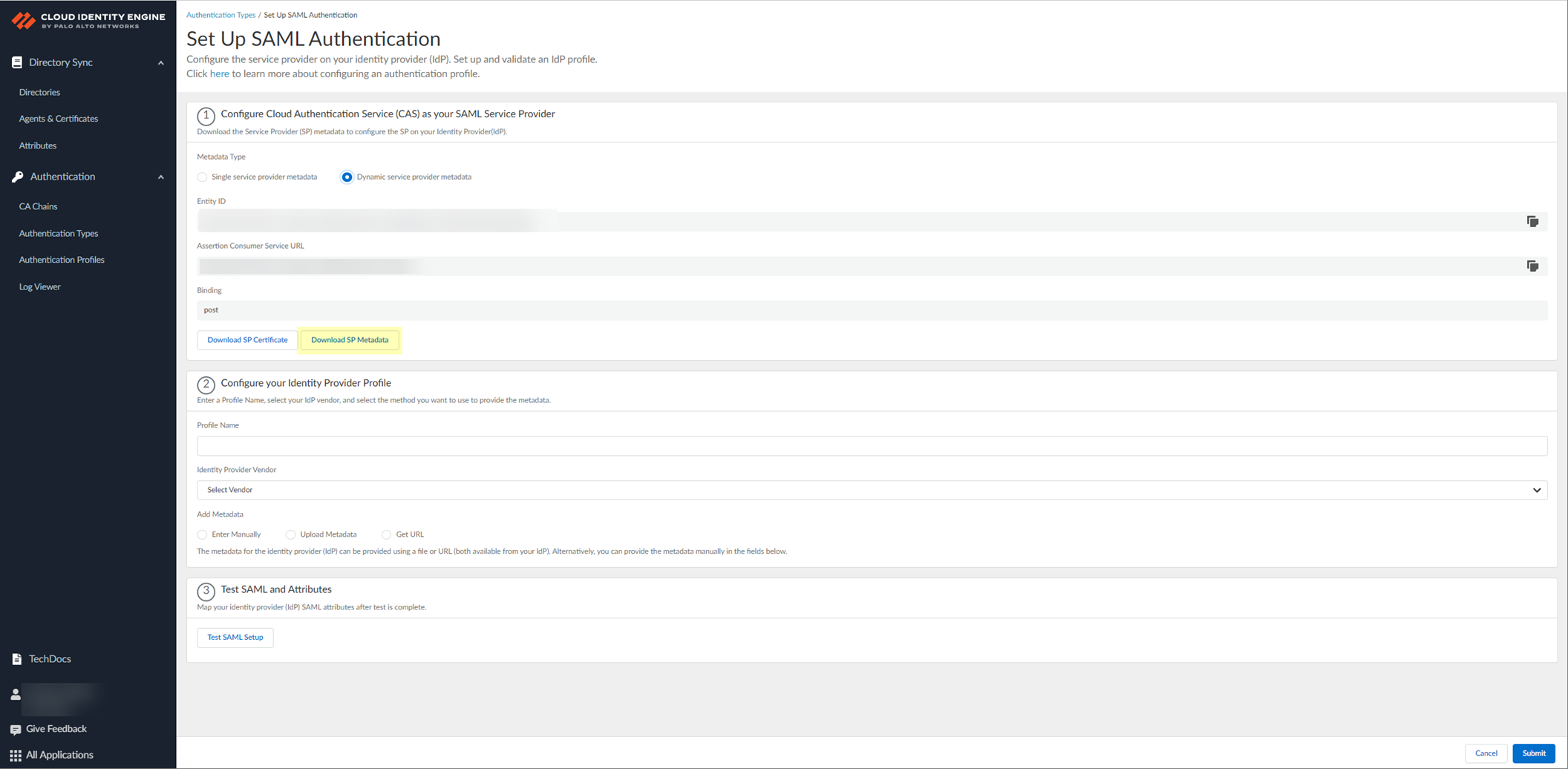
- Click Download SP Metadata and save the metadata in a secure location. For more information, refer to the first step in the procedure for configuring Azure as an IdP in the Cloud Identity Engine.
This step is mandatory for successful DPA configuration using SP metadata, even if you edit an existing Azure IdP configuration. The SP metadata provides the Entity ID, the Reply URL (Assertion Customer Service URL) and the Logout URL; you must manually enter the Sign on URL.
If you want to configure the authentication type so you can obtain the necessary information and you don't want to enter the metadata now, you can choose to Do It Later . This option allows you to generate the data you need to enter in the IdP for the next steps; however, you must enter the metadata before submitting the configuration to successfully use the authentication type with the Cloud Identity Engine.
- In the IdP administrator portal, download the SAML application for the Cloud Identity Engine from the gallery.
- Log in to the Azure Portal and select Enterprise Applications .
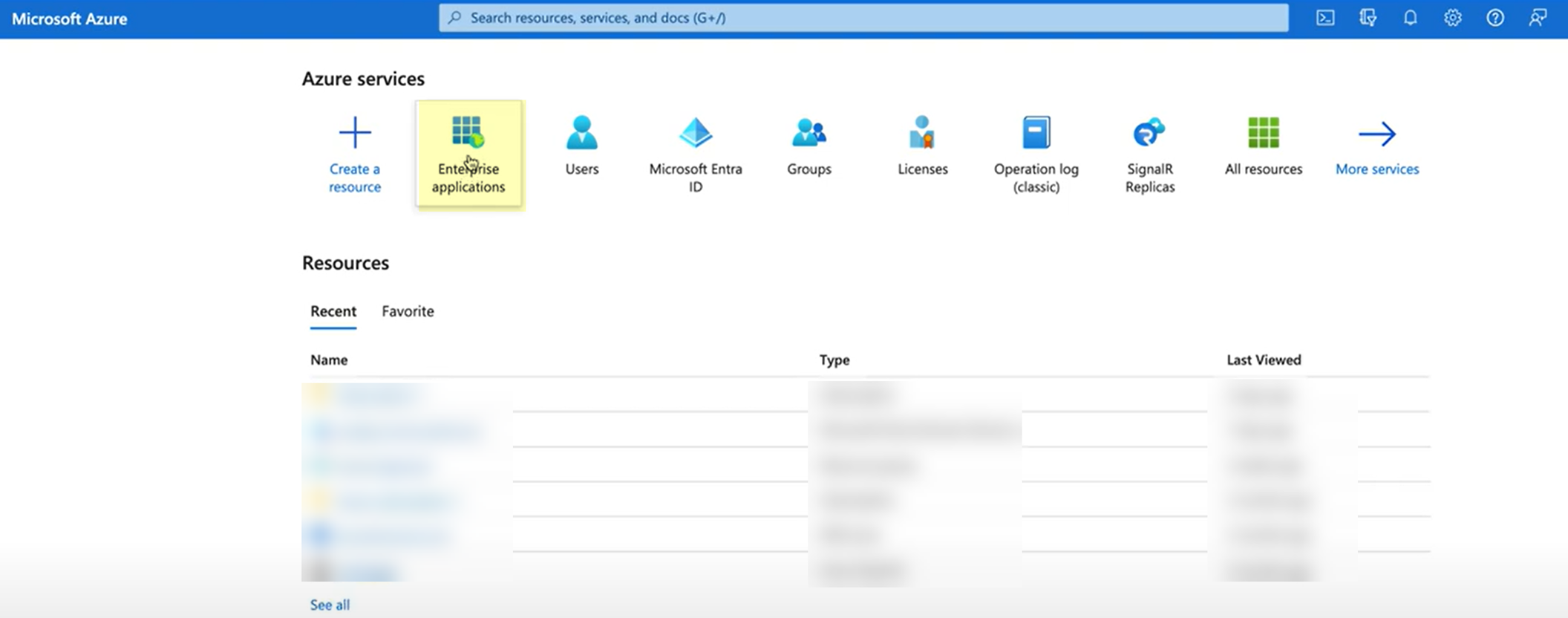
- Search for the Palo Alto Networks Cloud Identity Engine - Cloud Authentication Service gallery application and select it.

- (Optional) Edit the application Name .
- Create the configuration.
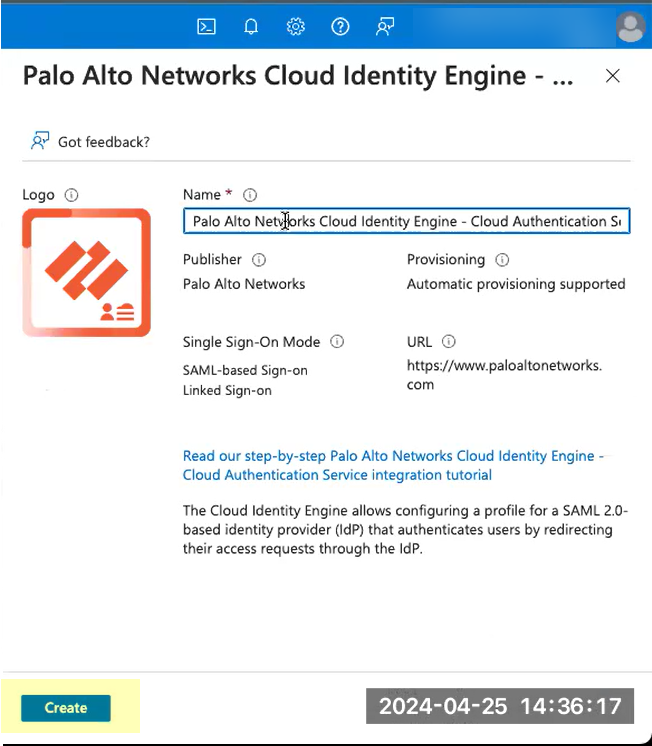
- For Set up single sign-on , click Get started .
- Depending on the method you used in step
2
, complete the necessary steps to configure the SAML application.
- If you copied the Entity ID and Assertion Consumer Service URL:
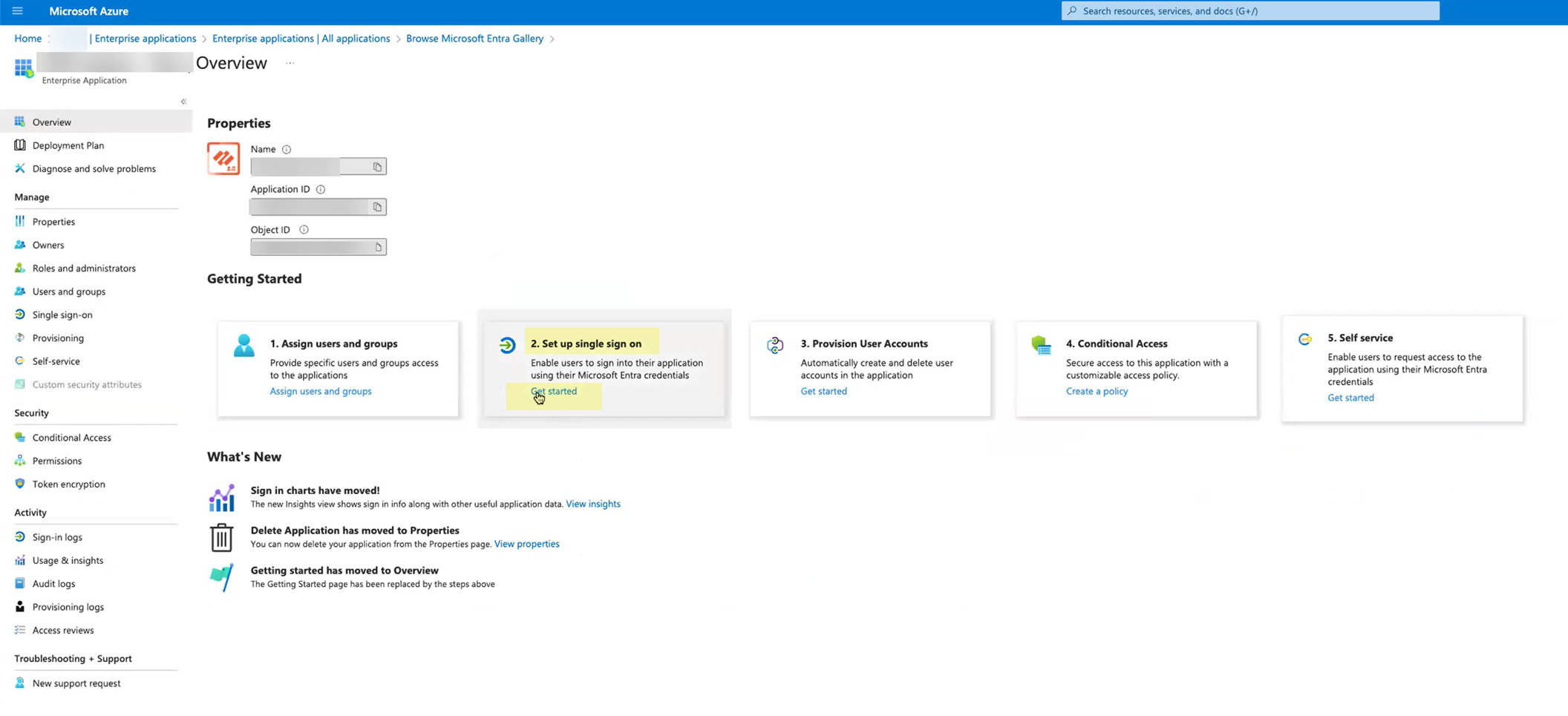
- Edit the Basic SAML Configuration you created.
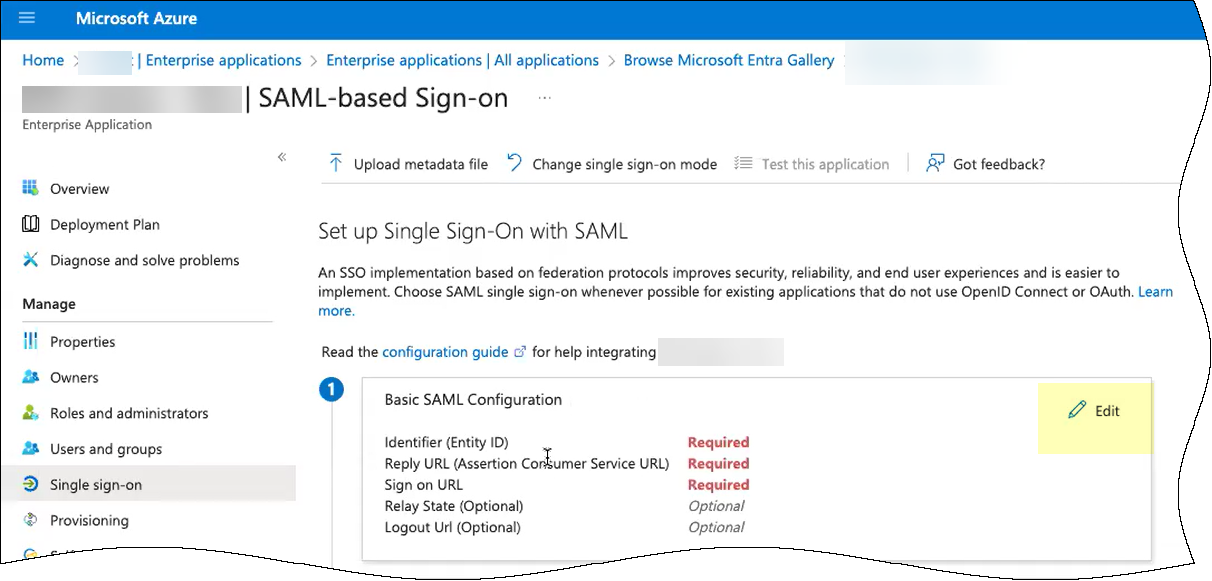
- Click Add identifier and paste the Entity ID you copied from the Cloud Identity Engine.
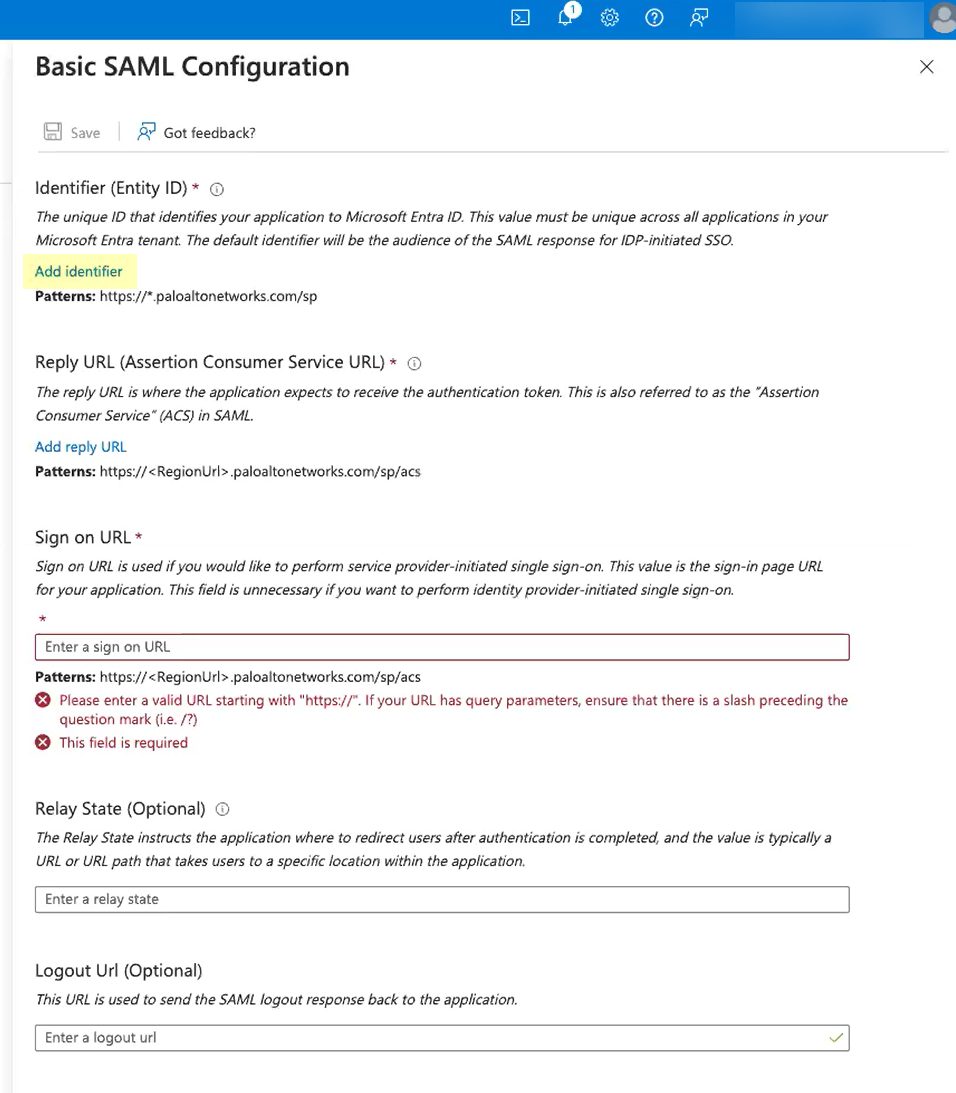
- Click Add reply URL and paste the Assertion Consumer Service URL you copied from the Cloud Identity Engine.
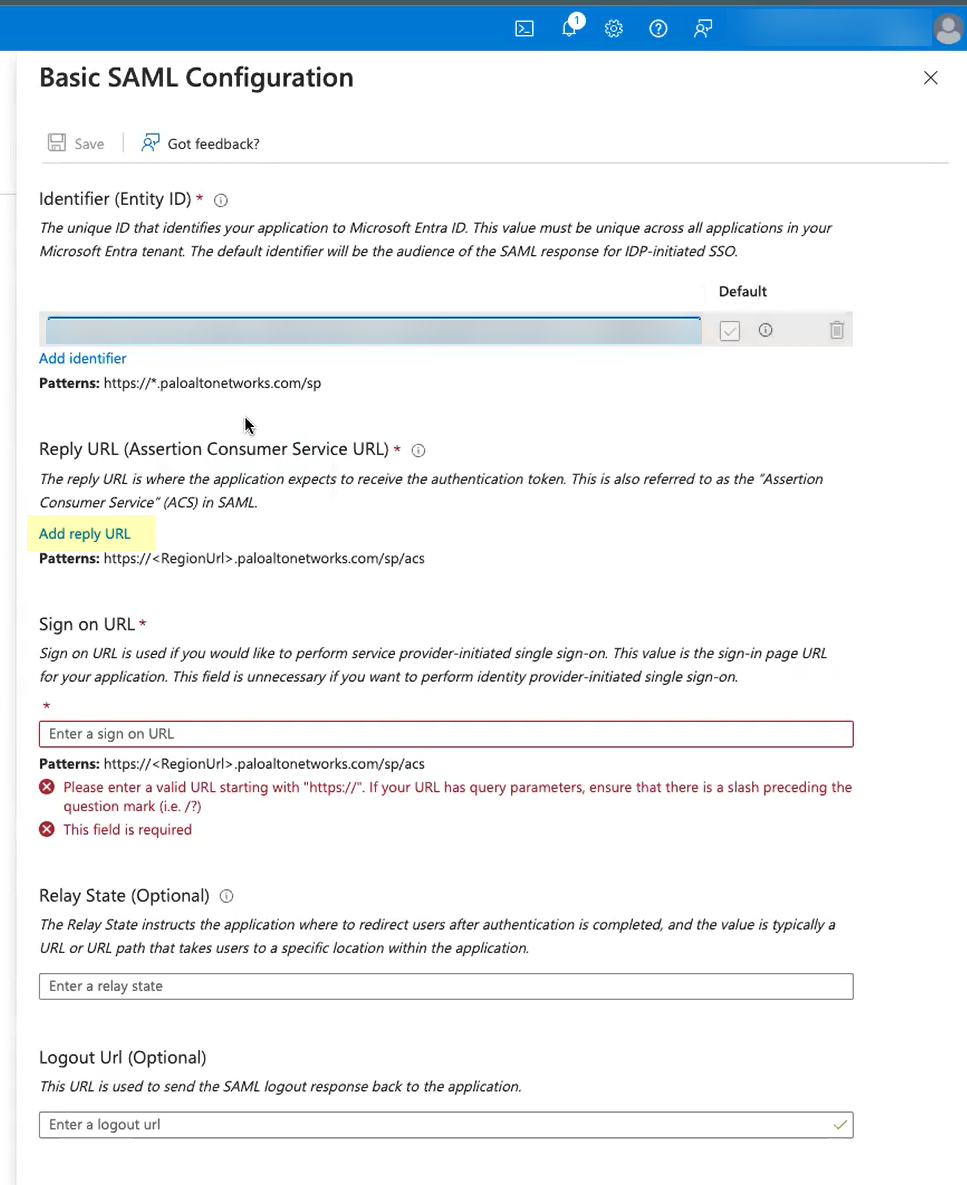
- Enter your regional endpoint as the Sign on URL using the following format: https://<RegionUrl>.paloaltonetworks.com/sp/acs (where <RegionUrl> is your regional endpoint). For more information on regional endpoints, see Configure Cloud Identity Engine Authentication on the Firewall or Panorama .
- Save your configuration.
- Close the window and Copy the App Federation Metadata URL .
- If you downloaded the SP metadata:
- Click Upload metadata file to upload the SP metadata file from the Cloud Identity Engine.
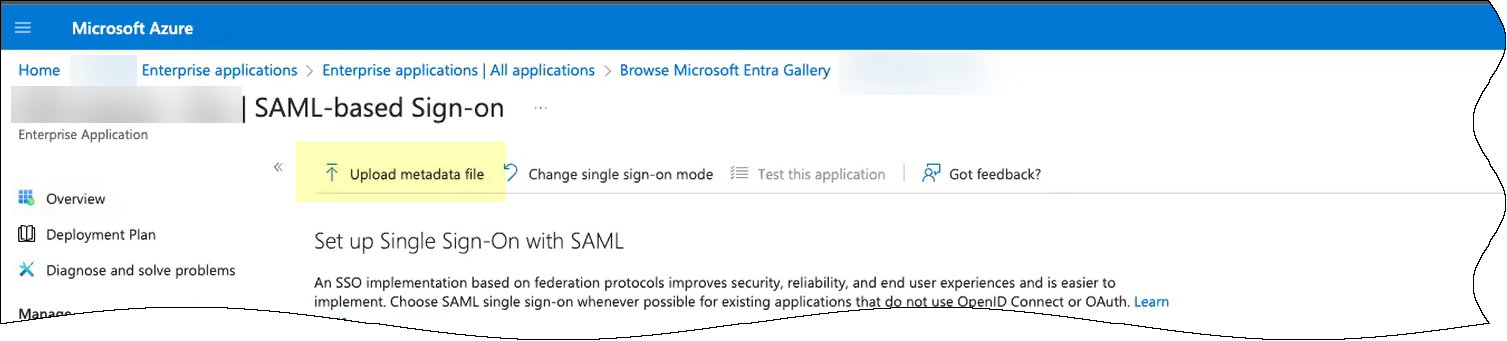
- Browse to the SP metadata file you downloaded from the Cloud Identity Engine.
- Add the file.
- Edit the Basic SAML Configuration you created.

- Enter your regional endpoint as the Sign on URL using the following format: https://<RegionUrl>.paloaltonetworks.com/sp/acs (where <RegionUrl> is your regional endpoint). For more information on regional endpoints, see Configure Cloud Identity Engine Authentication on the Firewall or Panorama .
- Save your configuration.
- Close the window and Copy the App Federation Metadata URL .
- Assign your account to the application and save the configuration.
- Assign your account to ensure your access to the application and to any other users you want to authenticate using the SAML application. For more information, refer to step 3 in configuring Azure as an IdP .
- Save the configuration.
- Continue the IdP configuration in the Cloud Identity Engine.
- Enter the remaining information to configure your identity provider (refer to step 5).
- In the Cloud Identity Engine, enter the App Federation Metadata URL you copied as the Identity Provider Metadata URL .
- Click Get URL to confirm the Cloud Identity Engine can connect to the URL.
This step is mandatory to confirm the configuration. If you don't click Get URL before clicking Test SAML Setup , the test isn't successful.
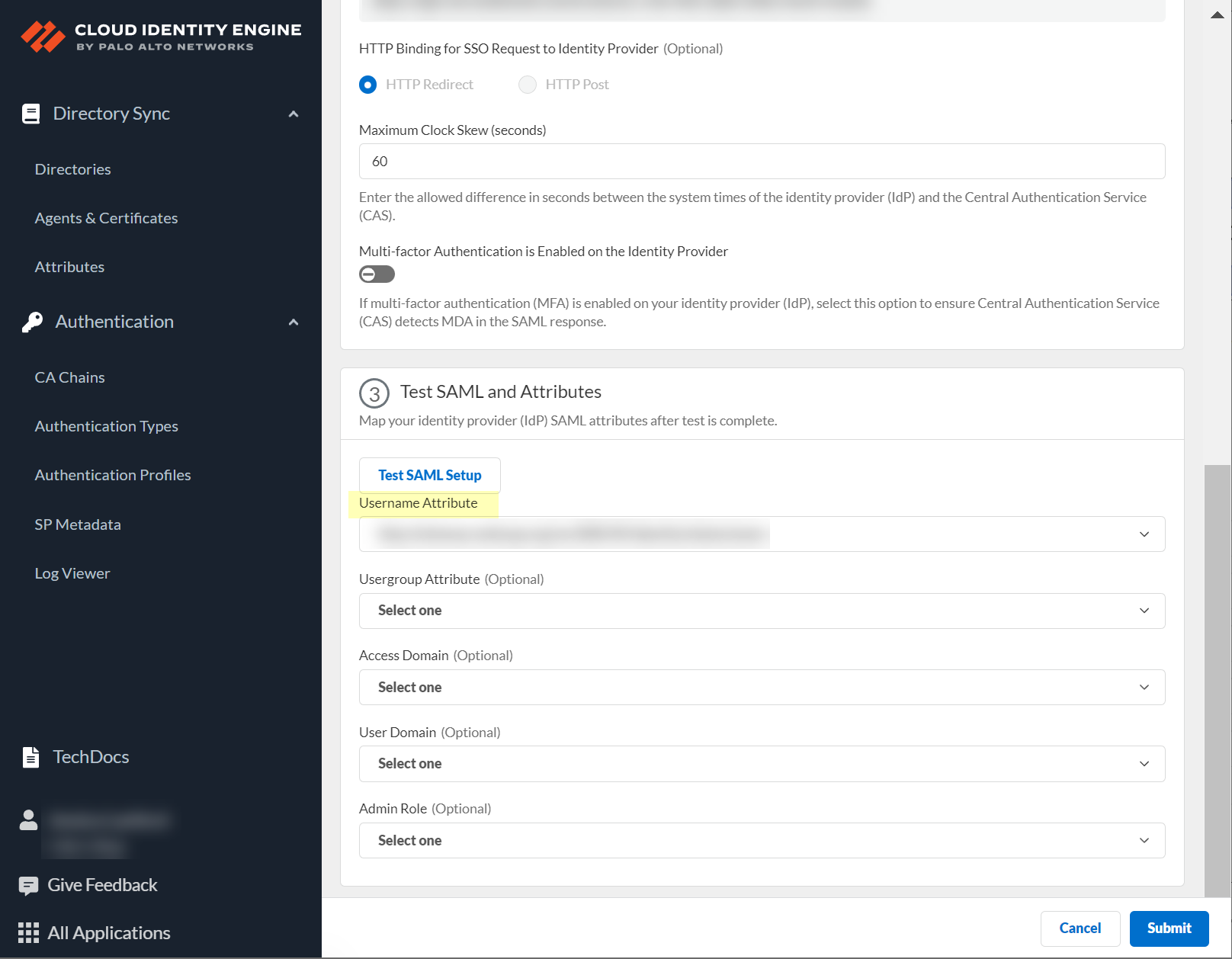
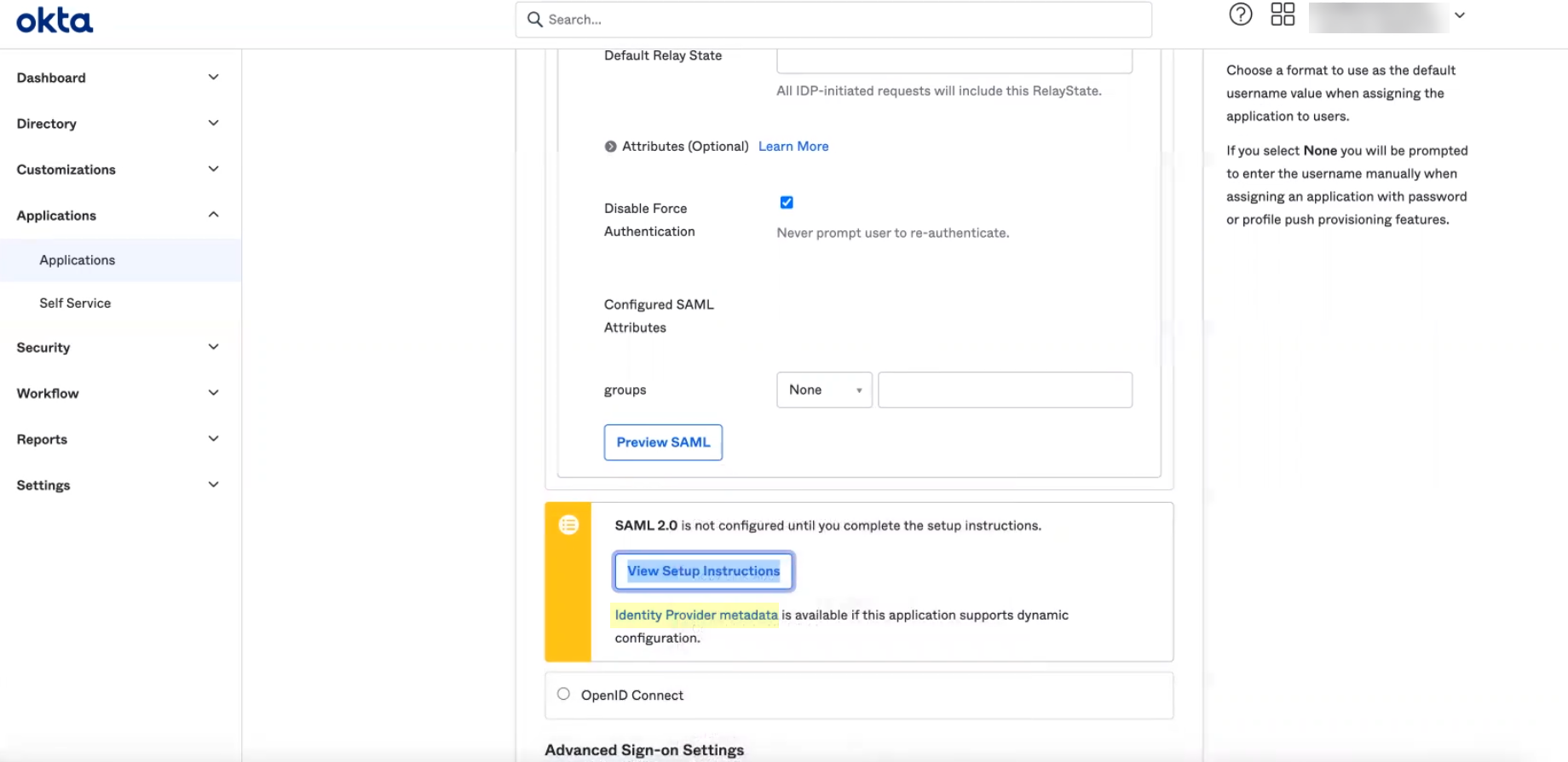
- Select whether Multi-factor Authentication is Enabled on the Identity Provider and whether you want to Force Authentication .
Refer to steps 6-7 in Configure Azure as an IdP in the Cloud Identity Engine for more information.
- Configure the SAML attributes for the Cloud Identity Engine to use for authentication.
- Click Test SAML Setup to verify the configuration.
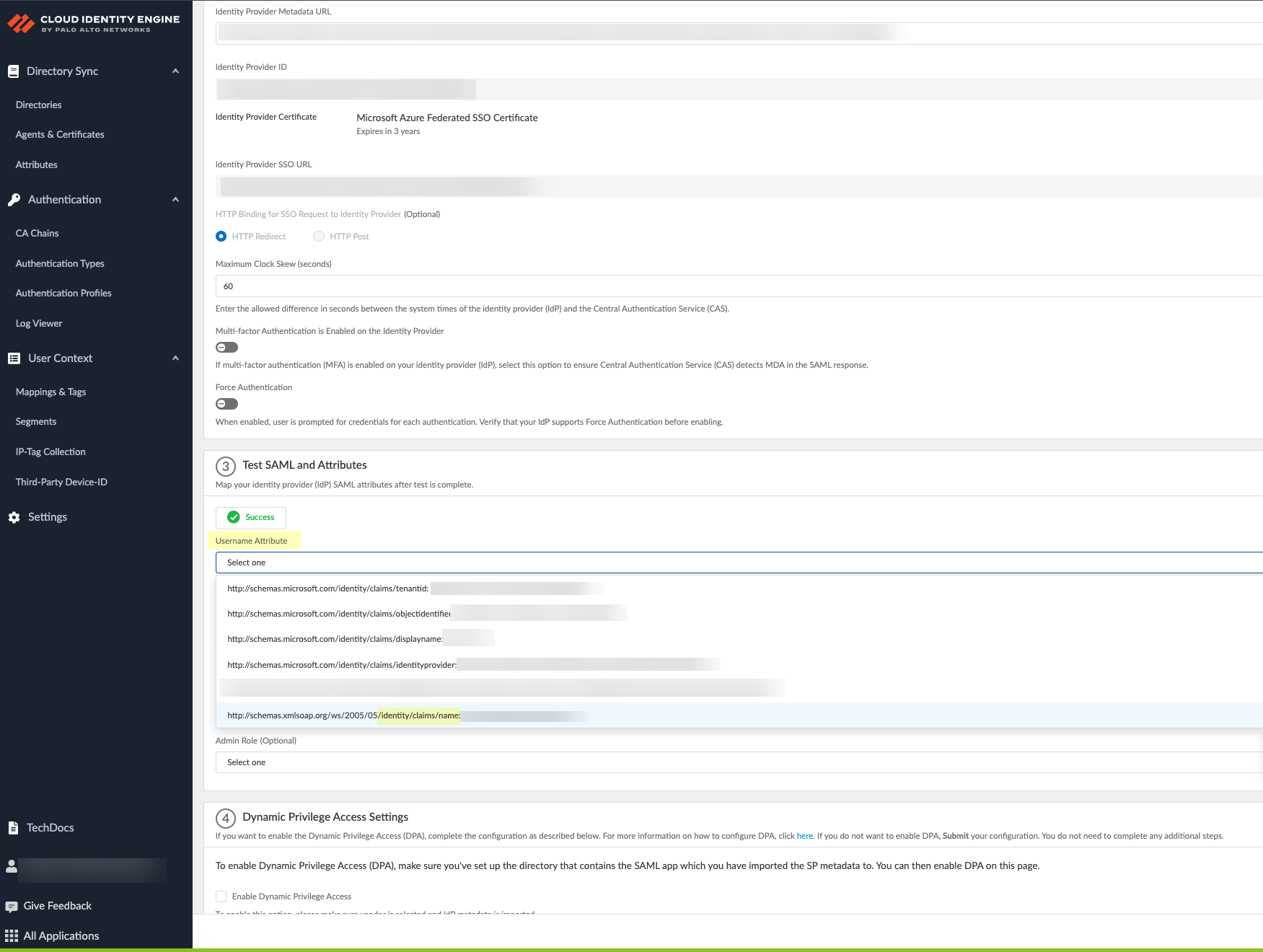
- Select the Username Attribute for the Cloud Identity Engine to use for authentication.
Select the username attribute that uses the Name ( /identity/claims/name: ) format. If you do not select the correct username attribute, user authentication for projects is not successful. For more information, refer to the Microsoft documentation .
- (Optional) Select other attributes to use for authentication, such as Usergroup Attribute , Access Domain , User Domain , and Admin Role .
- If you have not already done so, Collect enterprise applications data from your Azure directory . Sign in to confirm the changes and Submit the update to the configuration.
The Cloud Identity Engine begins a complete synchronization of the attributes (also known as a full sync ) when you submit the configuration. Wait until the sync is complete before continuing.
This step is mandatory to complete the configuration regardless of whether you're creating a new configuration or editing an existing configuration. You must complete this step before enabling Dynamic Privilege Access in the Cloud Identity Engine.
- Enable Dynamic Privilege Access in the Cloud Identity Engine authentication profile.
- Select Enable Dynamic Privilege Access .
- Click Detect Directory and SAML to allow the Cloud Identity Engine to detect available directories and SAML attributes.
When the Cloud Identity Engine completes the collection of the attributes, the Directory and SAML 2.0 Application information displays.
If the Cloud Identity Engine can't detect the SAML application, complete a full sync then reattempt this step.
- After confirming the information is correct, Submit the configuration.
- Configure an authentication profile in the Cloud Identity Engine to use the authentication type you configured.
Configure Security Risk for the Cloud Identity Engine
Security Risk for the Cloud Identity Engine obtains specific information to evaluate risk (such as an outdated OS, failed password attempts, or suspicious device activity) for users and devices. By using telemetry and receiving risk scores for these sources, the Cloud Identity Engine allows you to define the risk criteria for a group, then the Cloud Identity Engine automatically assigns users and devices to that group using the information it receives from your risk assessment sources. This enables closed-loop automation, since after you address the source of the risk for a user or device, the Cloud Identity Engine removes it from the group.
Microsoft Azure analyzes user behavior and sign-in events to determine a user risk score and create a list of risky users. By identifying suspicious or anomalous user activity and assigning a risk score, you can quickly assess user risk level, evaluate priority, and take actions to reduce risk.
SentinelOne reviews all device activity (such as processes) on the endpoint to assign specific attributes that determine the risk level of the endpoint.
The SentinelOne Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) agent monitors device activity and behavior. By specifying the attributes you want the agent to collect, you can identify at-risk device endpoints.
The bidirectional integration between Prisma Access and SentinelOne helps ensure your Zero Trust Security policy by continuously receiving device information and risk signals from SentinelOne and automatically enforcing access restrictions, such as quarantining the device.
You can also use the Strata Cloud Manager to view the list of devices currently in quarantine.
- If you want to obtain risk information about users,
Configure Azure for Security Risk in the Cloud Identity Engine
.
- If you want to obtain security posture and risk information about devices,
Configure SentinelOne for Security Risk in the Cloud Identity Engine
.
By continuously monitoring the device security posture and risk information from SentinelOne, updating and enforcing quarantine lists across all devices, and removing devices after remediation, Security Risk for the Cloud Identity Engine helps you enforce adaptive Security policy and just-in-time access.
- In the Cloud Identity Engine, select Security RiskRisk Sources .
- Click Add Risk Source .
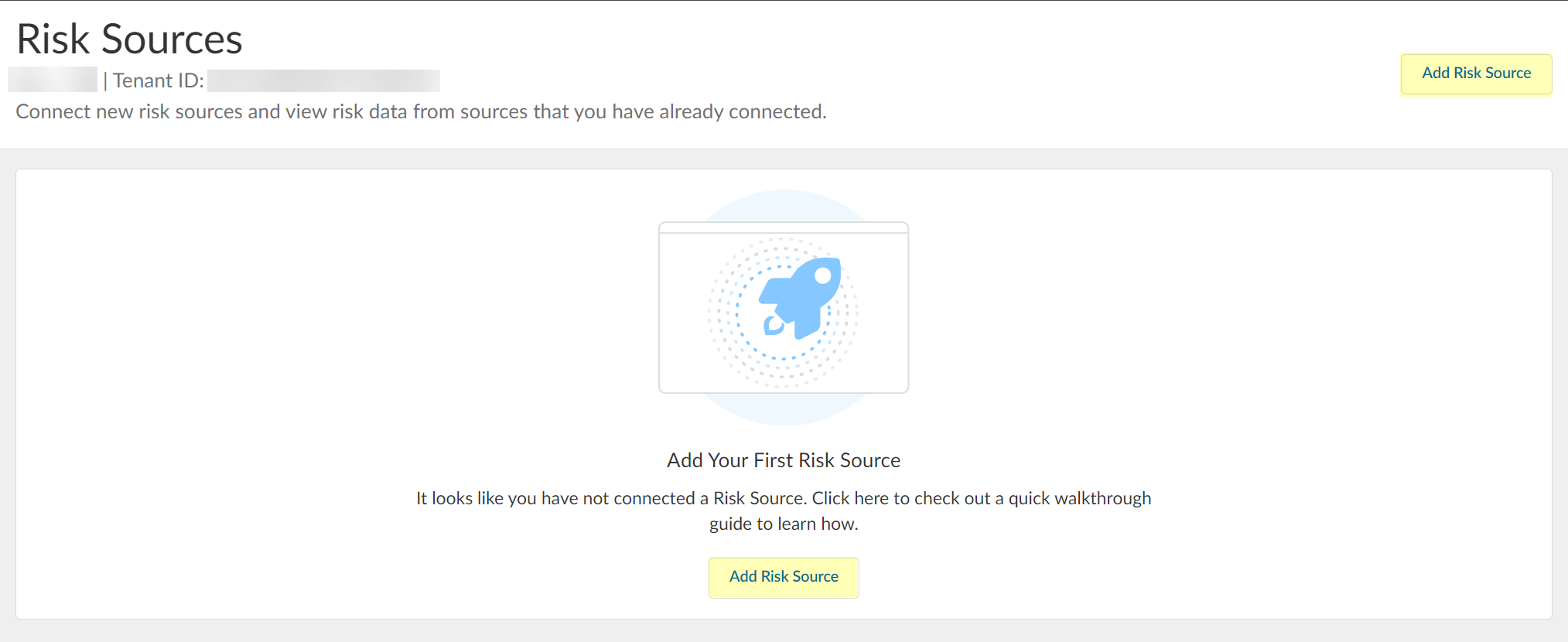
- Select the type of risk source you want to configure.
You can configure up to one Azure Active Directory source and up to one SentinelOne source.
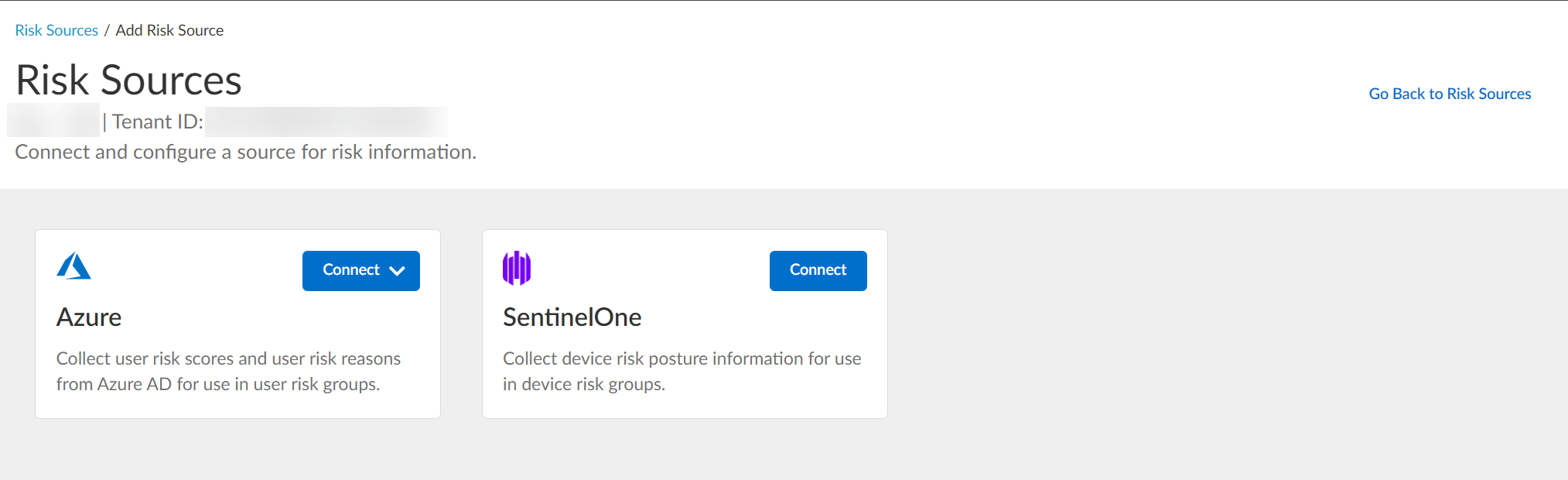
The Cloud Identity Engine uses the risk source you configure to obtain risk information.
- Azure — Click Connect and Configure a new Azure directory or select an Existing Directory to obtain risk information about users.
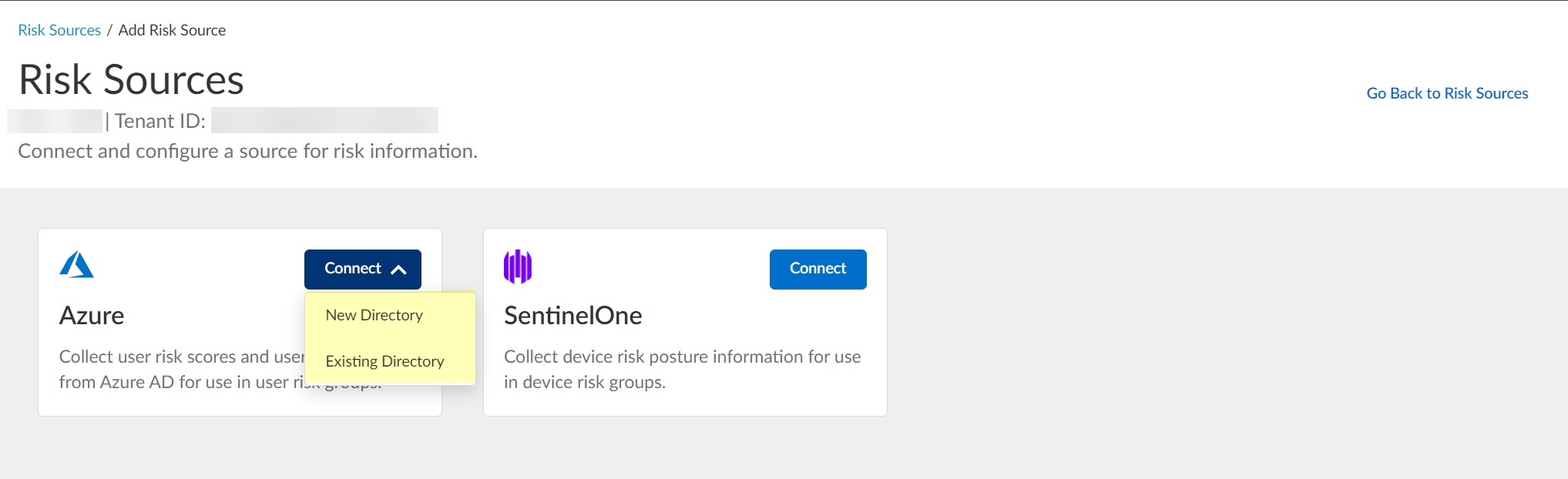
If you configure Security Risk to use a directory and you want to remove the directory from the Cloud Identity Engine, you must first remove the directory from the Security Risk configuration.
- SentinelOne —Click Connect and continue to
Configure SentinelOne for Security Risk in the Cloud Identity Engine
as a risk source to obtain risk information about devices.
Configure Azure for Security Risk in the Cloud Identity Engine
- View and optionally edit the dynamic risky user groups.
- In the Cloud Identity Engine, select Security RiskCloud Dynamic Groups .
- Select the Risky User Group tab to view the groups that the Cloud Identity Engine creates to isolate users who it identifies as risky. You can optionally click the Details icon to view more information about the specific group.
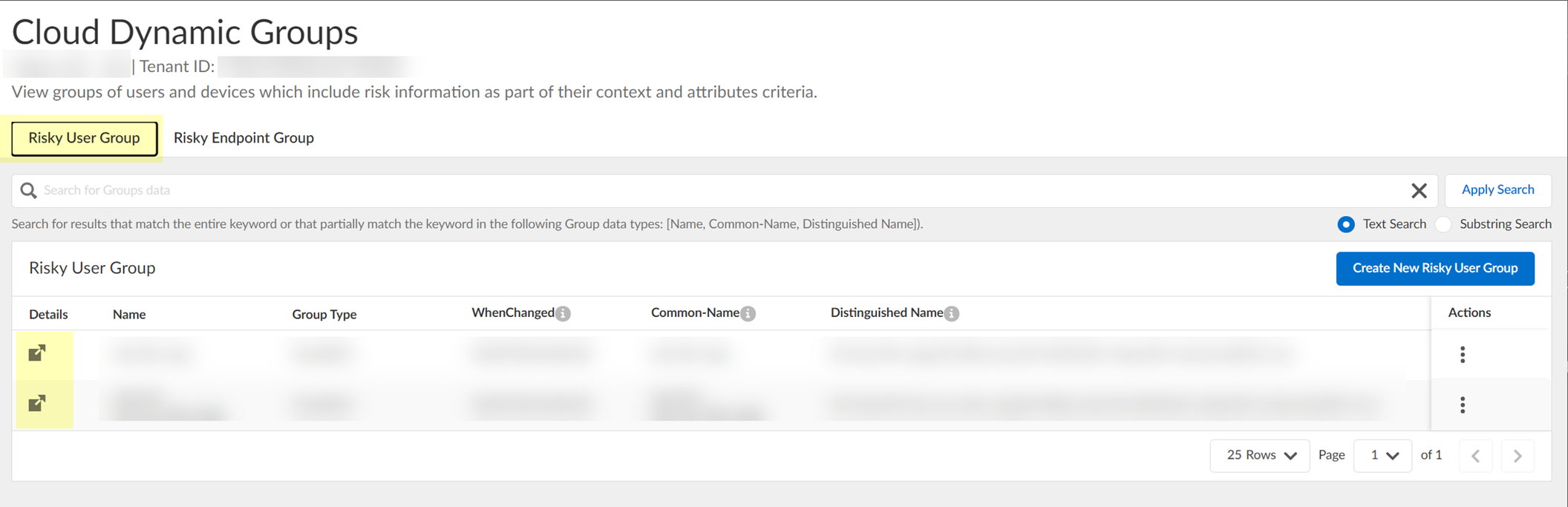
- (Optional) Search the groups by entering a search query then click Apply Search .
You can specify a Text Search or a Substring Search .
- (Optional) To include additional context and attributes for the cloud dynamic risky user group, select ActionsEdit , add the additional context and attributes, and Submit the changes.
- (Optional) To delete a group, select ActionsRemove and click Yes to confirm removal of the group.
- (Optional) Create a new cloud dynamic risky user group.
- Click Create New Risky User Group .
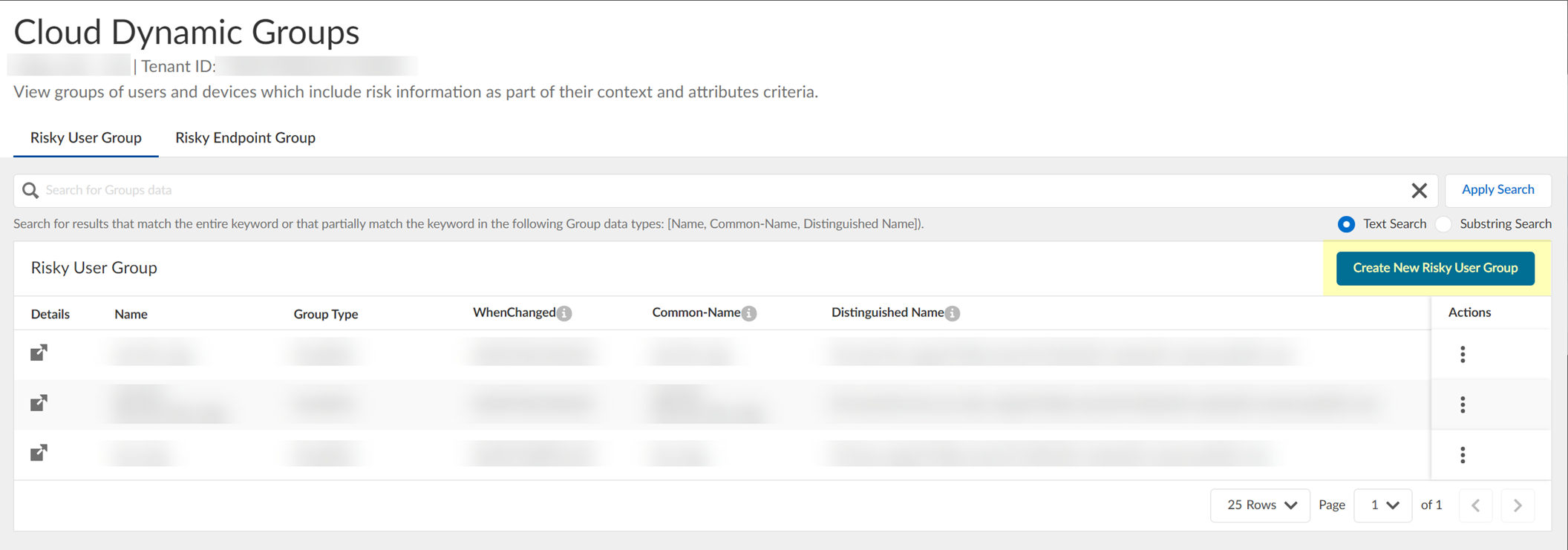
- Select Risky User as the Category .
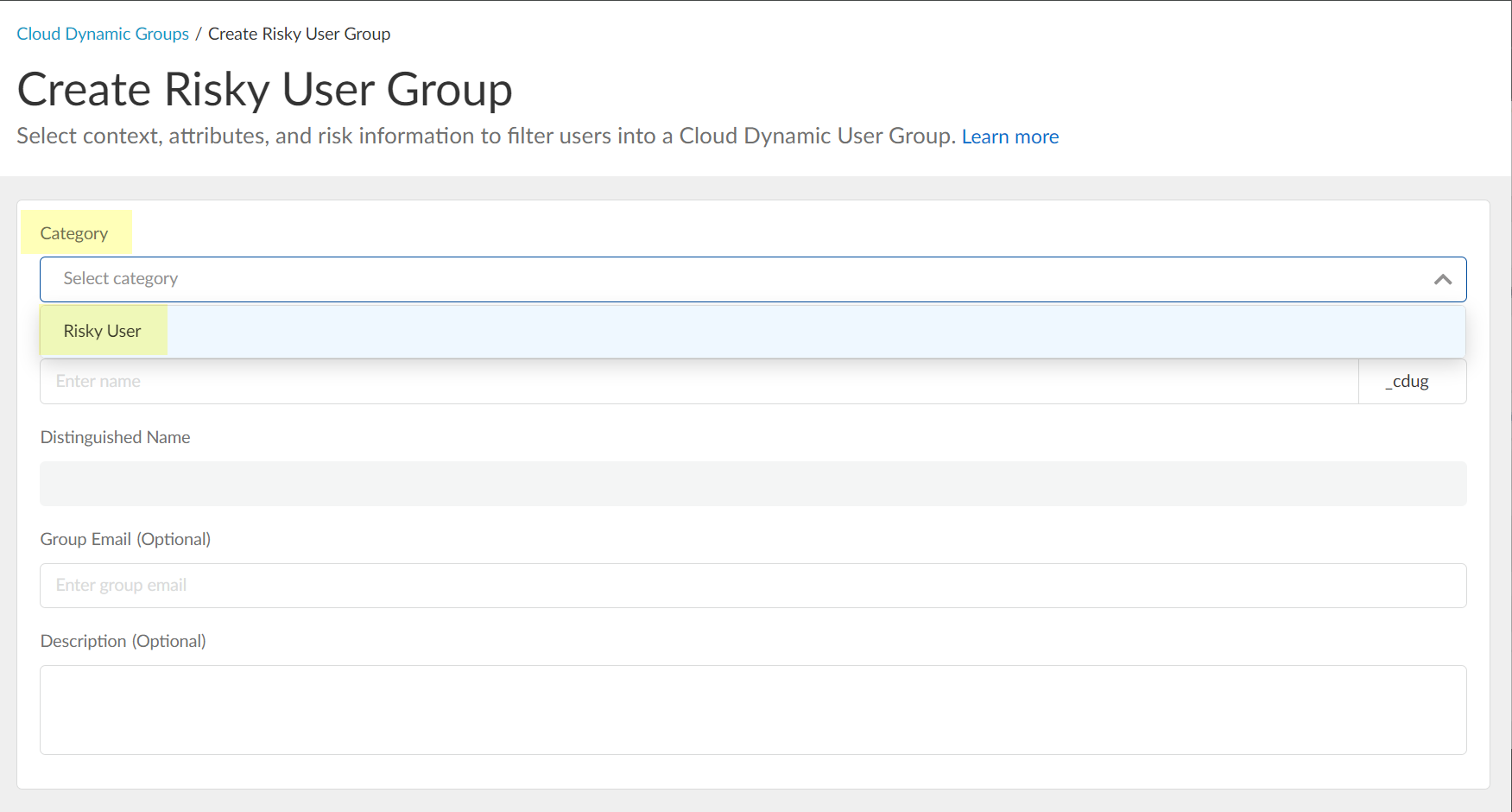
- Enter the Common Name you want to use for the dynamic risky user group.
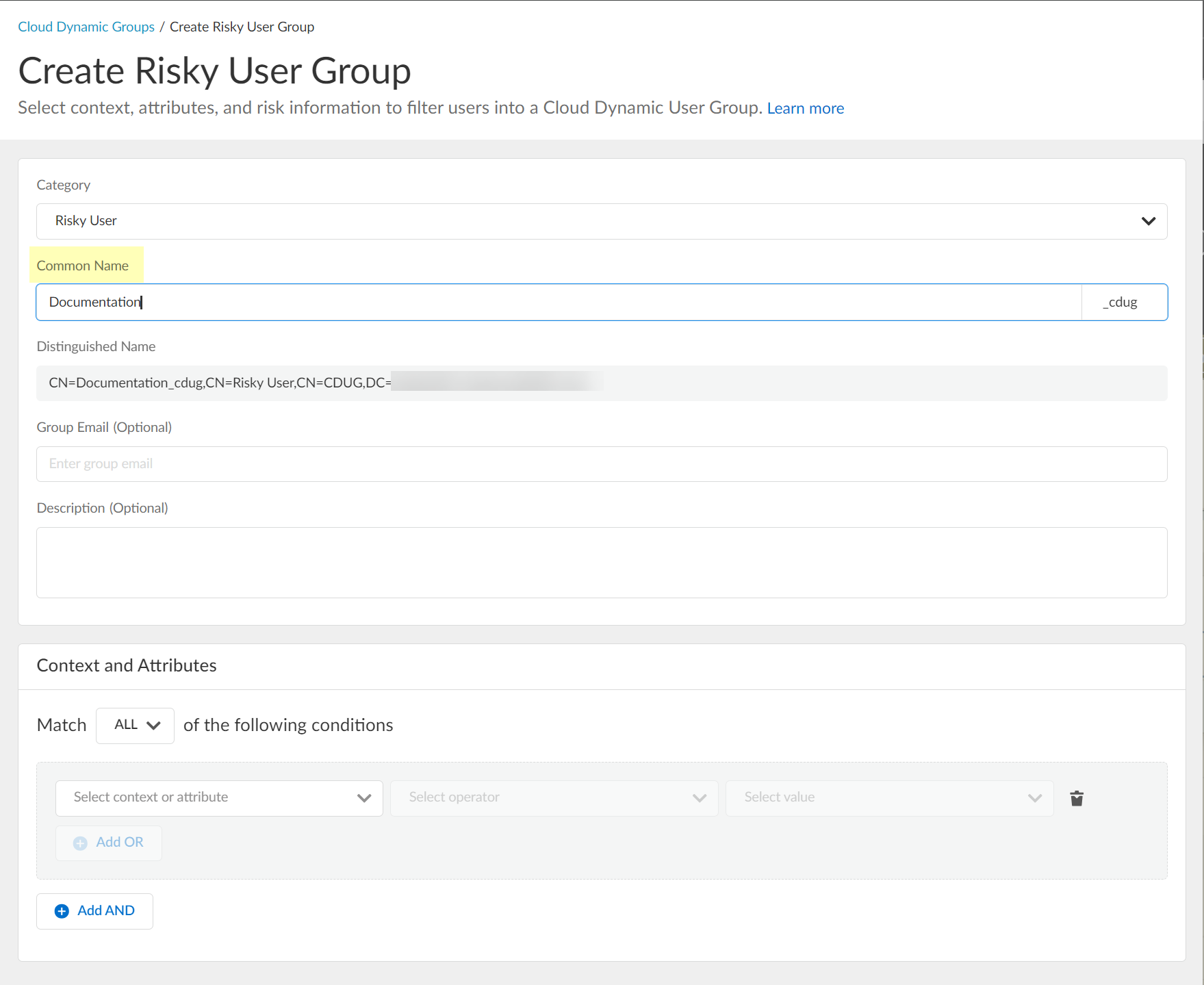
- (Optional) Enter a Group Email a Description for the group.
- Select the context and attributes to use for the dynamic risky user group.
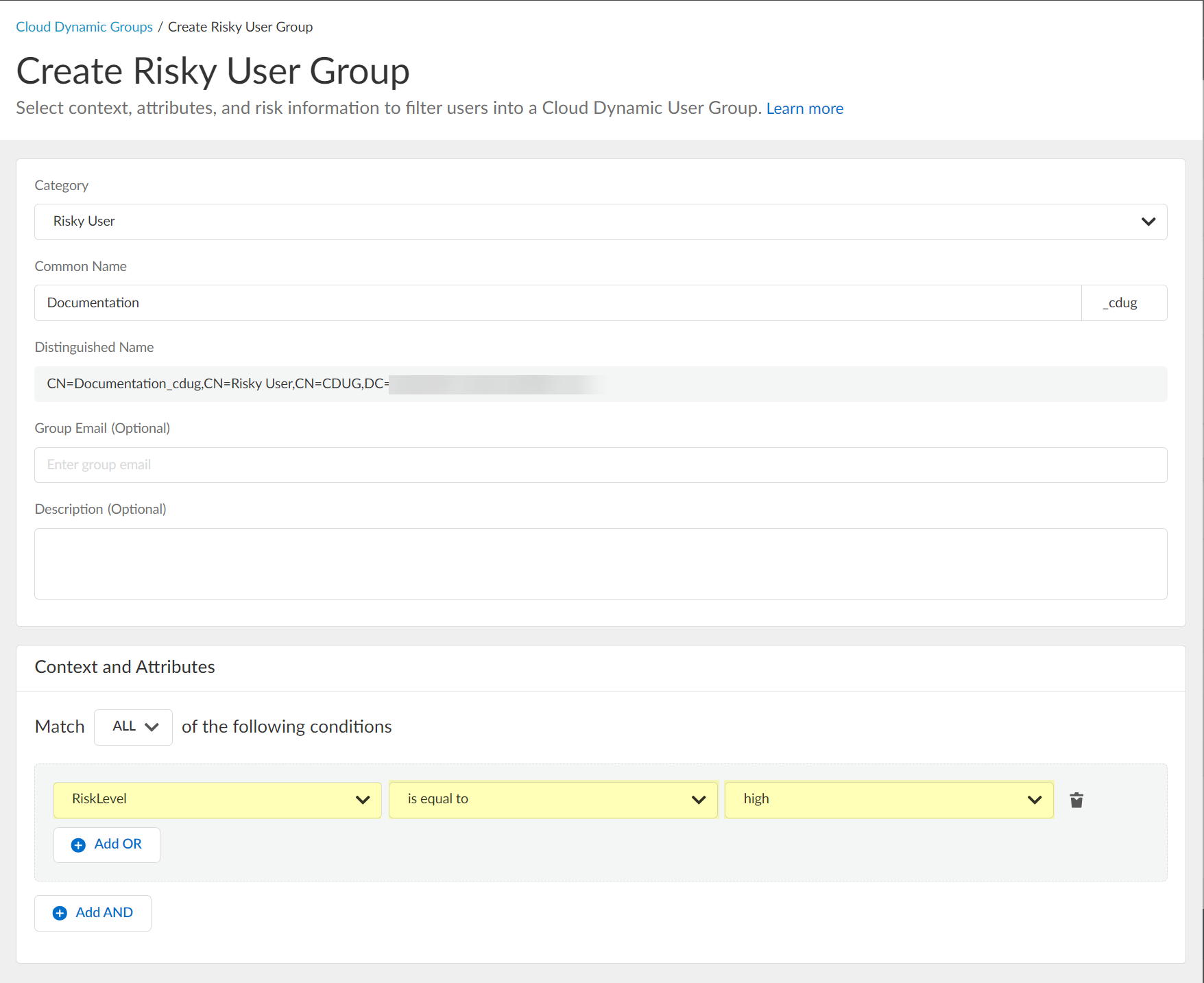
- (Optional) To include additional context and attributes, click Add OR and optionally Add AND and select the context and attributes to use for the dynamic risky user group.
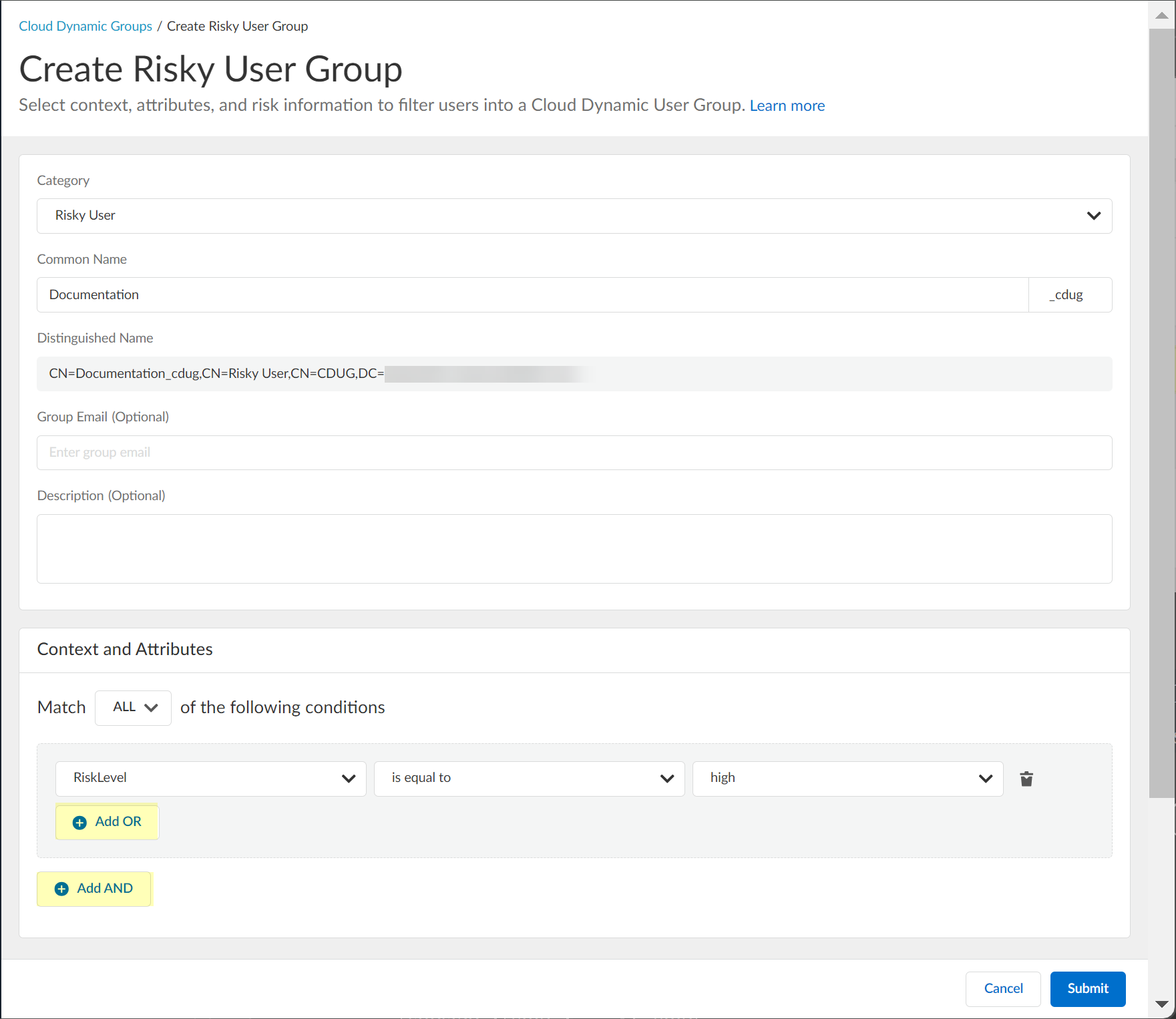
- Submit the configuration.
Configure SentinelOne for Security Risk in the Cloud Identity Engine
- To configure SentinelOne as a risk source for Security Risk, collect the necessary information from your SentinelOne configuration.
- Before logging in to SentinelOne, copy the URL without the /login part of the address and save it in a secure location.
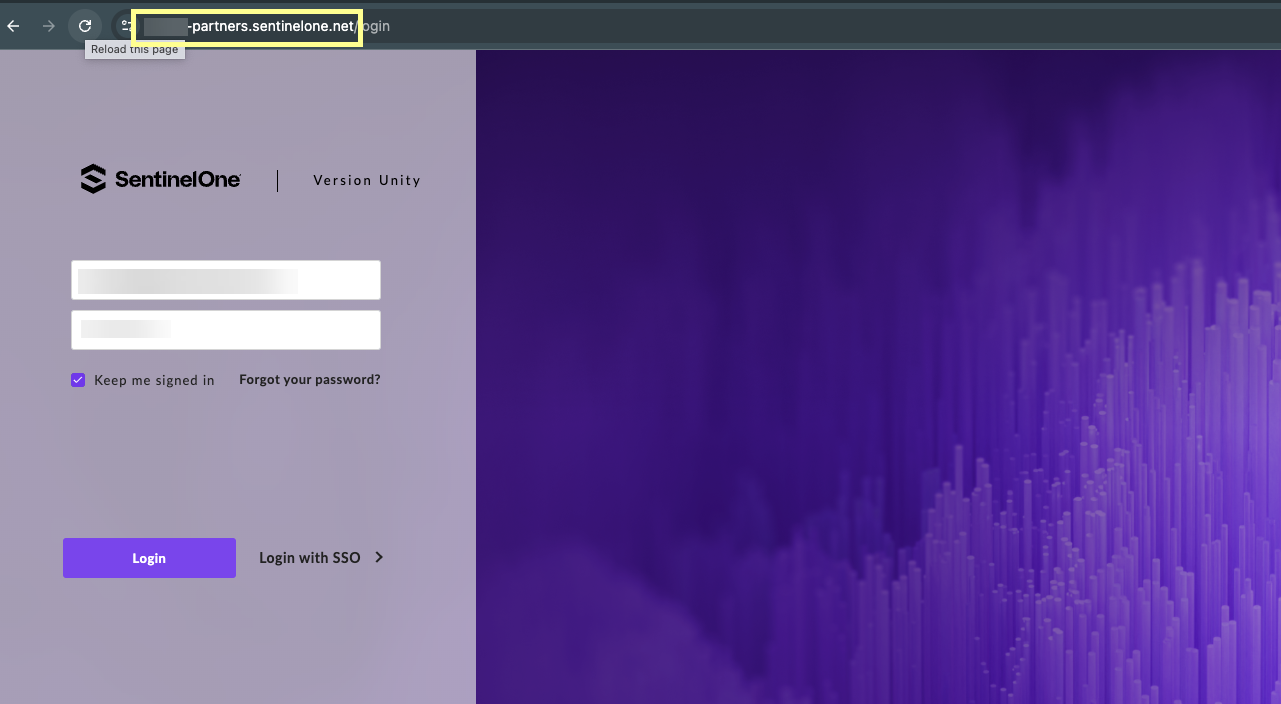
- Log in to SentinelOne and select SettingsUsersService Users .
- Click ActionsCreate New Service User .
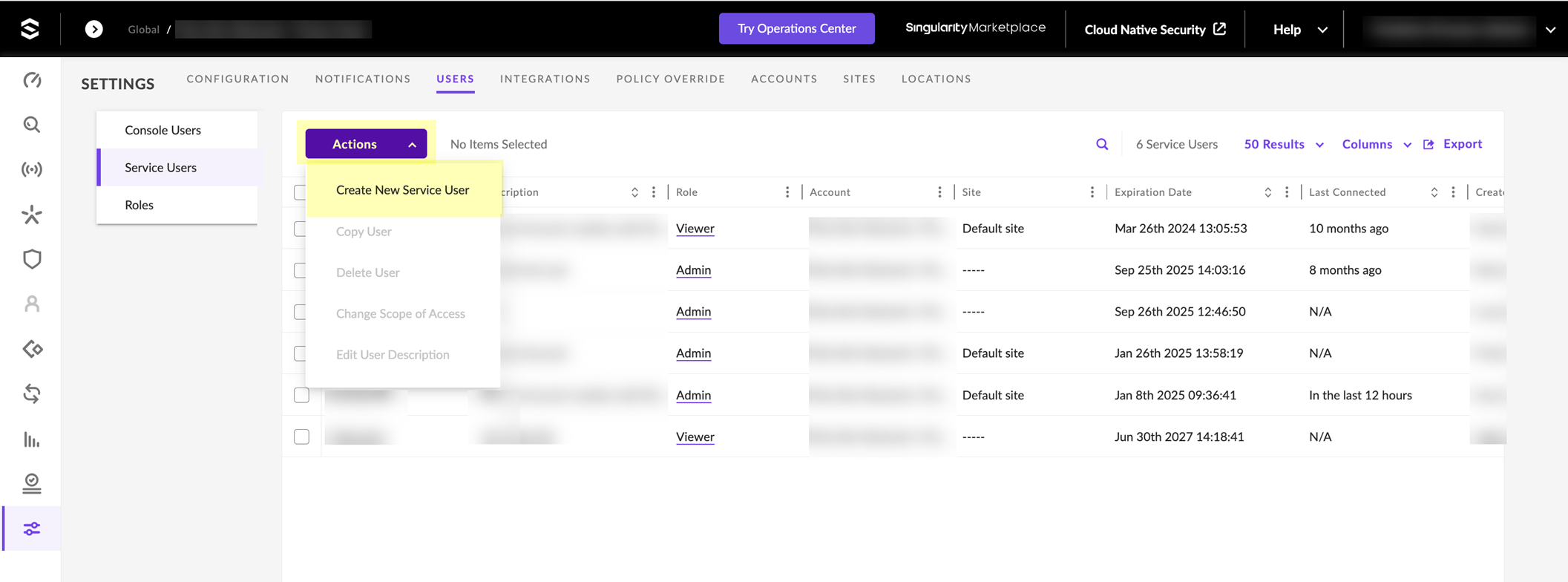
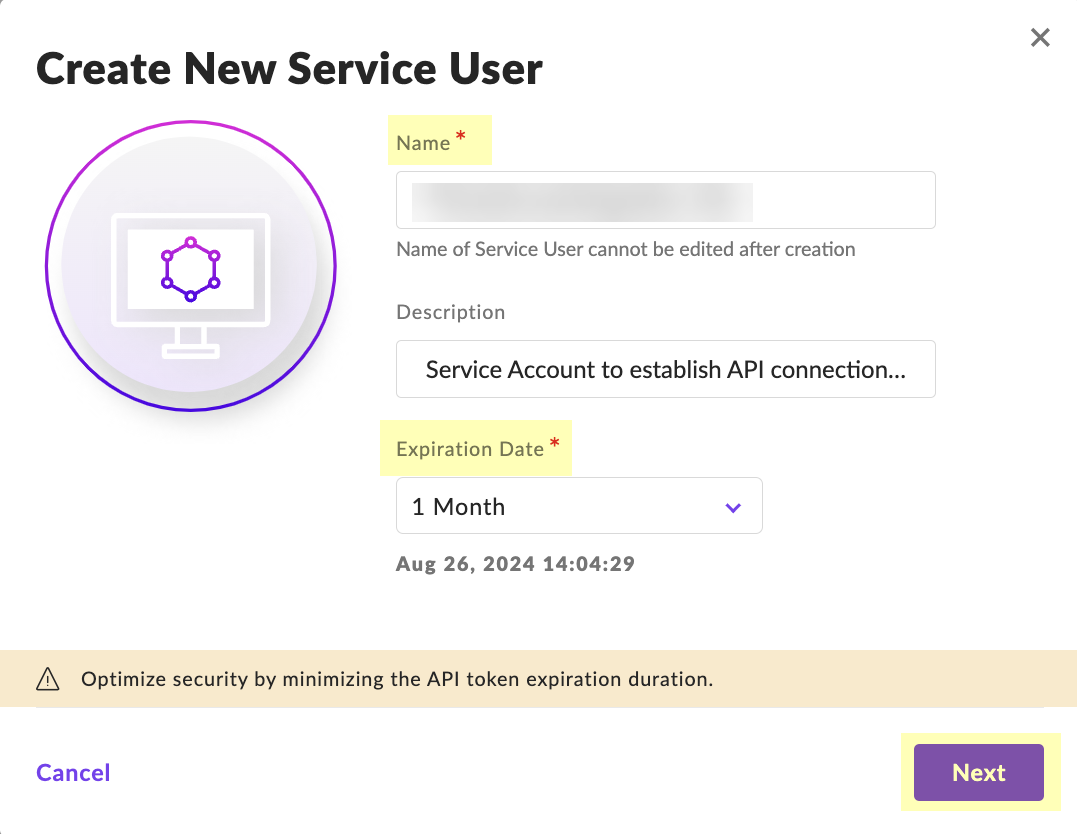
- Enter a Name for the service user account and select the Expiration Date then click Next .
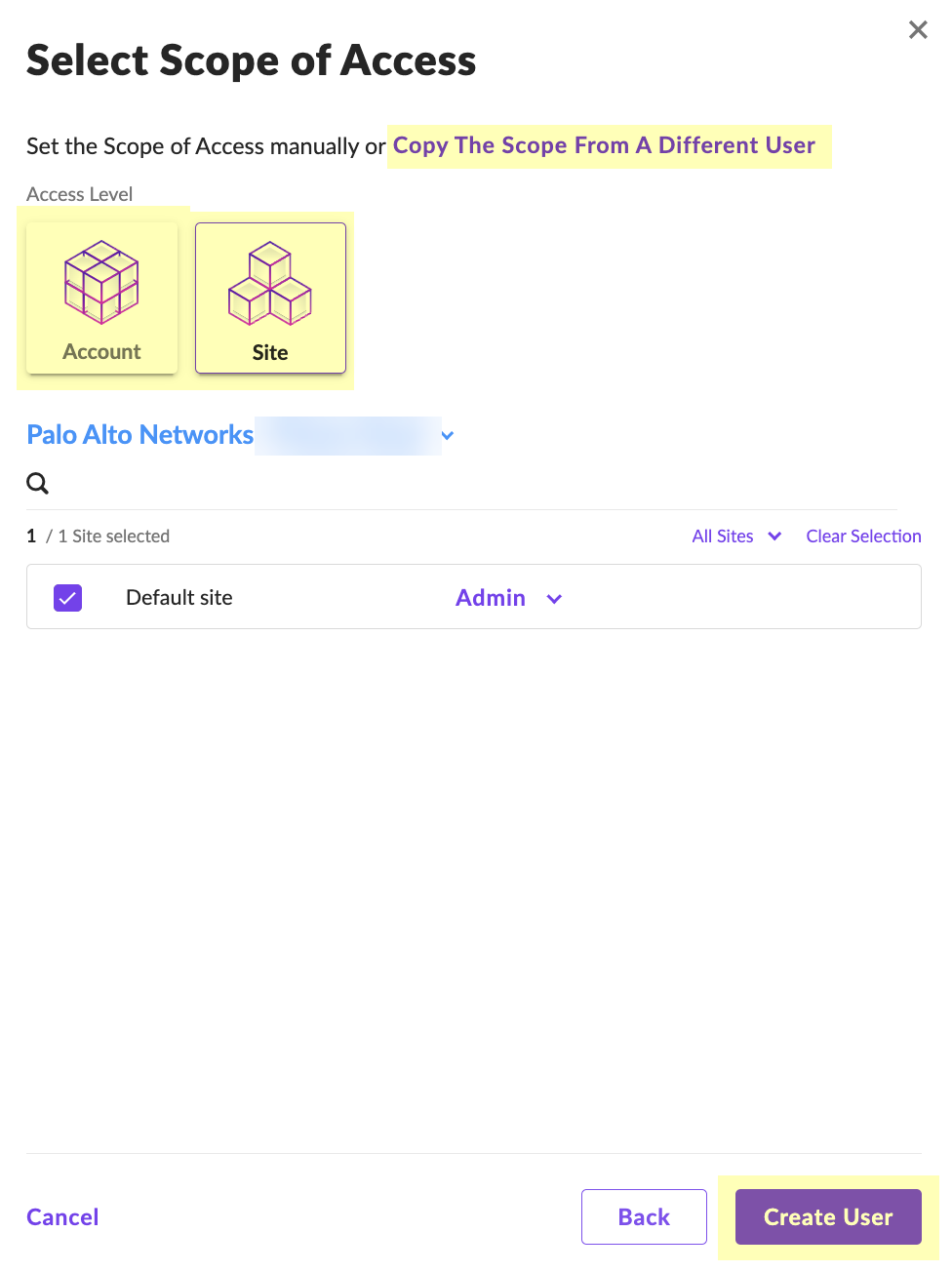
- Select Scope of Access and click Create User .
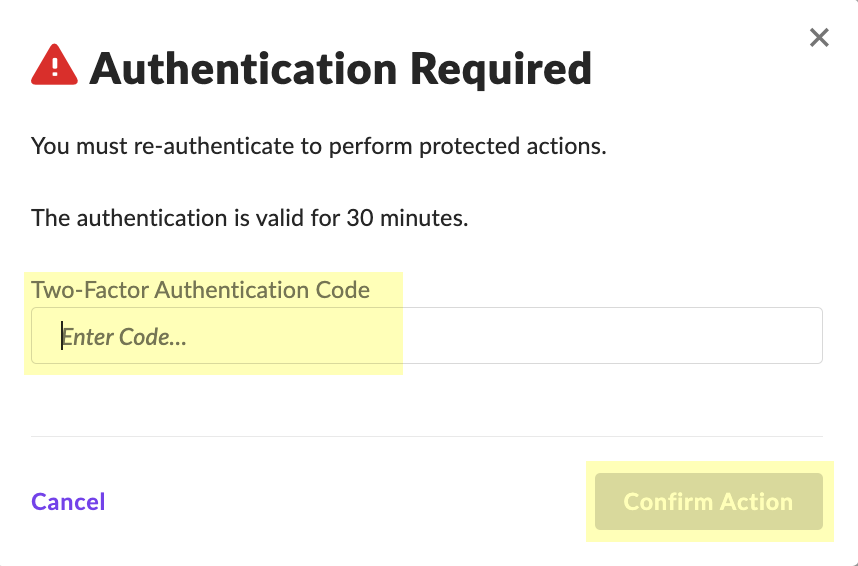
- Enter the Two-Factor Authentication Code within the 30-minute duration and click Confirm Action .
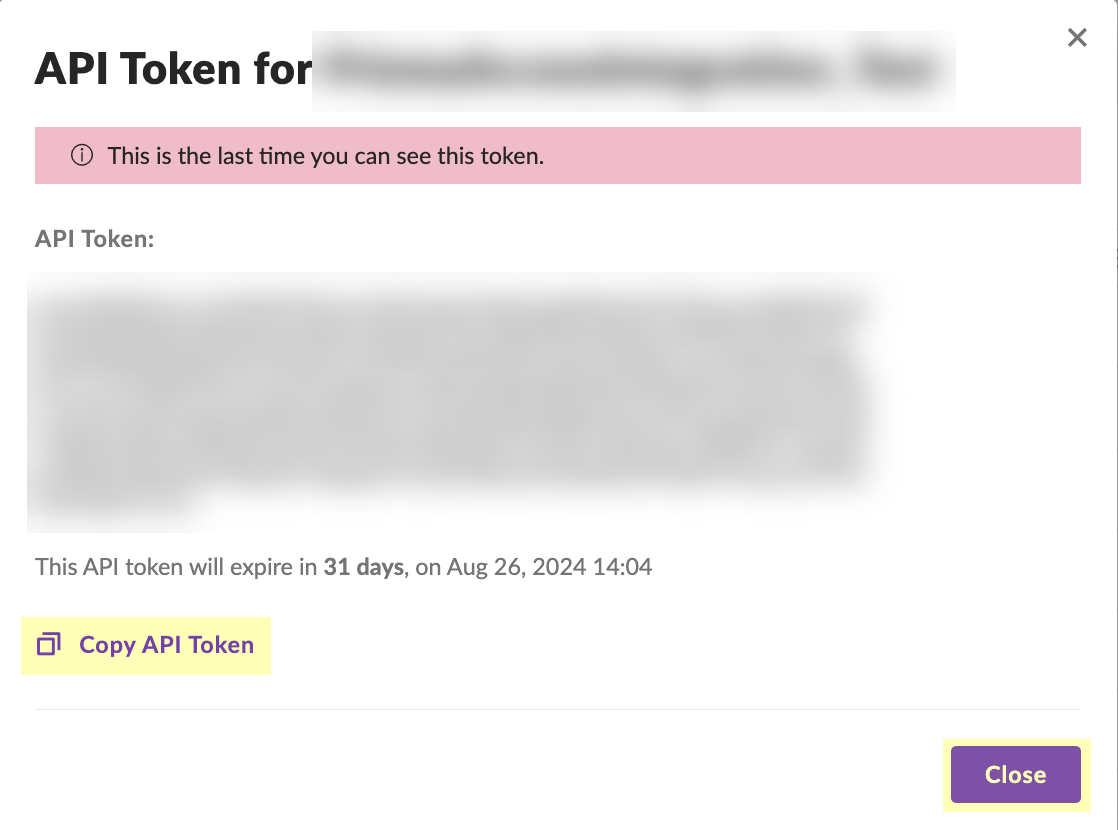
- Click Copy API Token to copy the API token and save it in a secure location. Because the API token only displays once, ensure you copy the token before clicking the Close button.
- (Optional but recommended) Click the Site button to confirm the creation of the site.
- Configure SentinelOne as a risk source in the Cloud Identity Engine.
- Enter the SentinelOne Source Name .
The source name must use lowercase.
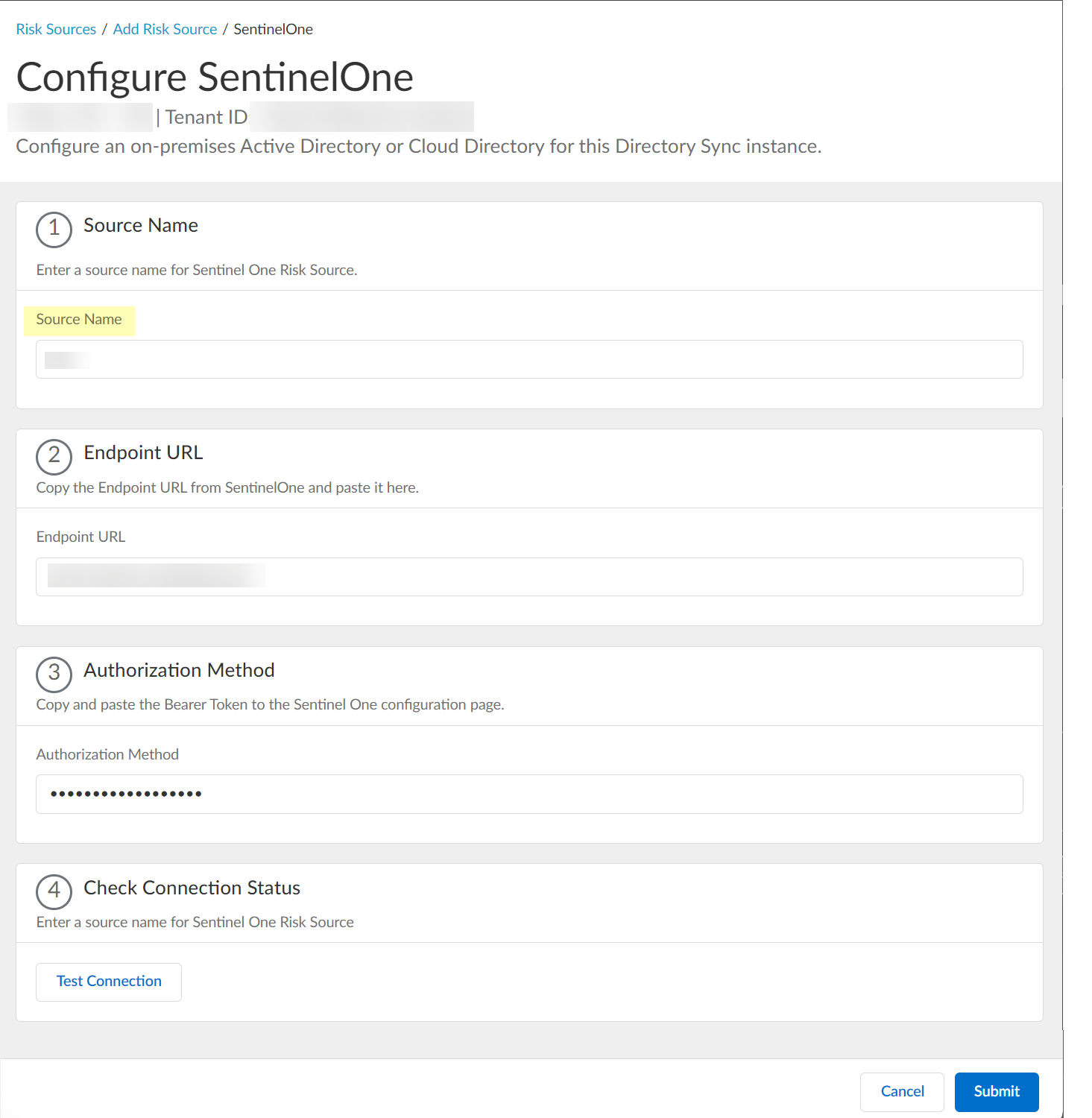
- Paste the Endpoint URL you copied from SentinelOne in step
1.a
.
- Paste the Authorization Method API token you copied in step
1.7
and paste it in your SentinelOne configuration.
- Click Test Connection to verify that the Cloud Identity Engine can communicate with your SentinelOne configuration.
- After confirming that the Cloud Identity Engine can successfully communicate with your provider using your SentinelOne configuration, Submit the SentinelOne configuration.
- View or edit the dynamic risky endpoint groups.
- In the Cloud Identity Engine, select Security RiskCloud Dynamic Groups .
- Select the Risky Endpoint Group tab to view the groups that the Cloud Identity Engine creates to isolate endpoints that it identifies as risky. You can optionally click the Details icon to view more information about the specific endpoint group.
The Cloud Identity Engine creates a default group without any attributes; you must specify the attributes you want to use for the group (see step
3.4
).
- (Optional) Search the groups by entering a search query then click Apply Search .
You can specify a Text Search or a Substring Search .
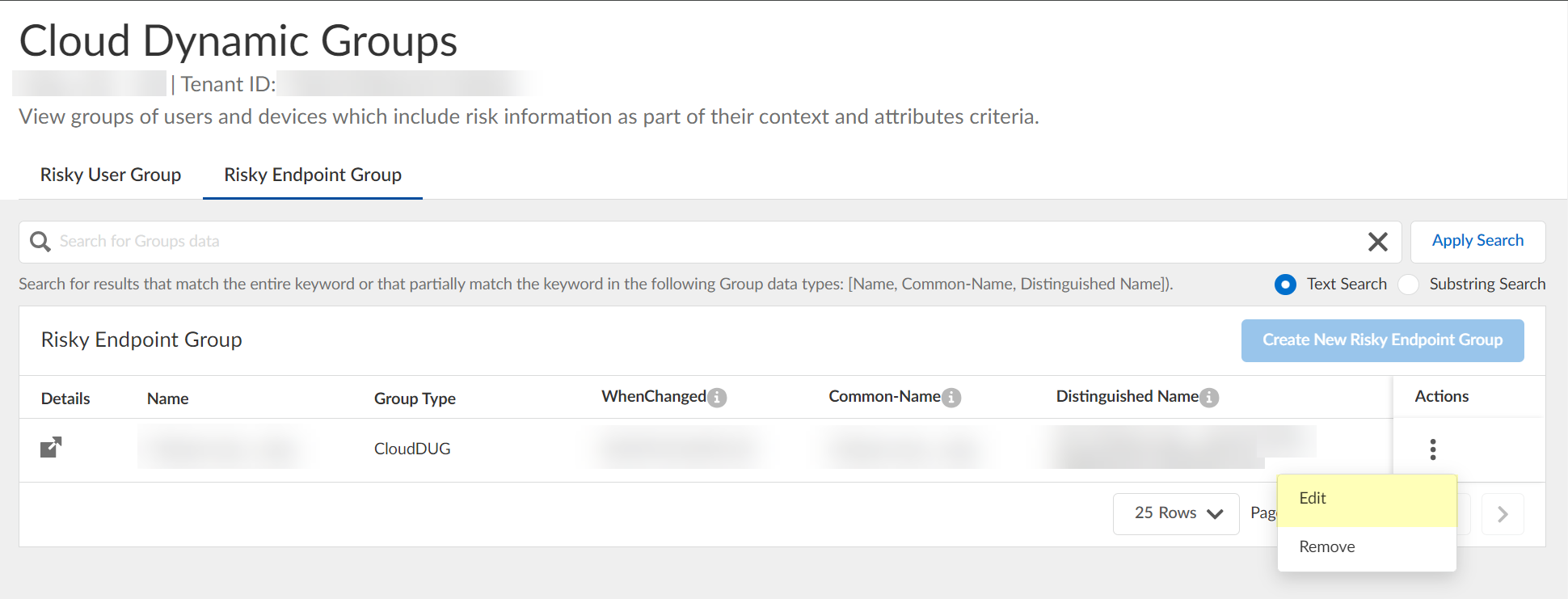
- Specify the context and attributes for the cloud dynamic risky endpoint group by selecting ActionsEdit , adding the context and attributes, and clicking Submit to confirm the changes.
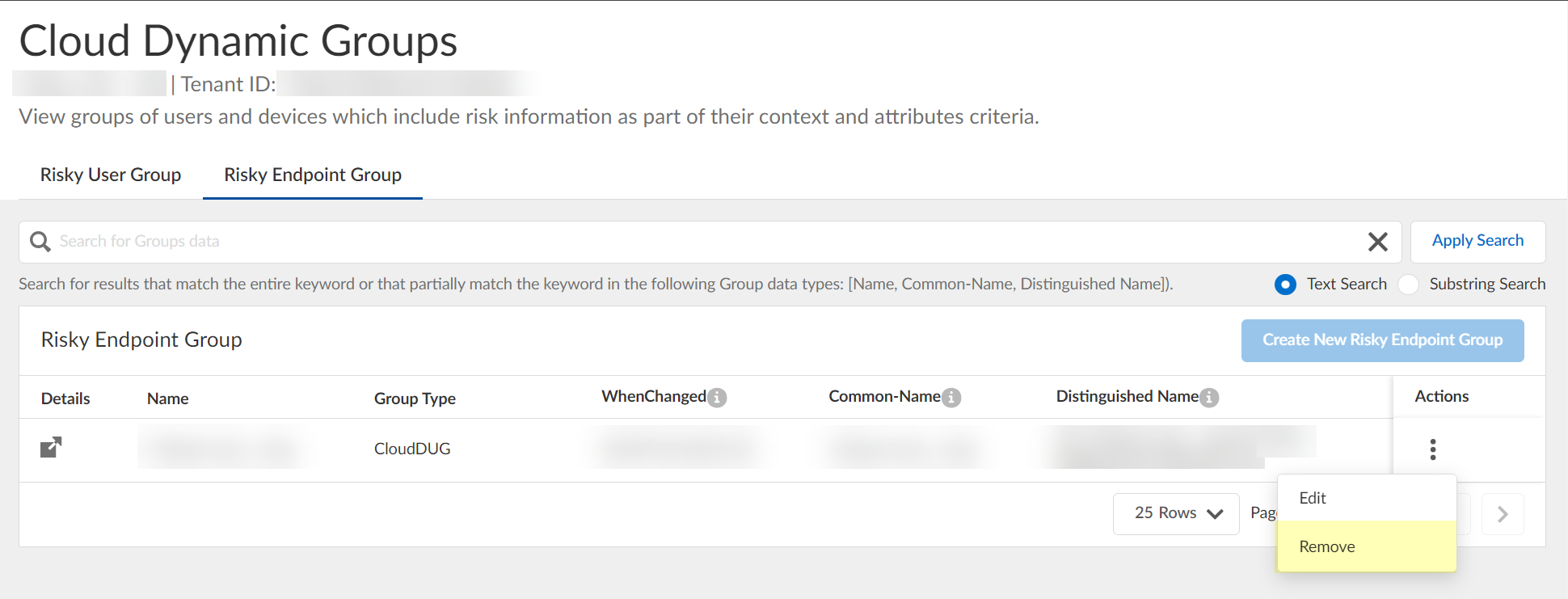
- (Optional) To delete a group, select ActionsRemove and click Yes to confirm removal of the group.
The Cloud Identity Engine does not currently support creation of a dynamic risky endpoint group if there is an existing group.
- Use Strata Cloud Manager to view the devices that have been quarantined .
The Cloud Identity Engine places devices in quarantine using device security posture information and risk signals from SentinelOne. It removes devices from the quarantine list only when the device no longer meets any of the match criteria in the Cloud Identity Engine configuration. If a device is in quarantine due to SentinelOne information, Palo Alto Networks does not recommend manually removing the device from the quarantine list using Strata Cloud Manager or Panorama.
- Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.
- Select ManageConfigurationNGFW and Prisma Access .
- Select Prisma Access as the Configuration Scope .
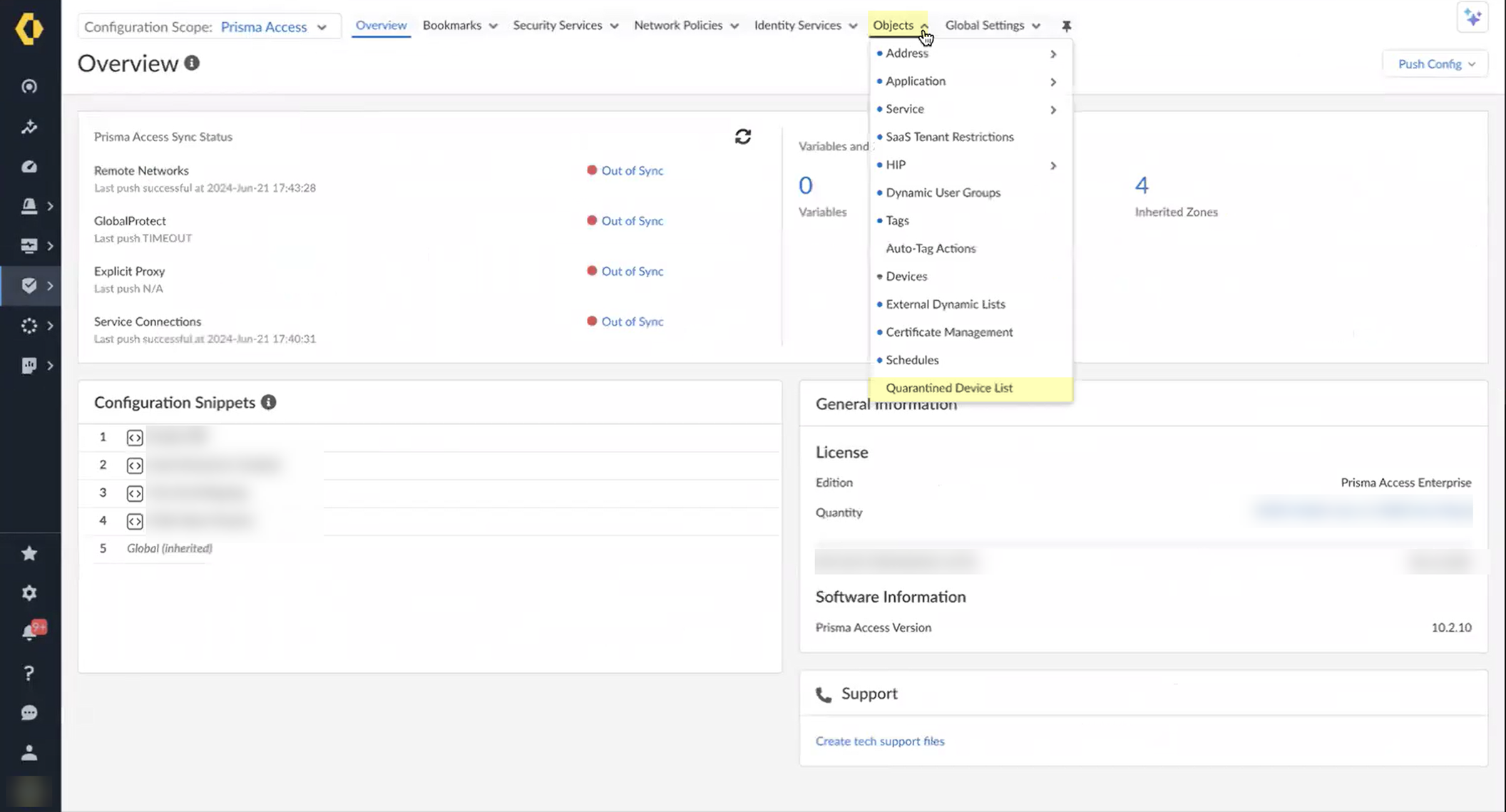
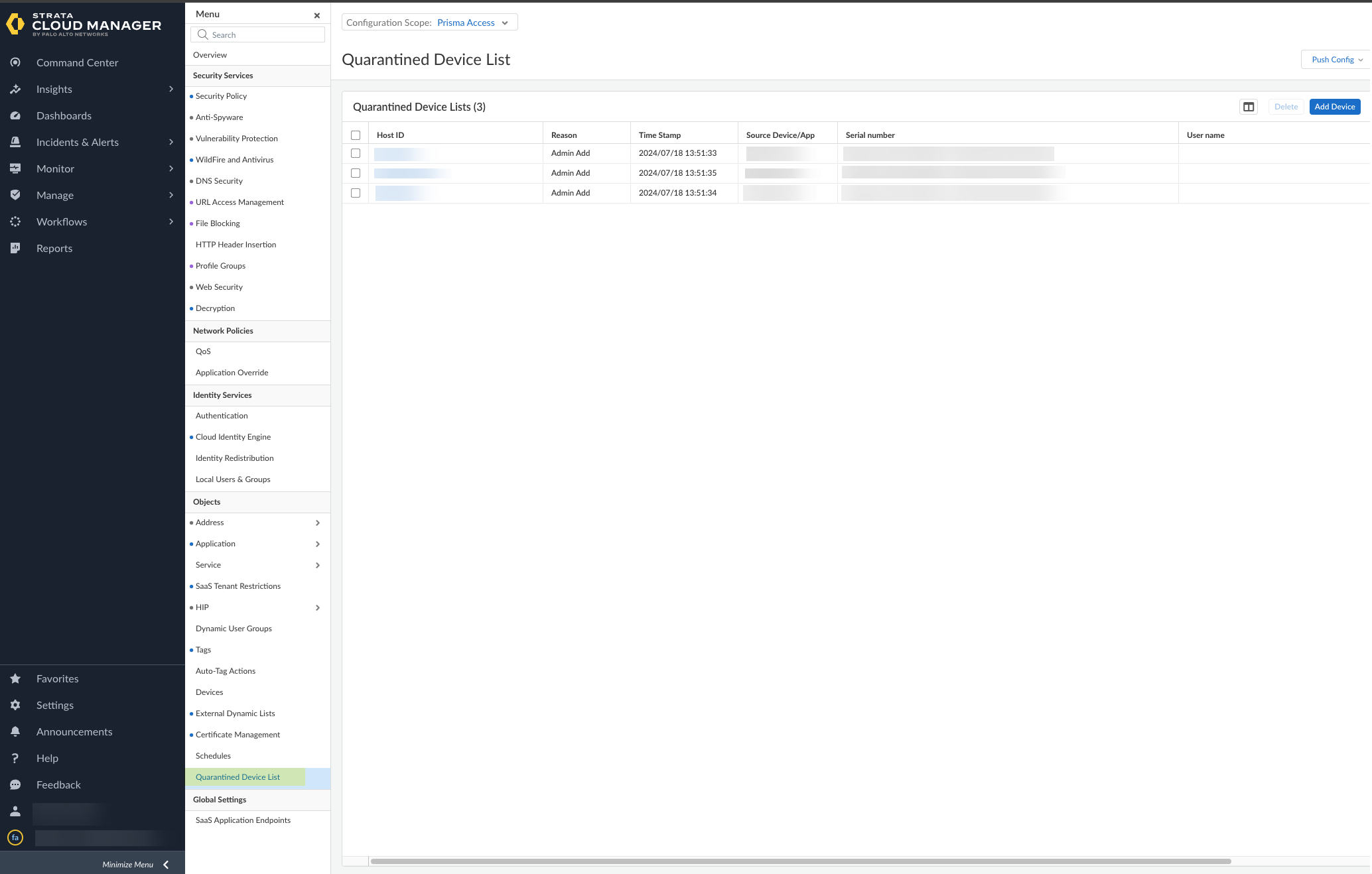
- Select ObjectsQuarantined Device List .
- Review the devices in the quarantine list to determine what remediation actions to take.
Manage the Cloud Identity Agent
After you have installed and configured the agent, learn how to ensure you are using the latest agent version. If you need to perform maintenance, you can stop and restart the agent’s connection to your tenant. To help troubleshoot any issues, learn more about the events logged by the agent and how to use the logs.
Configure Cloud Identity Agent Logs
The Cloud Identity agent logs Cloud Identity Engine events that occur on the agent host. You can use these logs to monitor informational events such as new connections ( Information—New connection 192.0.2.0: 49161 ), or for troubleshooting ( Error—Verification of Server Cert failed, stopping Cloud Identity Agent ). For example, the agent automatically generates logs if you test connectivity when you Configure the Cloud Identity Agent . You can also use the Event Viewer on the agent host to review logs created if the agent is unable to connect to the Cloud Identity Engine due to an incorrect bind DN or password, server unavailability, or other issue.
The agent displays logs in the order in which they were generated. To provide a consistent timestamp across timezones, logs include the timezone information in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), where the time offset is indicated by + or -. For the complete log history, check the CloudIdAgentDebug log file on the agent host, which permanently retains all logs.
- Launch the agent.
- Select FileDebug .
- Select the type of event you want to log.
The agent logs the events of the selected type and all subsequent types. For example, if you select Debug , the logs include error, warning, information, and debug events.
- If you select None , the Cloud Identity agent does not log events at any level.
- If you select Information , Warning , or Error , the agent deletes the data from the log after sending it to the debug log on the agent host.
- If you select Debug or Verbose , the received data is stored permanently on the disk until you delete the files.
To remove log files from the agent’s user interface, you can optionally Clear Cloud Identity Agent Logs .
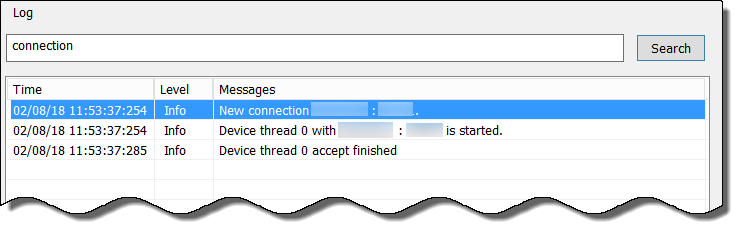
Search Cloud Identity Agent Logs
To troubleshoot issues with the Cloud Identity Engine, use keywords to search the Cloud Identity agent logs. For example, you could search for the IP address of a directory where the agent wasn’t able to connect to learn more about why the error occurred.
Search terms are case-sensitive.
- From the Cloud Identity agent, select Monitoring .
- Enter the search terms in the entry field to the left of Search .
- Click Search . The results are highlighted in blue below the entry field.
Clear Cloud Identity Agent Logs
You can clear outdated logs on the agent’s user interface. This does not delete the entries from the CloudIdAgentDebug log file on the agent host.
- From the Cloud Identity agent, select Monitoring .
- Click Clear Log .
Update the Cloud Identity Agent
Using the latest version of the agent is strongly recommended. If your Cloud Identity agent is not the latest version available, the Cloud Identity Engine app displays a notification.
Use the following procedure to update your Cloud Identity agent to the latest version.
When you upgrade the agent to version 1.7.0, it creates a backup of the existing agent configuration before removing the deprecated version of the agent. During installation of the new version of the agent, the existing configuration is automatically restored.
- Stop the connection to the Cloud Identity Engine service.
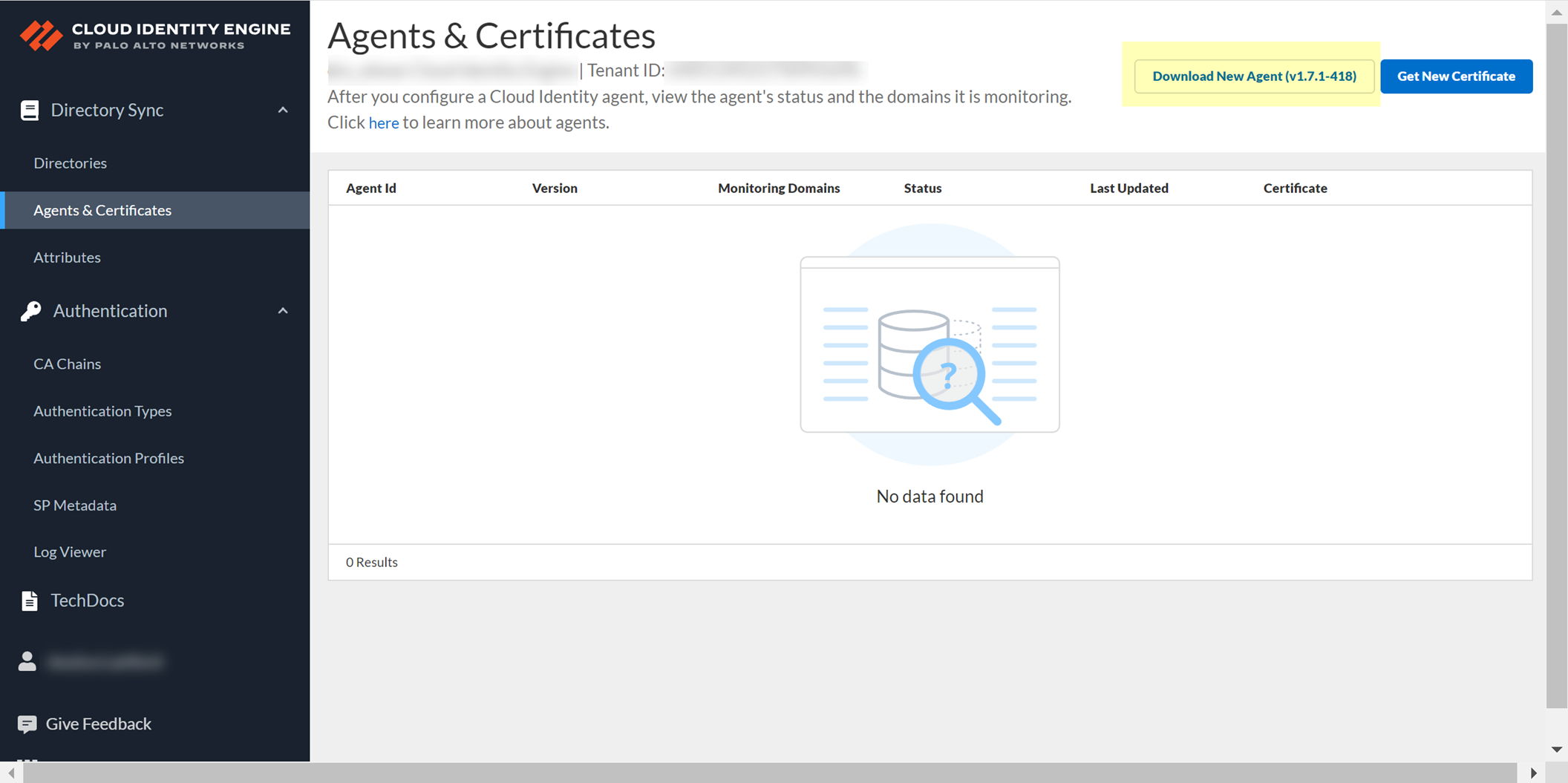
You must stop the connection between the agent and the service before you can update the agent. Check Agents & Certificates in the Cloud Identity Engine app to confirm the agent’s status.
- Uninstall the outdated agent from the host ( StartControl PanelPrograms and FeaturesCloud Identity AgentUninstall ).
You must uninstall the outdated agent from the host before installing the latest version of the agent.
- Log in to the hub and select the Cloud Identity Engine app.
- Select your Cloud Identity Engine tenant (if you have more than one) then select Agents & Certificate .
- Click Download New Agent , then Install the Cloud Identity Agent .
Start or Stop the Connection to the Cloud Identity Engine
When you start the Cloud Identity agent, it automatically starts communicating with the Cloud Identity Engine to synchronize the attributes. To prevent this communication (for example, if a directory server is unavailable or if you want to Remove the Cloud Identity Agent ), you can stop communication between the Cloud Identity agent and the Cloud Identity Engine. You can then restart the connection later to allow communication.
- On the agent host, start the Cloud Identity agent if it is not already running, then select Cloud Identity Configuration .
The current connection status of the agent displays at the lower-left corner of the window.
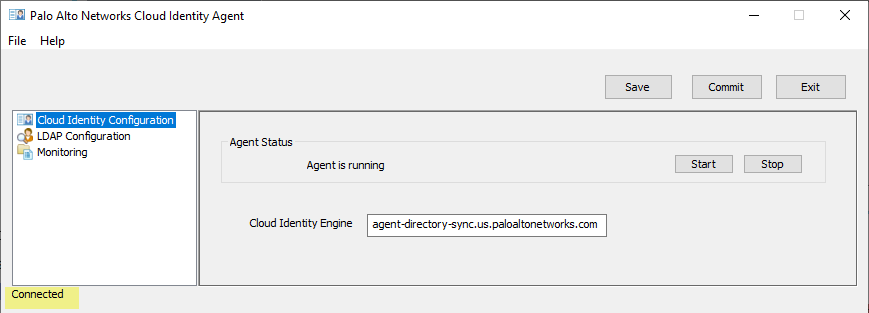
- Stop or re-establish the connection between the agent and the service.
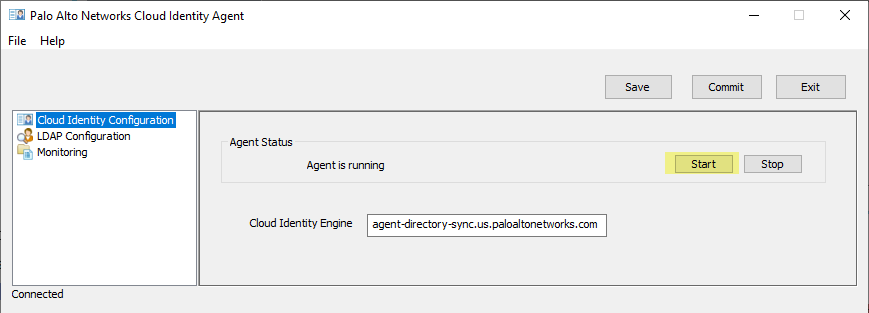
- To connect the agent to the Cloud Identity Engine, click Start .
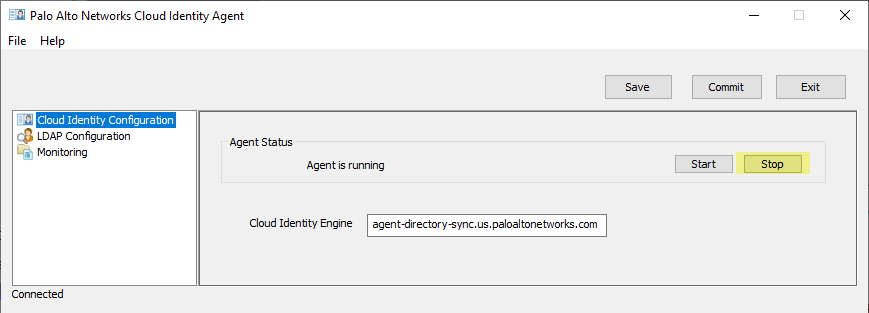
- To prevent the agent from communicating with the Cloud Identity Engine, click Stop .
Remove the Cloud Identity Agent
If you no longer need a Cloud Identity agent, you can remove it from your Cloud Identity Engine tenant.
- Stop the connection to the Cloud Identity Engine.
You must stop the connection between the agent and the Cloud Identity Engine before you can remove the agent.
- Uninstall the agent from the host server ( StartControl PanelPrograms and FeaturesCloud Identity AgentUninstall ).
- Log in to the hub and select the Cloud Identity Engine tenant that contains the agent you want to remove.
- Select Agents & Certificates .
- Confirm that the agent’s Status is Offline and Remove Agent .
You can only remove an agent that is offline (the connection between the agent and the Cloud Identity Engine is not active). If the agent is not offline, the Remove Agent button is not available.
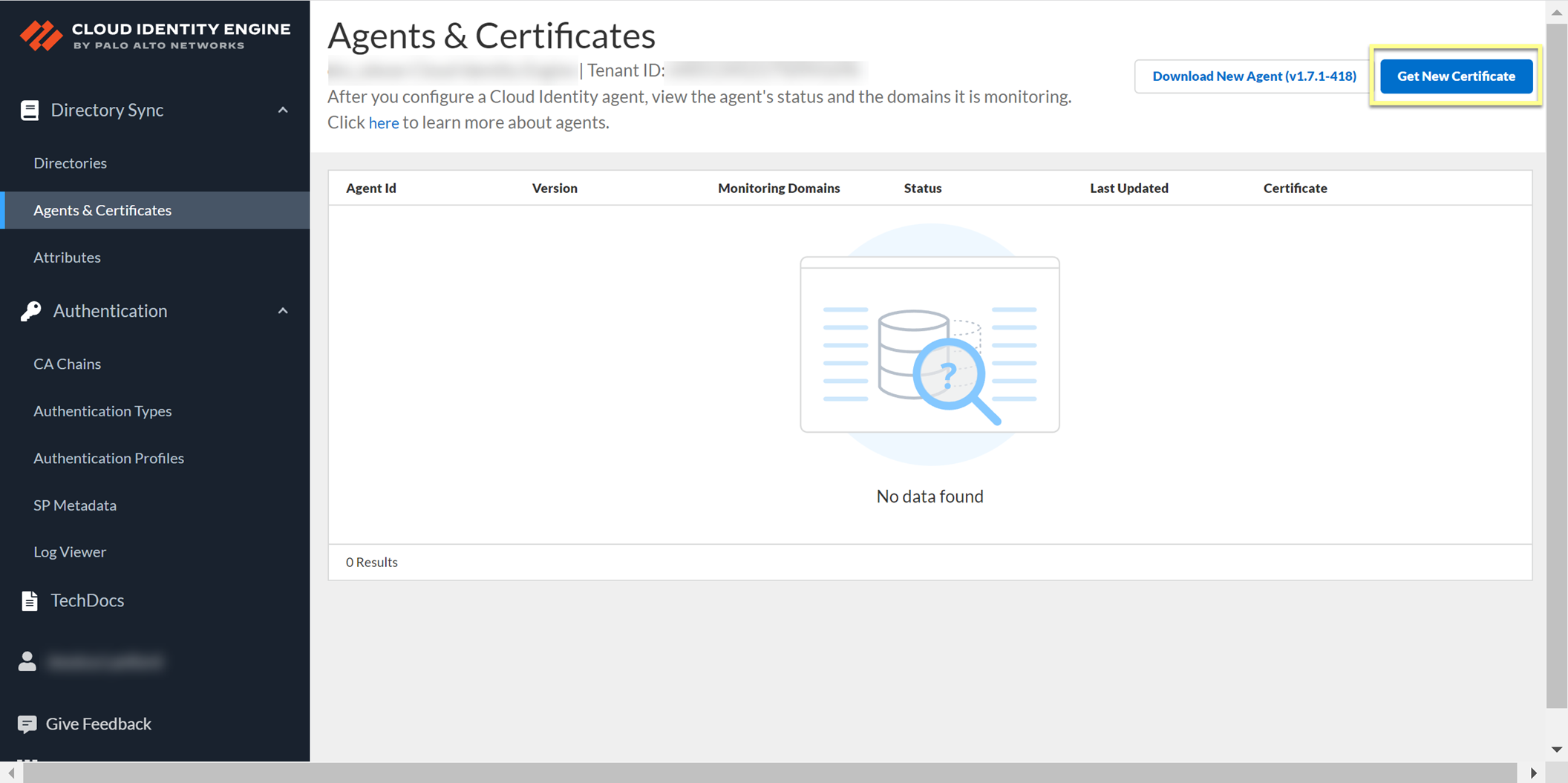
Manage Cloud Identity Engine Certificates
After you generate the certificate to Authenticate the Agent and the Cloud Identity Engine , you can view the certificate and its associated agent in the Cloud Identity Engine app.
The Cloud Identity agent version 1.5.0 and later versions automatically renews the certificate before it expires.
You can view the identification number and lifetime of the certificate on the Agents & Certificates page in the Cloud Identity Engine app.
If you need to Revoke Cloud Identity Agent Certificates , you must Delete Obsolete Cloud Identity Agent Certificates before you generate and install the new certificate.
To generate a new certificate for an agent, click Get New Certificate , then follow the steps to Authenticate the Agent and the Cloud Identity Engine .
Revoke Cloud Identity Agent Certificates
If a Cloud Identity agent’s certificate is compromised, revoke the certificate.
- Log in to the hub and select Cloud Identity Engine .
- Select the tenant associated with the agent with the compromised certificate.
- From the Cloud Identity Engine app, select Agents & Certificates .
- Revoke the certificate.
- Delete Obsolete Cloud Identity Agent Certificates to remove the previous certificate.
- Generate a new certificate to Authenticate the Agent and the Cloud Identity Engine and install it on the agent host.
Delete Obsolete Cloud Identity Agent Certificates
You must delete the previous certificate for the agent before installing the new certificate. If you do not delete the previous certificate, the Cloud Identity Engine may reference the previous certificate instead of the new certificate.
- On the agent host, open Microsoft Management Control (MMC) by selecting StartRun , then entering MMC .
- Select FileAdd/Remove Snap-In .
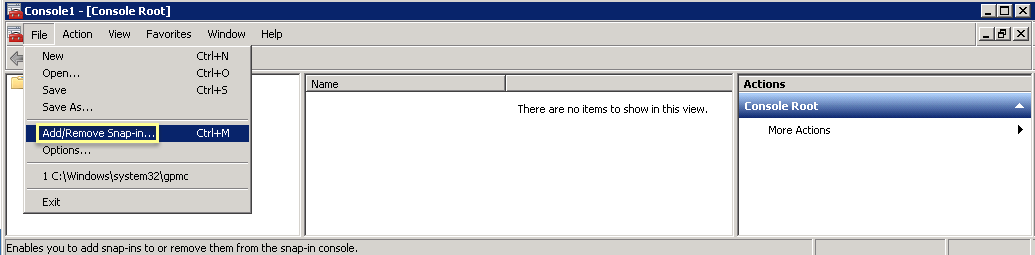
- Select CertificatesAdd .
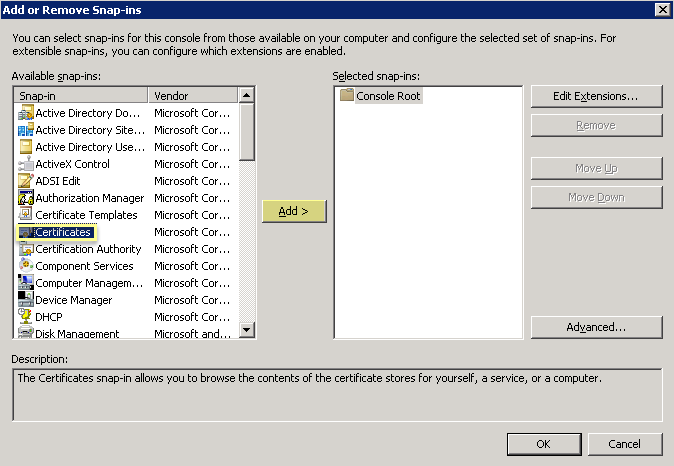
- Select Computer AccountNext .
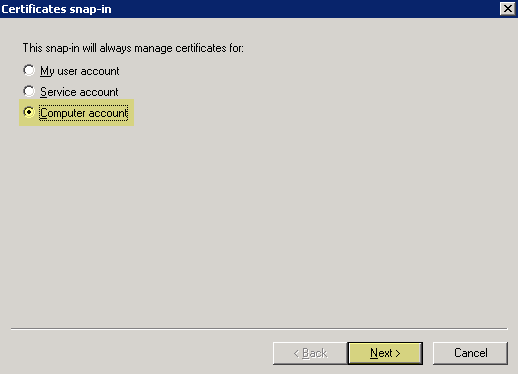
- Select Local ComputerFinish .
- Click OK , then navigate to Console RootCertificates (Local Computer)PersonalCertificates .
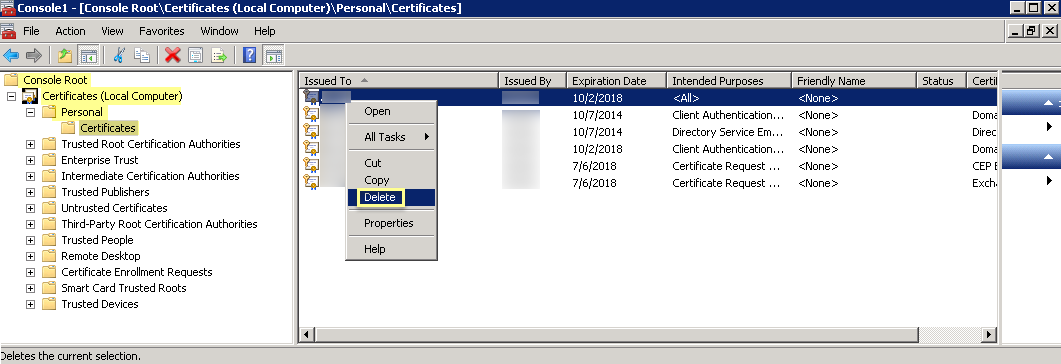
- Select the previous certificate from the list.
- Right-click the certificate, then Delete and click Yes to confirm the deletion.
- Generate a new certificate to Authenticate the Agent and the Cloud Identity Engine and install it on the agent host.
Associate the Cloud Identity Engine with Palo Alto Networks Apps
The following procedures describe the steps for the support account view in the Hub. If you are using the tenant account view, association is not necessary for a tenant service group ( TSG ). For more information, refer to the Hub Getting Started guide.
By associating your Cloud Identity Engine tenants with other Palo Alto Networks apps, you can allow these apps and services to access your directory information for reporting and policy enforcement. You can associate the Cloud Identity Engine tenant with another app during activation or with an existing app at any time.
To share user attributes with multiple apps, associate the same Cloud Identity Engine tenant with each app.
Associate the Cloud Identity Engine During Activation
The following procedures describe the steps for the support account view in the Hub. If you are using the tenant account view, association is not necessary for a tenant service group ( TSG ). For more information, refer to the Hub Getting Started guide.
- Using your Auth Code, activate the Palo Alto Networks cloud app you want to associate with the Cloud Identity Engine tenant.
- Enter the information required to activate the application, such as an Instance Name and a Region , which will vary depending on the app.
- Select the Cloud Identity Engine tenant you want to associate with the app.
Only Cloud Identity Engine tenants that are compatible with the Palo Alto Networks cloud application are displayed in the drop-down list. For example, a Cloud Identity Engine tenant assigned to the US region would be compatible with another Palo Alto Networks cloud service app assigned to the US region. If the Cloud Identity Engine field is not available, the Palo Alto Networks cloud services app you selected does not support the Cloud Identity Engine.
- Agree and Activate the app.
Associate the Cloud Identity Engine with an Existing App
The following procedures describe the steps for the support account view in the Hub. If you are using the tenant account view, association is not necessary for a tenant service group ( TSG ). For more information, refer to the Hub Getting Started guide.
- Log in to the hub, click Settings (

) then Manage Apps .
- Select the app you want to associate with the Cloud Identity Engine tenant.
- Select the Cloud Identity Engine tenant you want to associate with the app and click OK .
Only Cloud Identity Engine tenants that are compatible with the Palo Alto Networks cloud application are displayed in the drop-down list. For example, a Cloud Identity Engine tenant assigned to the US region would be compatible with another Palo Alto Networks cloud service app assigned to the US region. If the Cloud Identity Engine field is not available, the Palo Alto Networks cloud services app you selected does not support the Cloud Identity Engine.
After you associate the app, the Cloud Identity Engine tenant name displays in the Cloud Identity Engine column in the hub ( SettingsManage Apps ).
Authenticate Users with the Cloud Identity Engine
Learn how to deploy the Cloud Identity Engine for user authentication by configuring a SAML 2.0-based identity provider (IdP), a client certificate and certificate authority (CA) chain, or both. After specifying how you want to authenticate your users, set up your authentication profile to define your authentication security policy and optionally configure the authentication policy on your firewall or Panorama. After you’ve done that, configure the Cloud Identity Engine as a User-ID source for group mapping and user mapping to enforce group-based policy.
Configure a SAML 2.0 Authentication Type
You can configure SAML 2.0-compliant identity providers (IdPs) in the Cloud Identity Engine to authenticate your users. The following topics provide detailed steps on how to configure specific IdPs as authentication types in the Cloud Identity Engine.
Configure Azure as an IdP in the Cloud Identity Engine
- Download the Cloud Identity Engine integration in the Azure Portal.
- If you have not already done so, activate the Cloud Identity Engine app.
- Log in to the Azure Portal and select Azure Active Directory .
Make sure you complete all the necessary steps in the Azure portal.
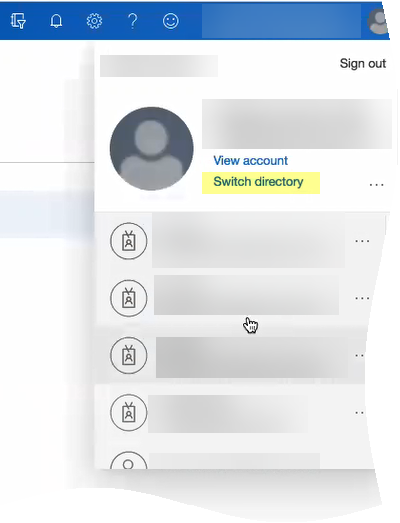
If you have more than one directory, Switch directory to select the directory you want to use with the Cloud Identity Engine.
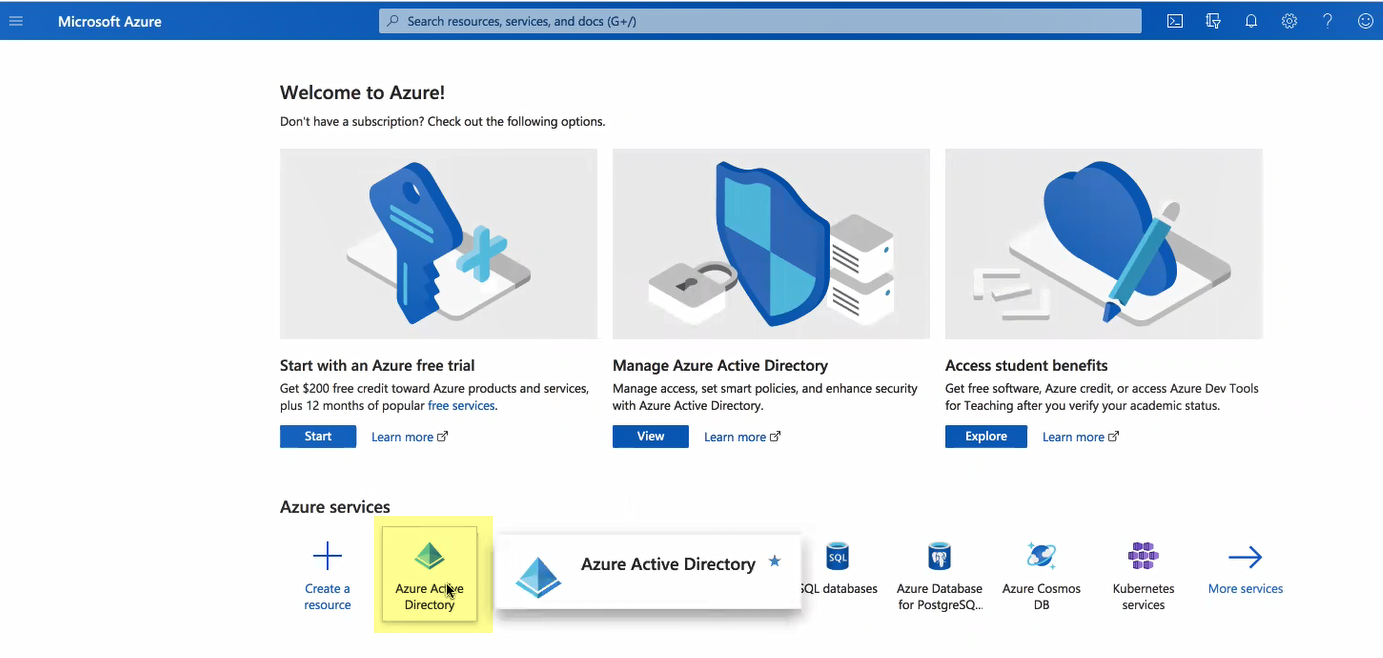
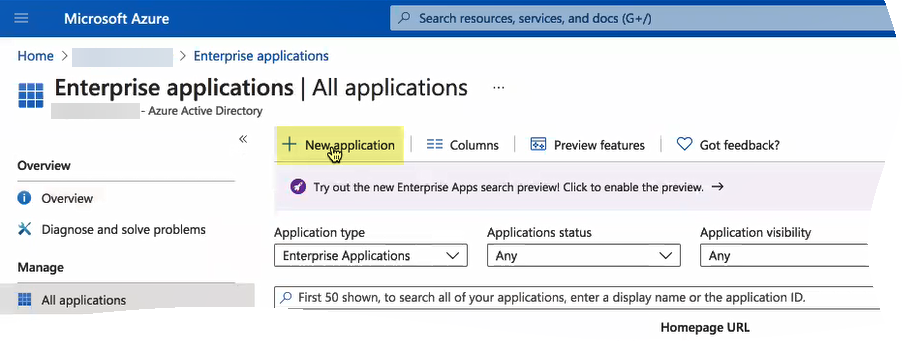
- Select Enterprise applications and click New application .
- Add from the gallery then enter Palo Alto Networks Cloud Identity Engine - Cloud Authentication Service and download the Azure AD single-sign on integration.
- After the application loads, select Users and groups , then Add user/group to Assign them to this application.
Select the users and groups you want to use the Azure IdP in the Cloud Identity Engine for authentication.
Be sure to assign the account you're using so you can test the configuration when it's complete. You may need to refresh the page after adding accounts to successfully complete the test.
- Select Single sign-on then select SAML .
- Upload Metadata File by browsing to the metadata file that you downloaded from the Cloud Identity Engine app and click Add .
- After the metadata uploads, Save your configuration.
- (Optional) Edit your User Attributes & Claims to Add a new claim or Edit an existing claim.
If you attempt to test the configuration on the Azure Admin Console, a 404 error displays because the test is triggered by the IdP and the Cloud Identity Engine supports authentication requests initiated by the service provider.
- Configure Azure AD for the Cloud Identity Engine.
- Select Single sign-on then select SAML .
- Edit the Basic SAML Configuration settings.
- Upload metadata file and select the metadata file you downloaded from the Cloud Identity Engine in the first step.
- Enter your regional endpoint as the Sign-on URL using the following format: https://<RegionUrl>.paloaltonetworks.com/sp/acs (where <RegionUrl> is your regional endpoint). For more information on regional endpoints, see Configure Cloud Identity Engine Authentication on the Firewall or Panorama .
- Copy the App Federation Metadata Url and save it to a secure location.
At this point in the process, you may see the option to Test sign-in . If you try to test the single sign-on configuration now, the test won't be successful. You can test your configuration to verify it's correct in step
9
.
- Add and assign users who you want to require to use Azure AD for authentication.
- Select Azure Active Directory then select UsersAll users .
- Create a New user and enter a Name , User name .
- Select Show password , copy the password to a secure location, and Create the user.
- In the Palo Alto Networks Cloud Identity Engine - Cloud Authentication Service integration in the Azure Portal, select Users and groups .
- Add user then select Users and groups .
- Add Azure as an authentication type in the Cloud Identity Engine app.
- In the Cloud Identity Engine app, select AuthenticationAuthentication Types then click Add New Authentication Type .
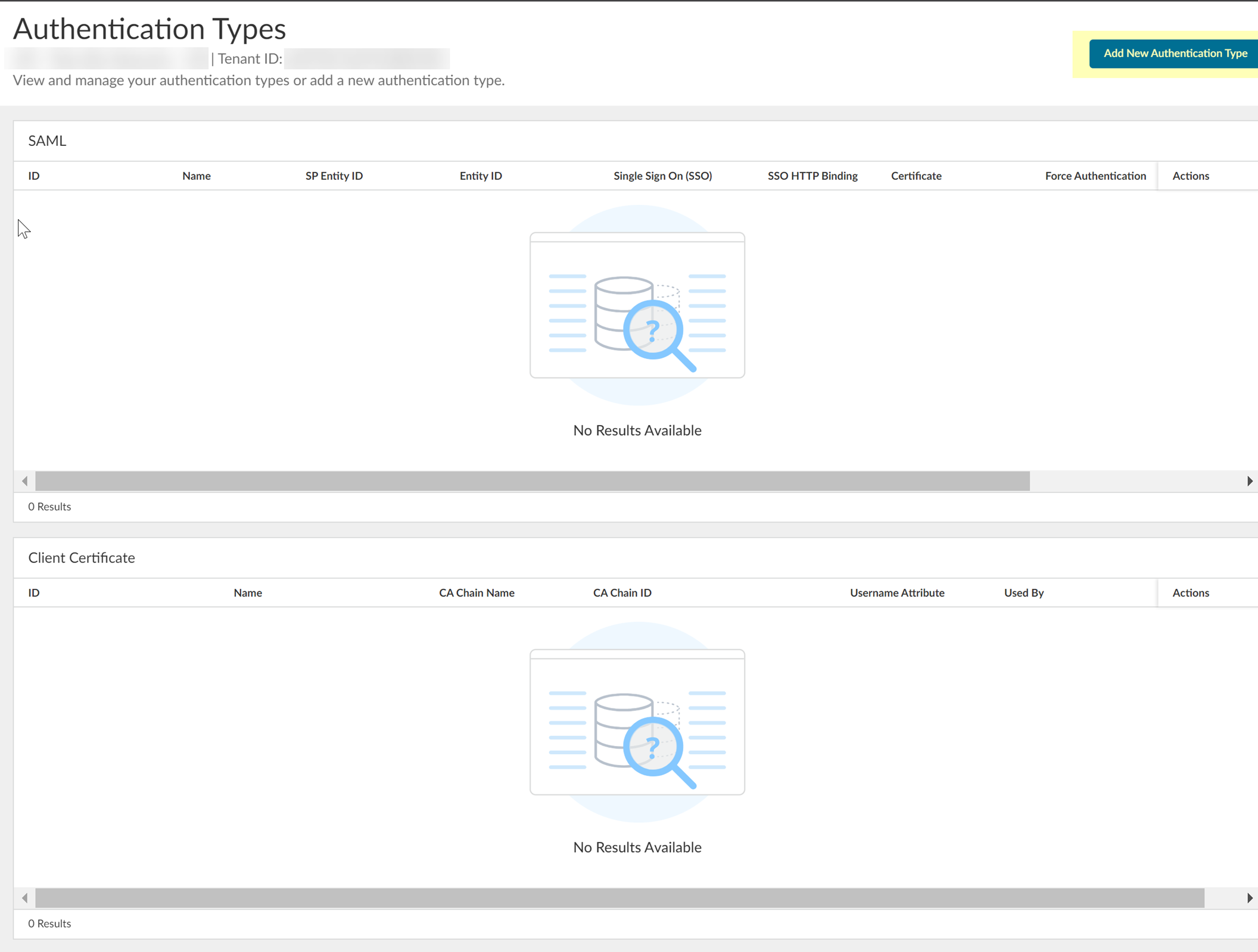
- Set Up a SAML 2.0 authentication type.
- Select the Metadata Type you want to use.
- To use the client credential flow, the auth code flow, or SCIM, select Single service provider metadata .
- To Configure Dynamic Privilege Access in the Cloud Identity Engine , select Dynamic service provider metadata .
- Copy the Entity ID and Assertion Consumer Service URL and save them in a secure location.
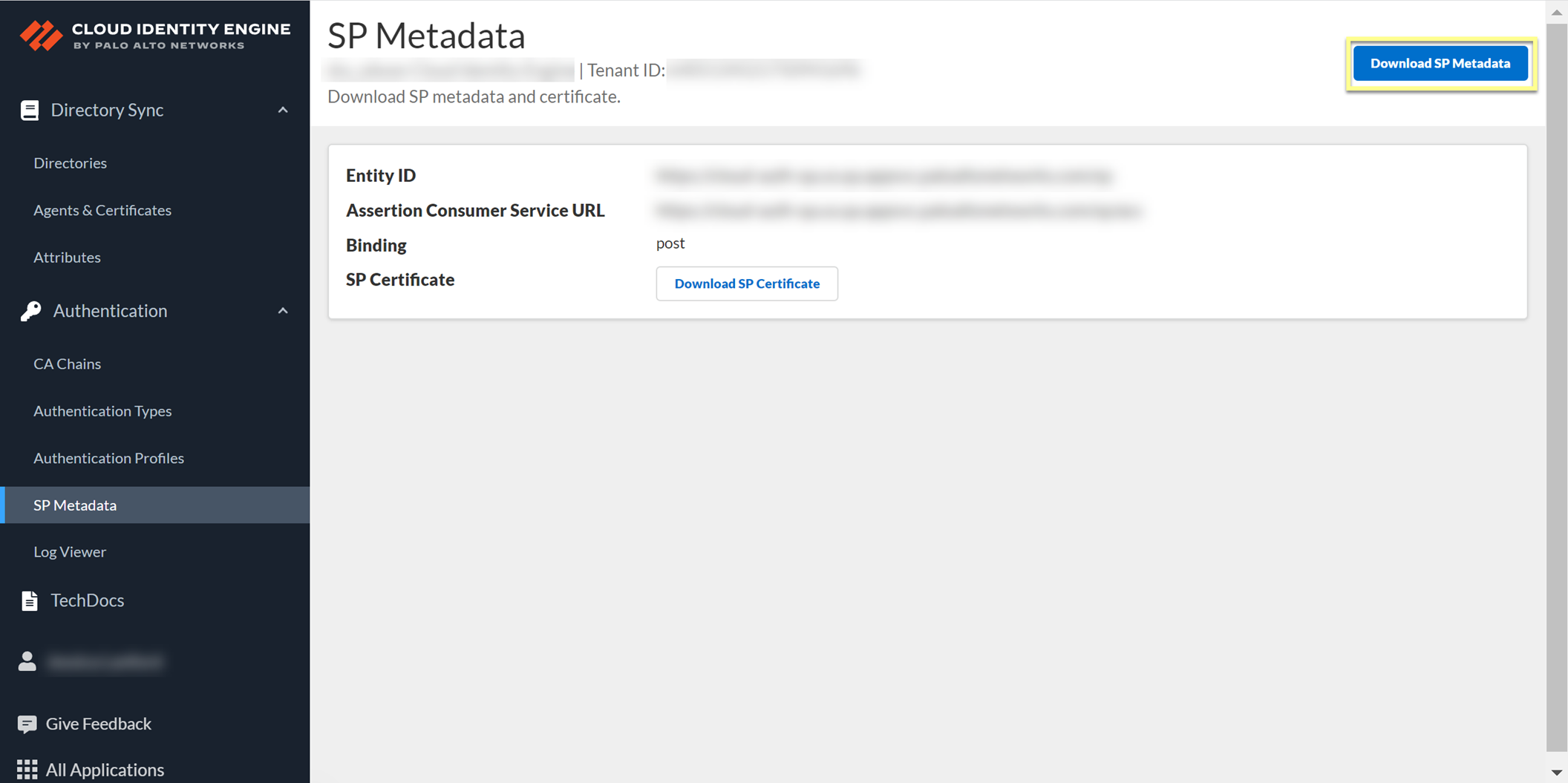
- Download SP Certificate and Download SP Metadata and save them in a secure location.
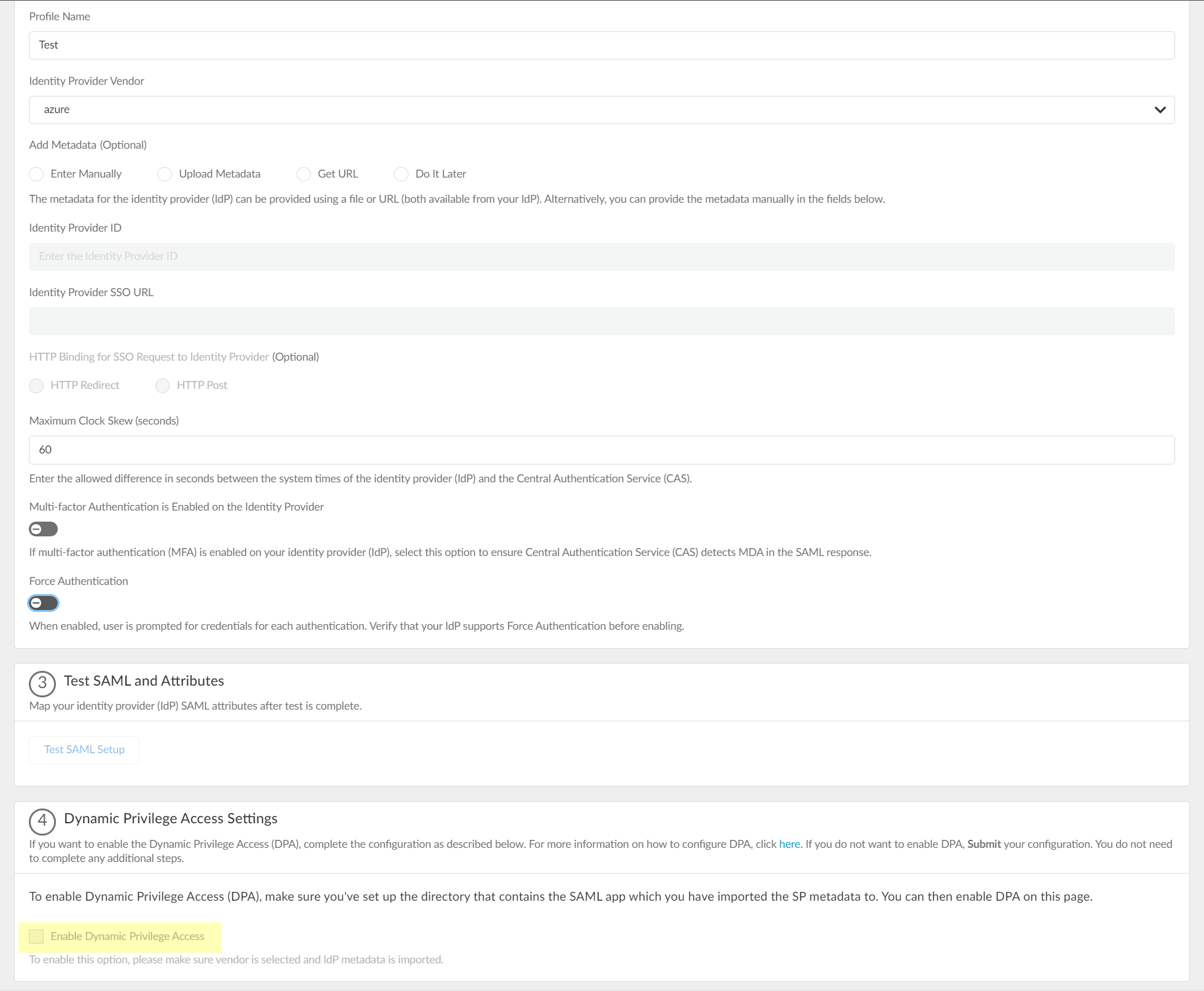
- Enter a unique and descriptive Profile Name .
- Select Azure as your Identity Provider Vendor .
- Select the method you want to use to Add Metadata .
- If you want to enter the information manually, copy the identity provider ID and SSO URL, download the certificate, then enter the information in the Cloud Identity Engine IdP profile.
1. Copy the necessary information from the Azure Portal and enter it in the IdP profile on the Cloud Identity Engine app as indicated in the following table:
|
Copy or Download from Azure Portal |
Enter in Cloud Identity Engine IdP Profile |
|
Copy the Azure AD Identifier . |
Enter it as the Identity Provider ID . |
|
Download the Certificate (Base64) . |
Click Browse files to select the Identity Provider Certificate you downloaded from the Azure Portal. |
|
Copy the Login URL . |
Enter the URL as the Identity Provider SSO URL . |
2.
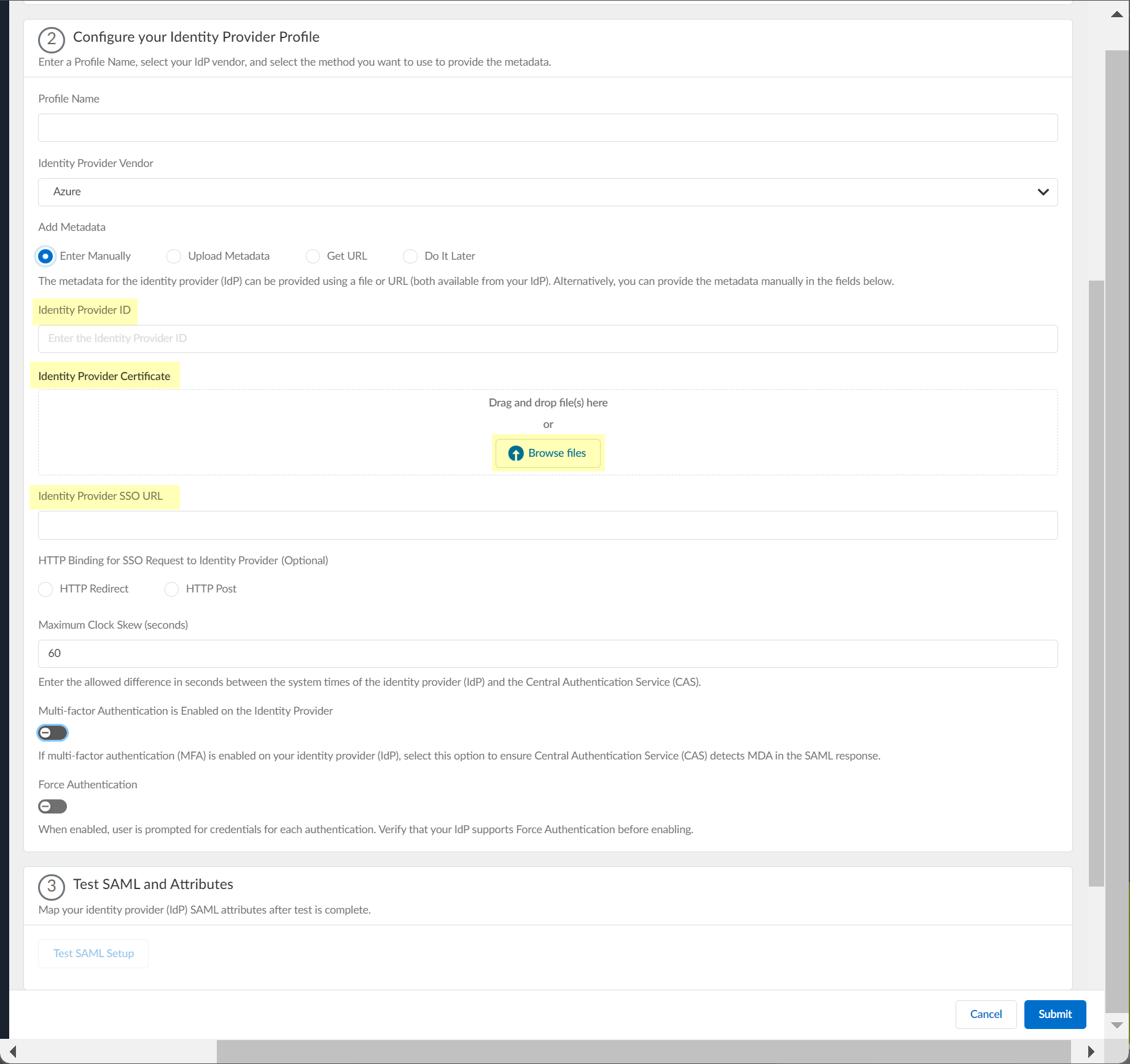
3. (Optional) Select the HTTP Binding for SSO Request to Identity Provider (Optional) method you want to use for the SAML binding that allows the firewall and IdP to exchange request and response messages:
- HTTP Redirect —Transmit SAML messages through URL parameters.
- HTTP Post —Transmit SAML messages using base64-encoded HTML.
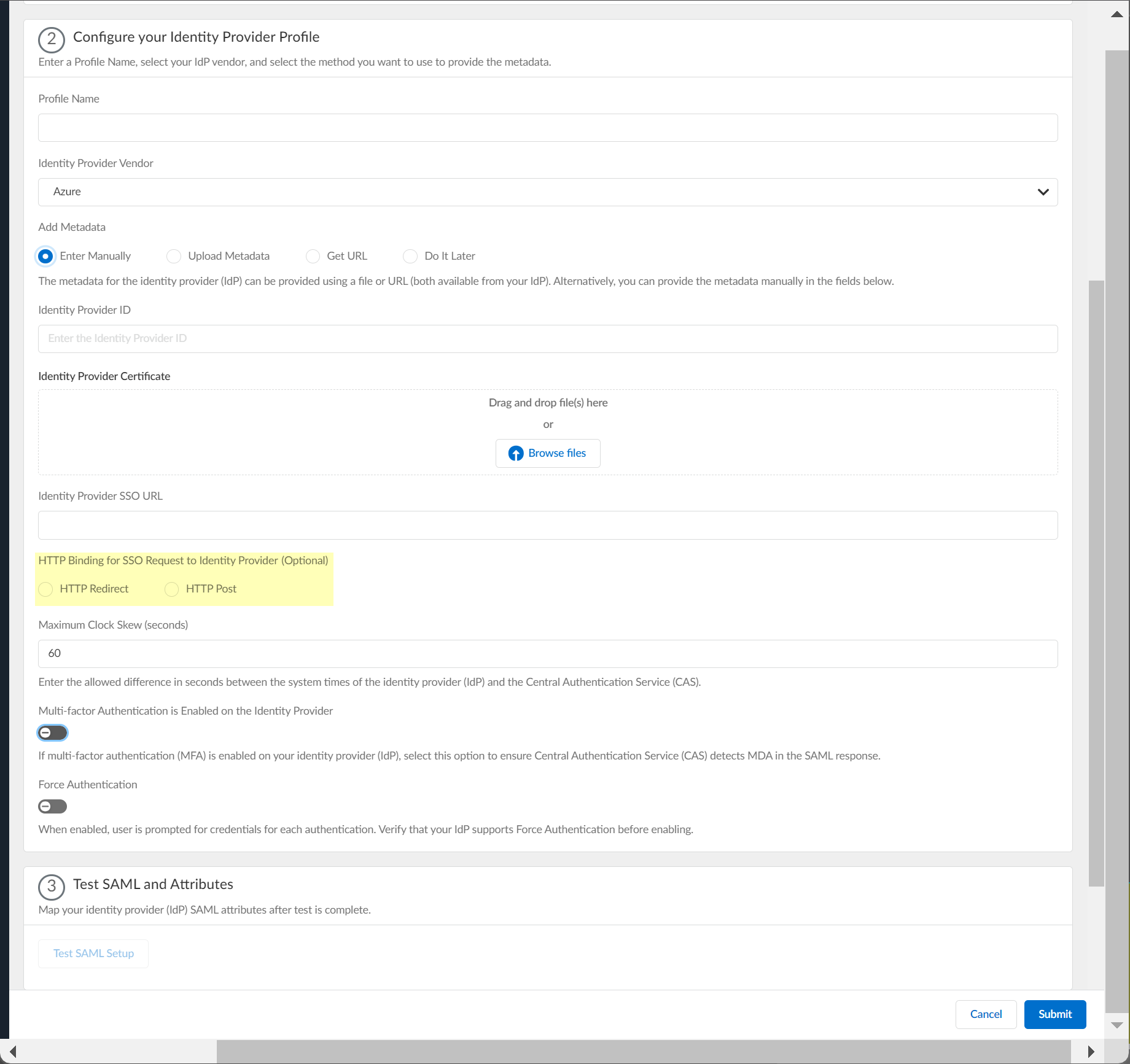
- If you want to upload a metadata file, download the metadata file from your IdP management system.
1. In the Azure Portal, Download the Federation Metadata XML and Save it to a secure location.
2. In the Cloud Identity Engine app, click Browse files to select the metadata file, then Open the metadata file.
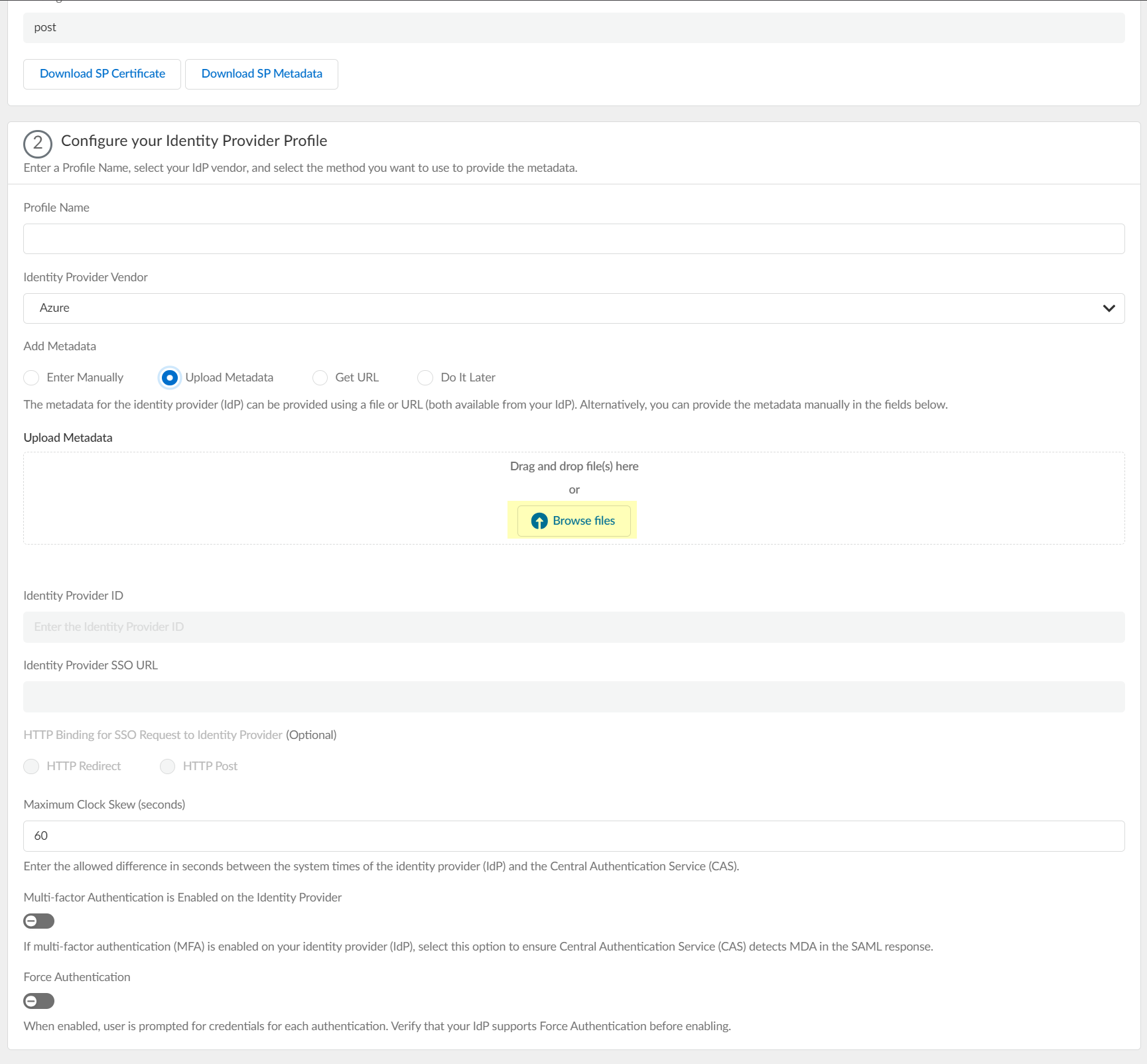
- If you want to use a URL to retrieve the metadata, copy the App Federation Metadata Url , then paste it in the profile as the Identity Provider Metadata URL and click Get URL to obtain the metadata.
Palo Alto Networks recommends using this method to configure Azure as an IdP.
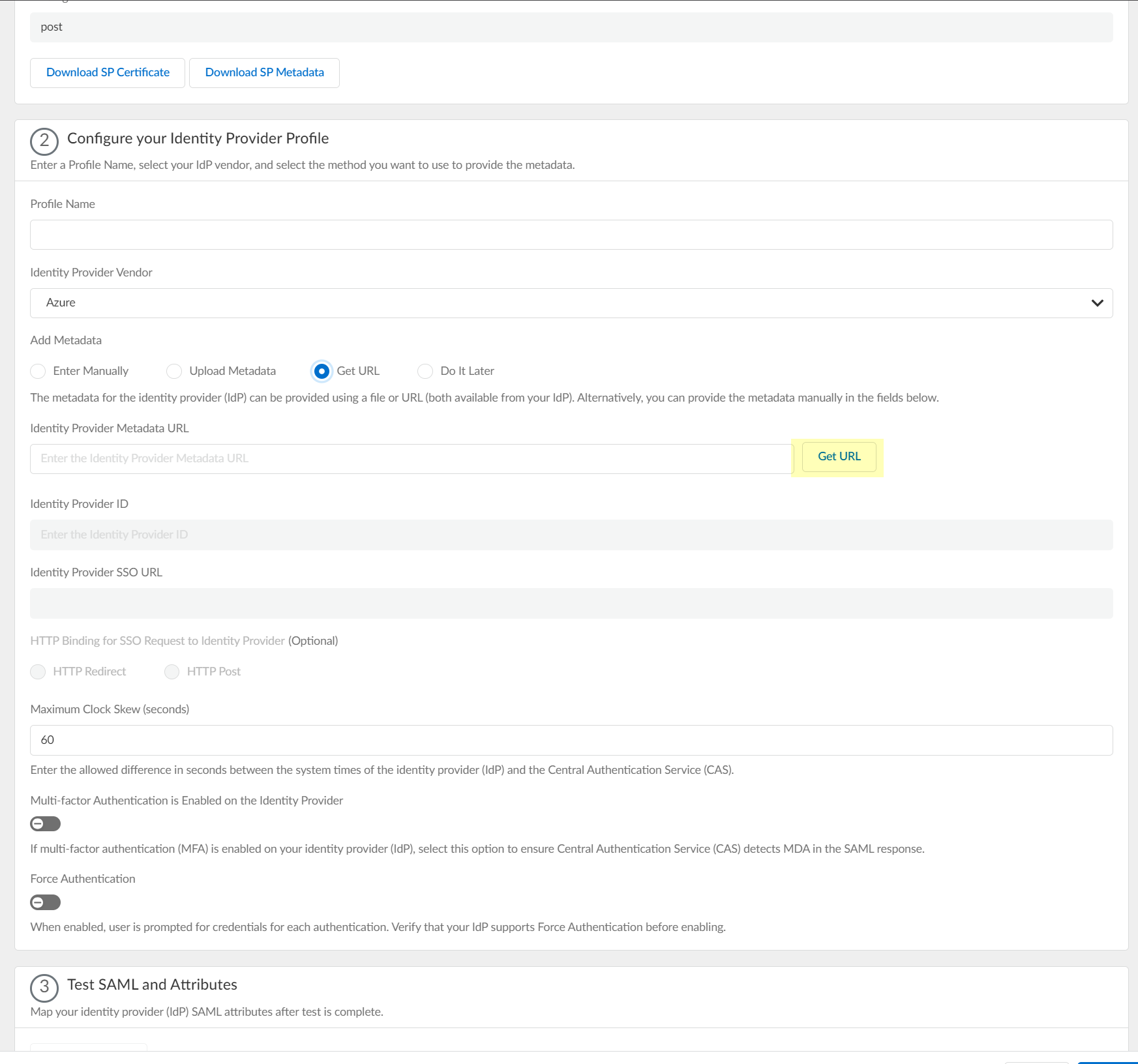
- If you don't want to enter the configuration information now, you can Do it later . This option allows you to submit the profile without including configuration information. However, you must edit the profile to include the configuration information to use the authentication type in an authentication profile.
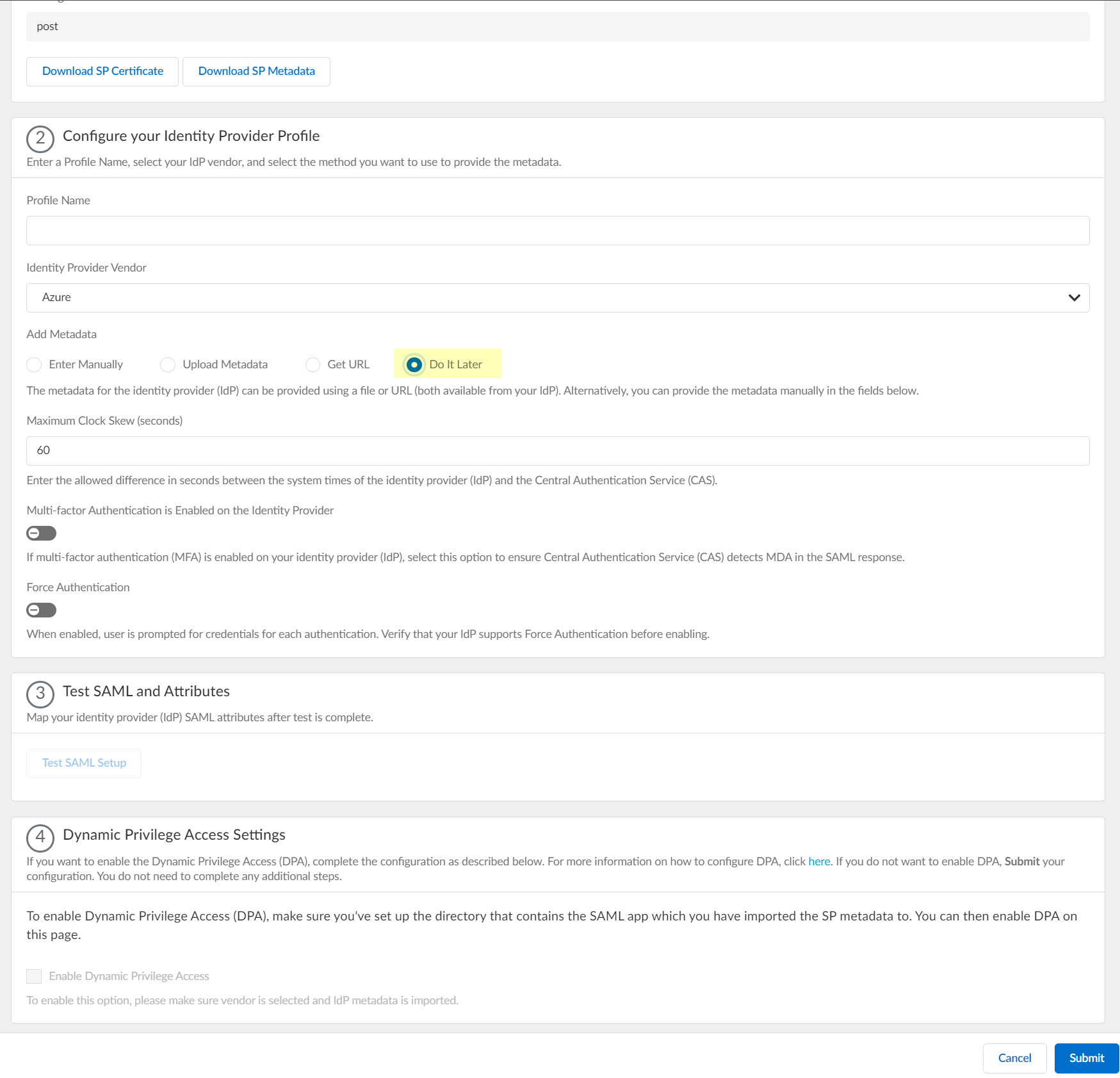
- Specify the Maximum Clock Skew (seconds) , which is the allowed difference in seconds between the system times of the IdP and the firewall at the moment when the firewall validates IdP messages (default is 60; range is 1–900). If the difference exceeds this value, authentication fails.
- Select Multi-factor Authentication is Enabled on the Identity Provider if your Azure configuration uses multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- To require users to log in using their credentials to reconnect to GlobalProtect, enable Force Authentication .
- Click Test SAML setup to verify the profile configuration.
This step is necessary to confirm that your firewall and IdP can communicate.
If you do not provide the vendor information, the SAML test passes so that you can still submit the configuration.
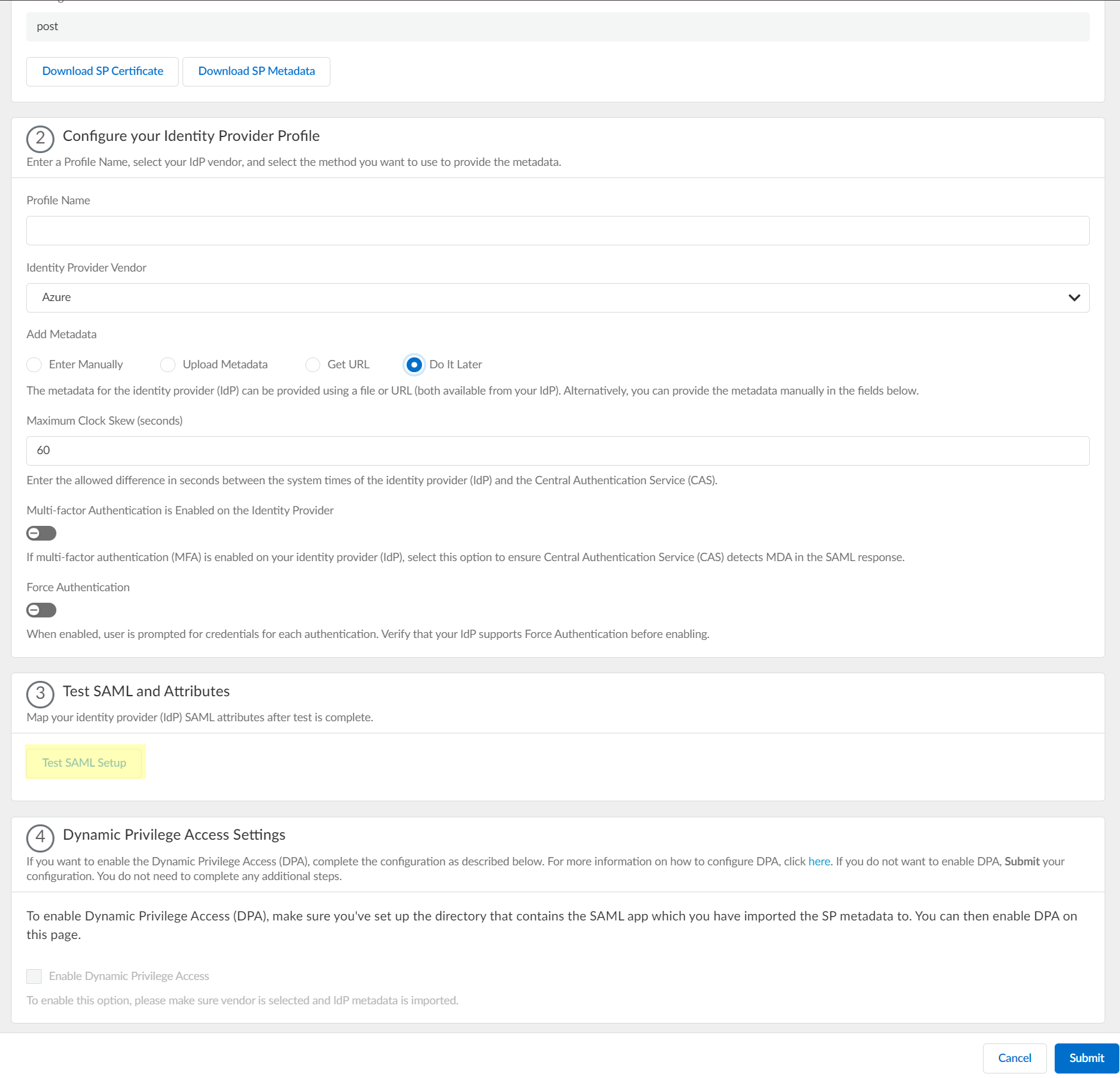
- Select the SAML attributes you want the firewall to use for authentication and Submit the IdP profile.
- In the Azure Portal, Edit the User Attributes & Claims .
- (Optional) In the Cloud Identity Engine app, enter the Username Attribute , Usergroup Attribute , Access Domain , User Domain , and Admin Role .
- Submit the profile.
- If you want to Enable Dynamic Privilege Access , ensure completion of the prerequisites before enabling this option, then Submit your changes to confirm the configuration.
For more information, refer to Configure Dynamic Privilege Access in the Cloud Identity Engine .
Configure Okta as an IdP in the Cloud Identity Engine
If you want to use Okta to authenticate users with the Cloud Identity Engine, there are two ways to configure Okta authentication with the Cloud Identity Engine:
- Integrate Okta as a Gallery Application
Recommended
- Integrate Okta as a Custom Application
- Select the method you want to use to integrate the Okta authentication in the Cloud Identity Engine and complete the steps in the Okta management console.
- Integrate Okta as a Gallery Application
Recommended
- Integrate Okta as a Custom Application
- Set up the Okta authentication in the Cloud Identity Engine.
1. If you have not already done so, activate the Cloud Identity Engine app.
2. In the Cloud Identity Engine app, select AuthenticationSP MetadataDownload SP Metadata and Save the metadata in a secure location.
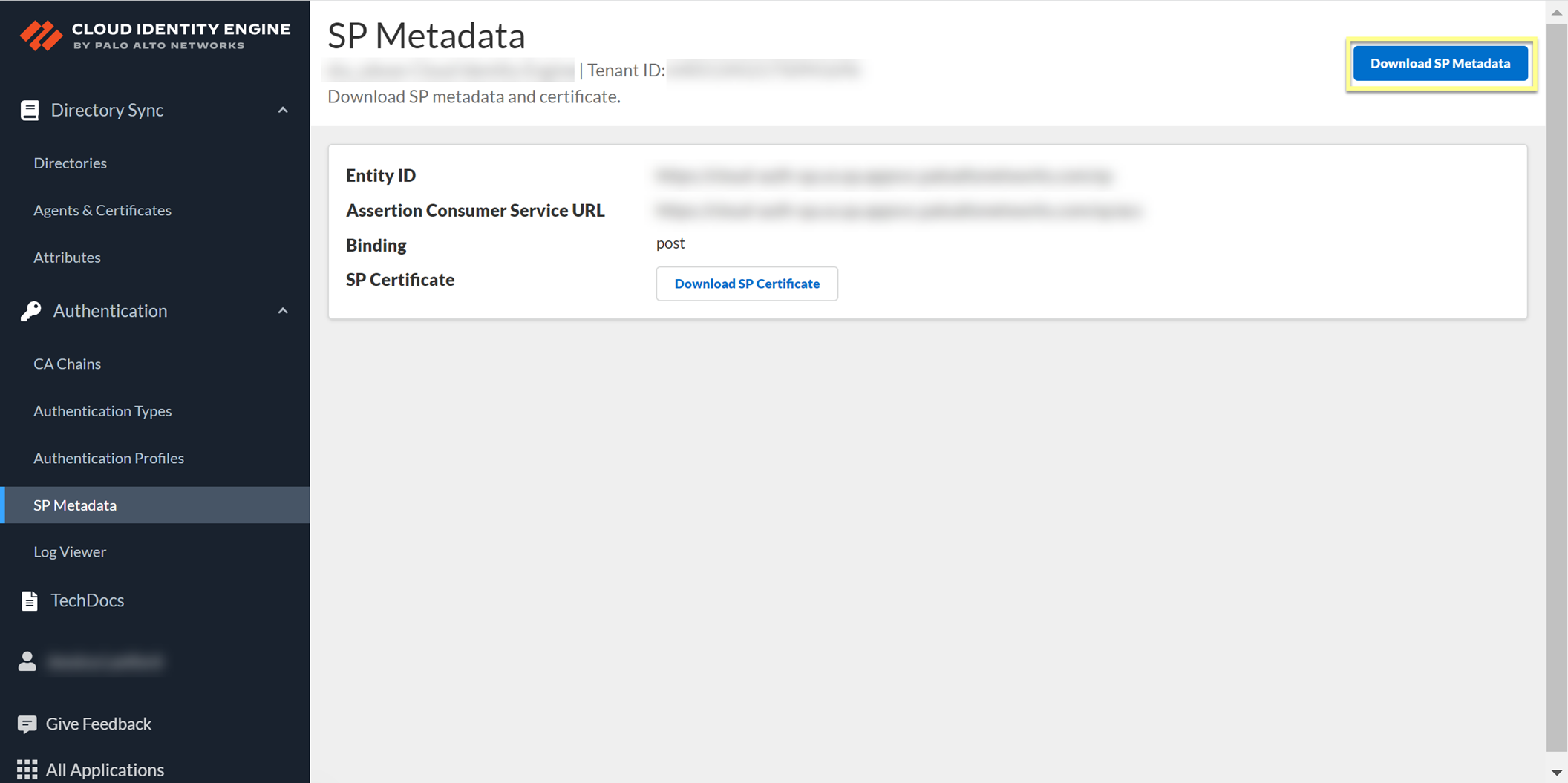
- Add Okta as an authentication type in the Cloud Identity Engine app.
1. Select Authentication Types and click Add New Authentication Type .
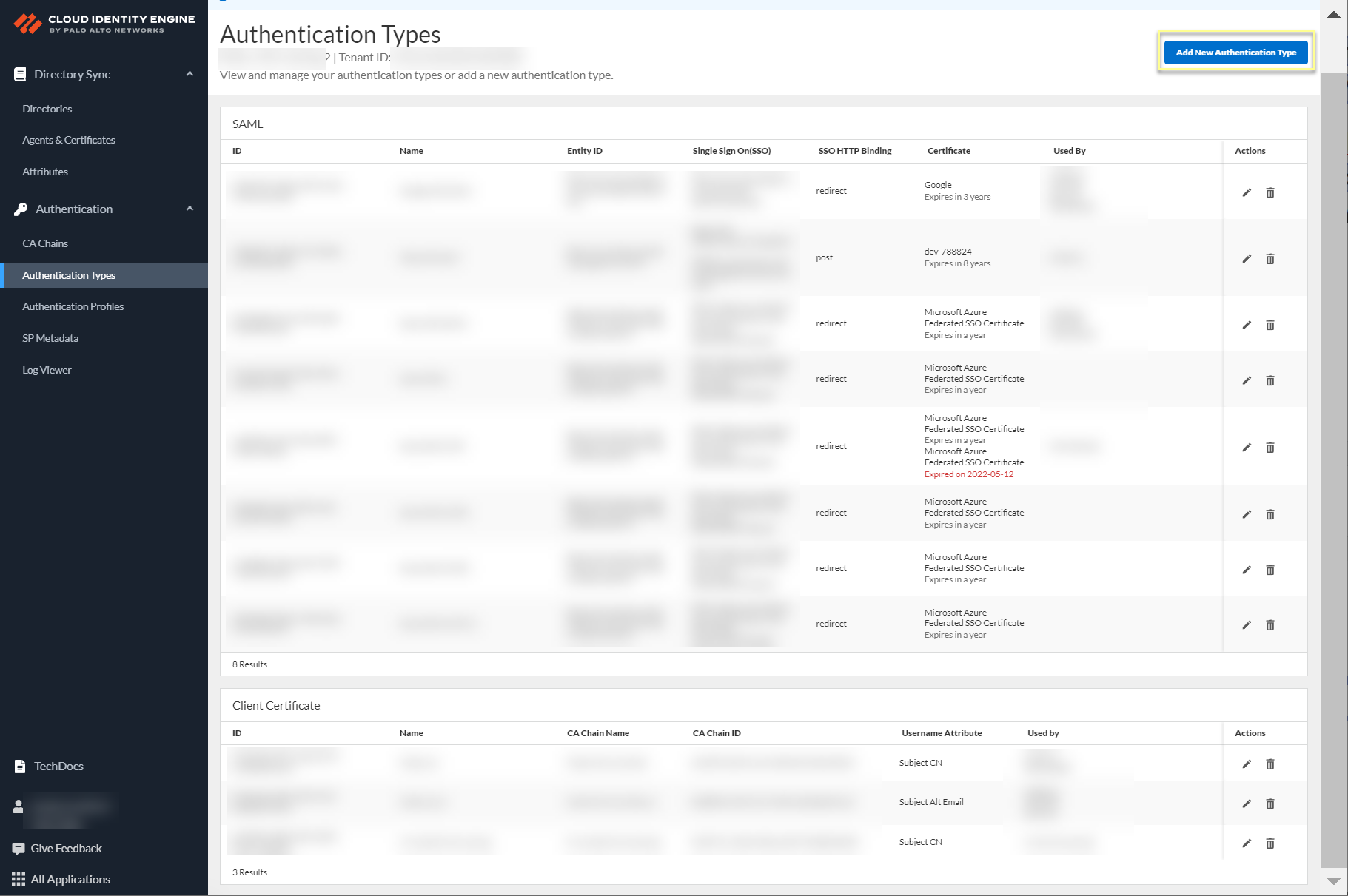
2. Set Up a SAML 2.0 authentication type.
3. Enter a Profile Name .
4. Select Okta as your Identity Provider Vendor .
- Select the method you want to use to Add Metadata and Submit the IdP profile.
- If you want to enter the information manually, copy the identity provider ID and SSO URL, download the certificate, then enter the information in the Cloud Identity Engine IdP profile.
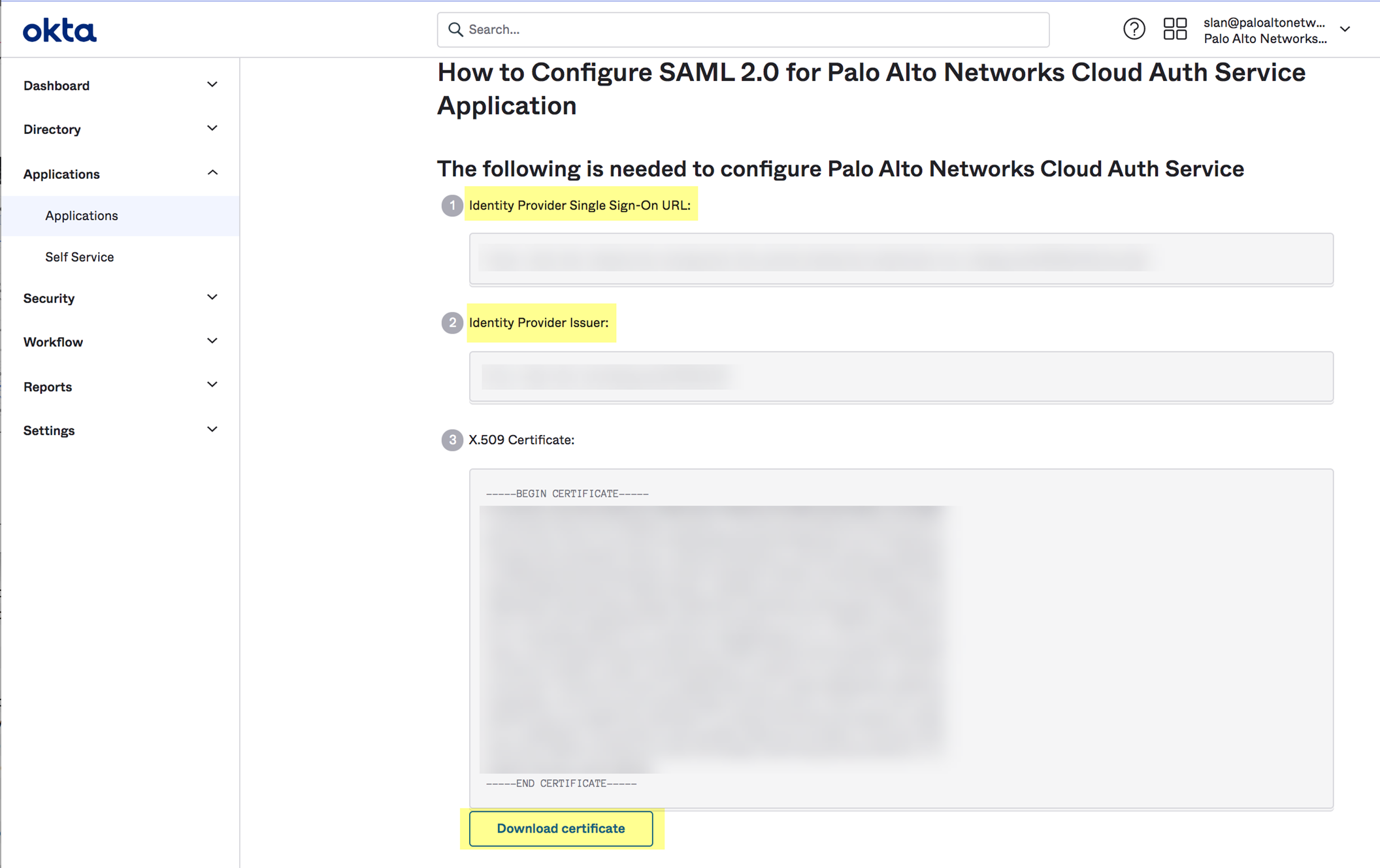
- In the Okta Admin Console, click Identity Provider metadata .
- Copy the necessary information from the Okta Admin Console and enter it in the IdP profile on the Cloud Identity Engine app as indicated in the following table:
|
Copy or Download from Okta Admin Console |
Enter in Cloud Identity Engine |
|
Copy the Identity Provider Issuer . |
Enter it as the Identity Provider ID . |
|
Download the X.509 Certificate . |
Click to Upload the certificate from the Okta Admin Console. |
|
Copy the Identity Provider Single Sign-On URL . |
Enter the URL as the Identity Provider SSO URL . |
-
- Select the HTTP Binding for SSO Request to IdP method you want to use for the SAML binding that allows the firewall and IdP to exchange request and response messages:
- HTTP Redirect —Transmit SAML messages through URL parameters.
- HTTP Post —Transmit SAML messages using base64-encoded HTML.
- If you want to upload a metadata file, download the metadata file from your IdP management system.
- In the Okta Admin Console, click View Setup Info and copy the IDP metadata and save it to a secure location.
- In the Cloud Identity Engine app, click Browse Files to select the metadata file then Open the metadata file.
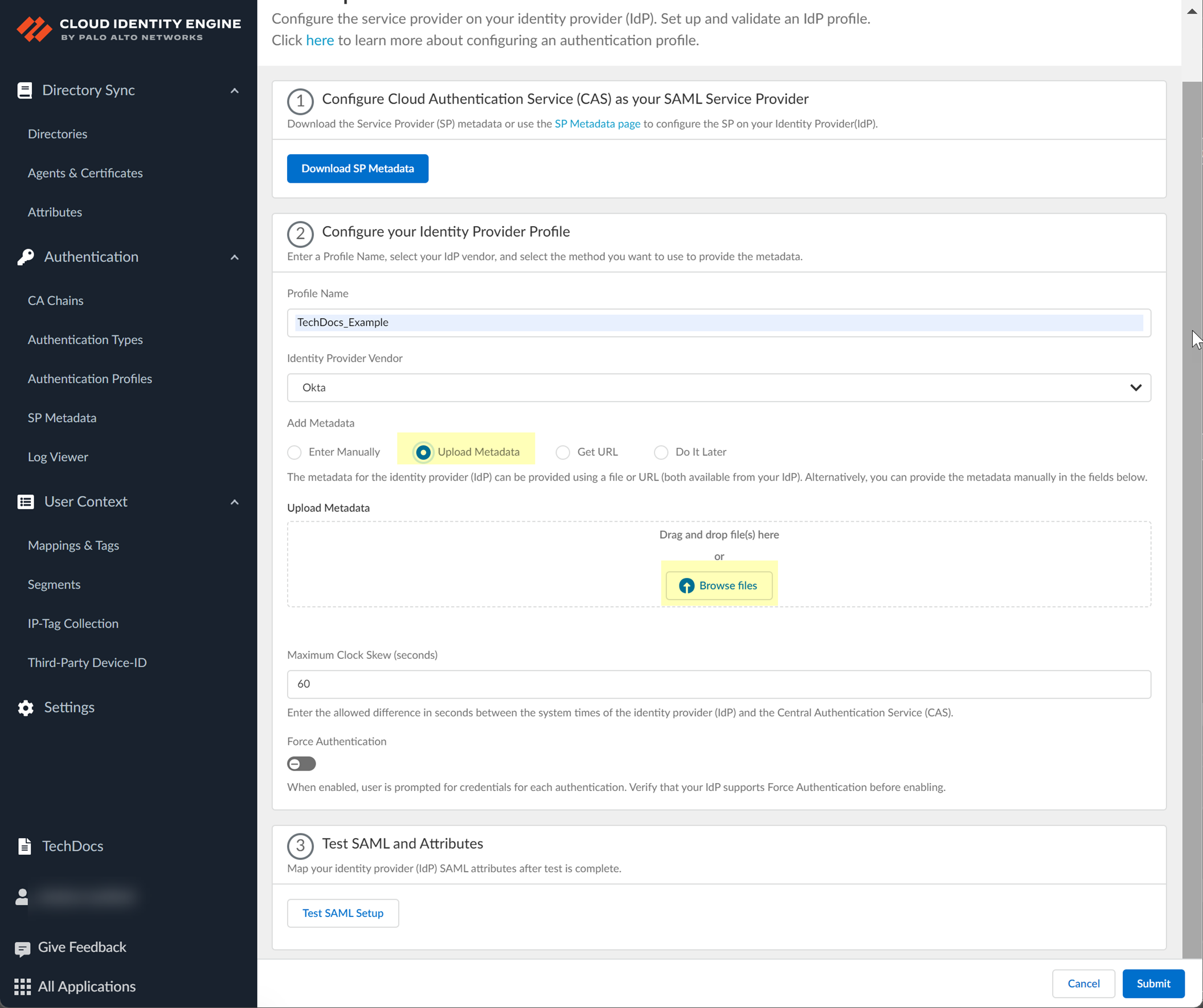
- If you want to use a URL to retrieve the metadata, copy the IDP metadata from step
4.2
. Paste it in the profile and click Get URL to obtain the metadata.
#id4126bb2e-0974-45b8-81da-c13f5db29908_li_l5n_bz5_3xb
- If you don't want to enter the configuration information now, you can Do it later . This option allows you to submit the profile without including configuration information. However, you must edit the profile to include the configuration information to use the authentication type in an authentication profile.
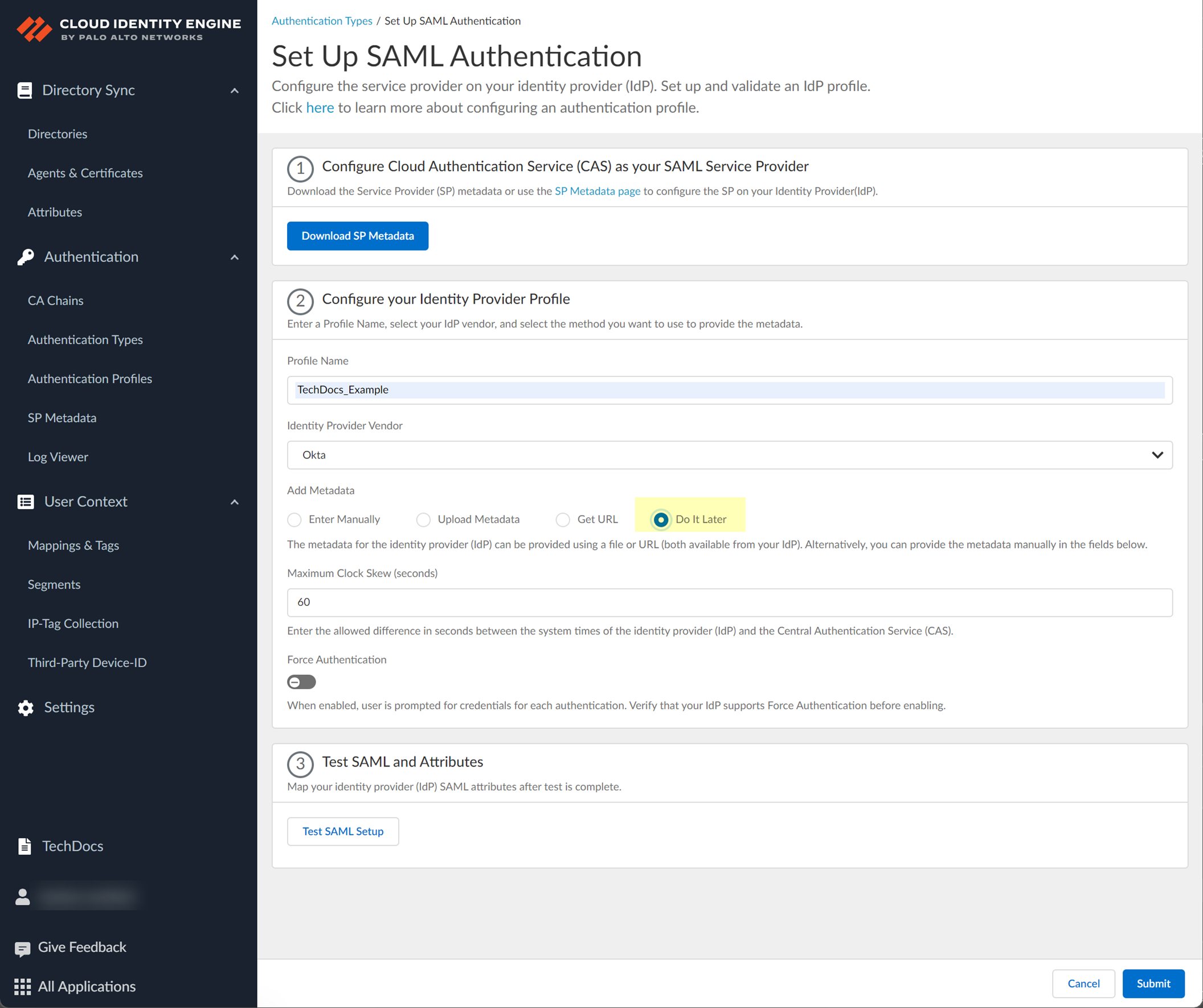
- Specify the Maximum Clock Skew (seconds) , which is the allowed difference in seconds between the system times of the IdP and the firewall at the moment when the firewall validates IdP messages (default is 60; range is 1–900). If the difference exceeds this value, authentication fails.
- To require users to log in using their credentials to reconnect to GlobalProtect, enable Force Authentication .
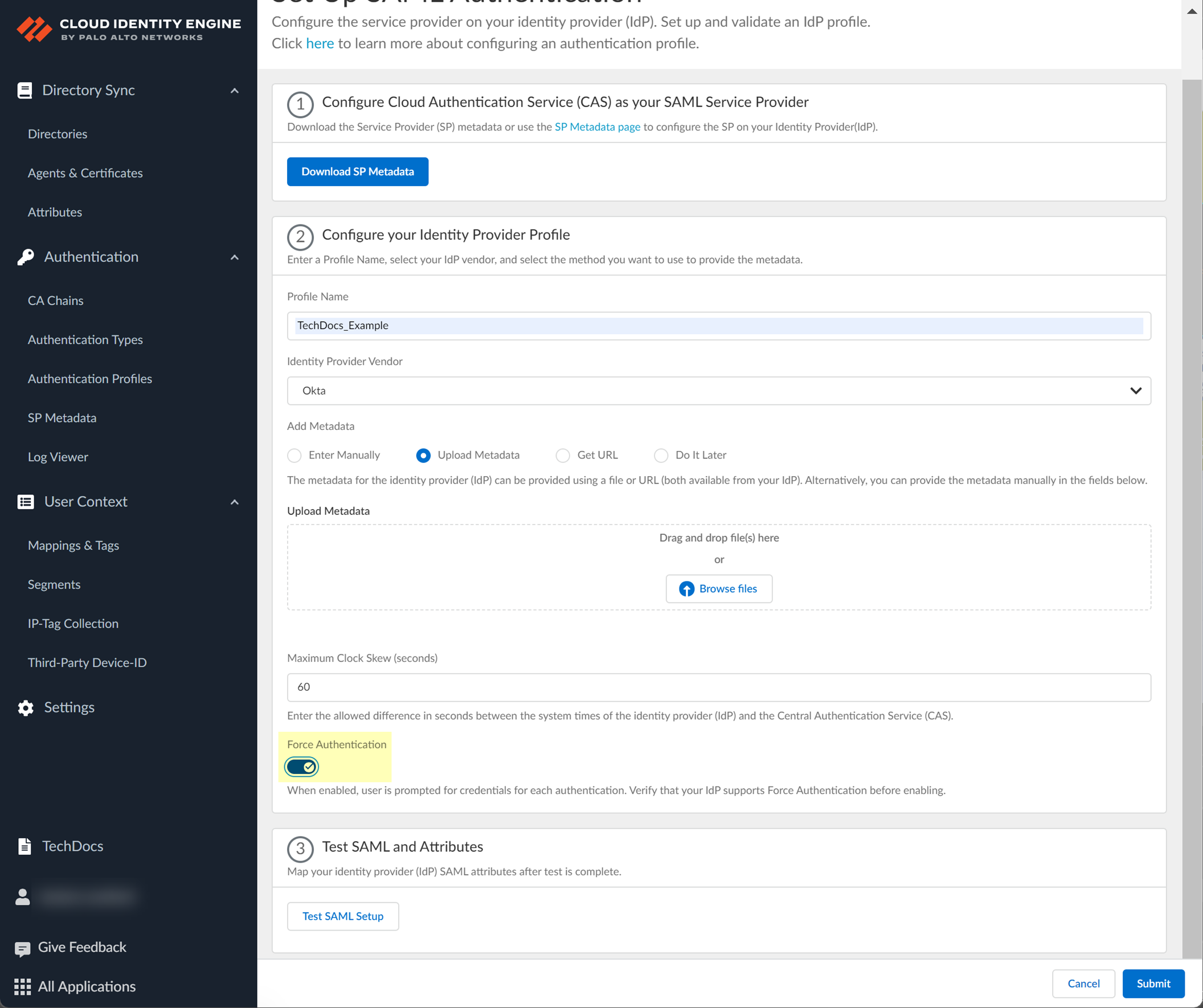
- Test SAML setup to verify the profile configuration.
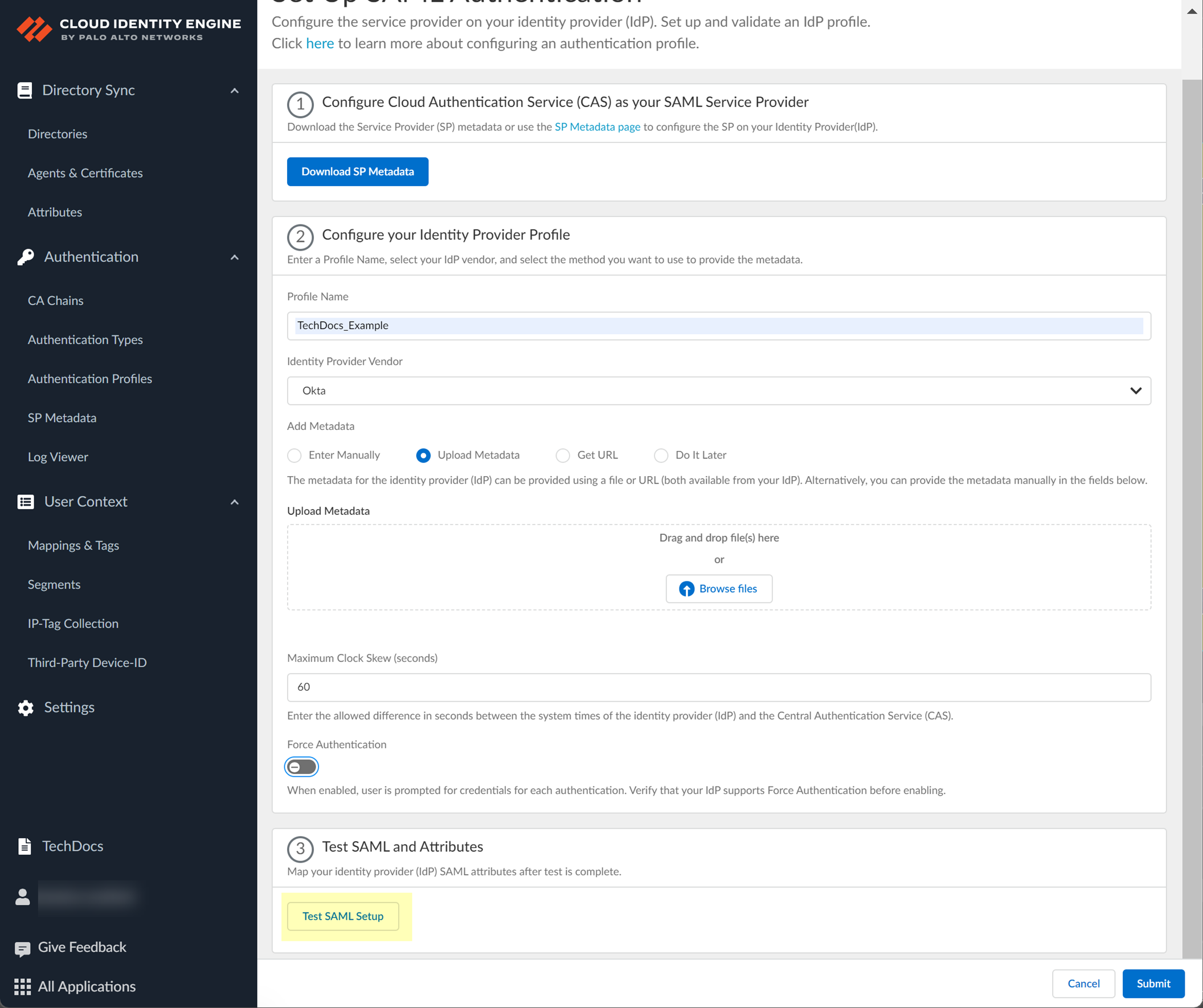
This step is necessary to confirm that your firewall and IdP can communicate.
- Select the SAML attributes you want the firewall to use for authentication and Submit the IdP profile.
You must select the username attribute in the Okta Admin Console for the attribute to display in the Cloud Identity Engine.
1. In the Okta Admin Console, Edit the User Attributes & Claims .
2. In the Cloud Identity Engine app, select the Username Attribute and optionally, the Usergroup Attribute , Access Domain , User Domain , and Admin Role .
If you're using the Cloud Identity Engine for SAML authentication with GlobalProtect Clientless VPN, you must configure the User Domain attribute to the same value as the userdomain field in the Okta Admin Console ( ApplicationsApplicationsSAML 2.0General ).

Integrate Okta as a Gallery Application
Palo Alto Networks strongly recommends that you integrate Okta in the Cloud Identity Engine as a gallery application. Complete the following steps to add and configure the Okta gallery application in the Cloud Identity Engine. Be sure to complete all the steps here and in the Okta documentation .
- Log in to the Okta Admin Console and select ApplicationsApplications .
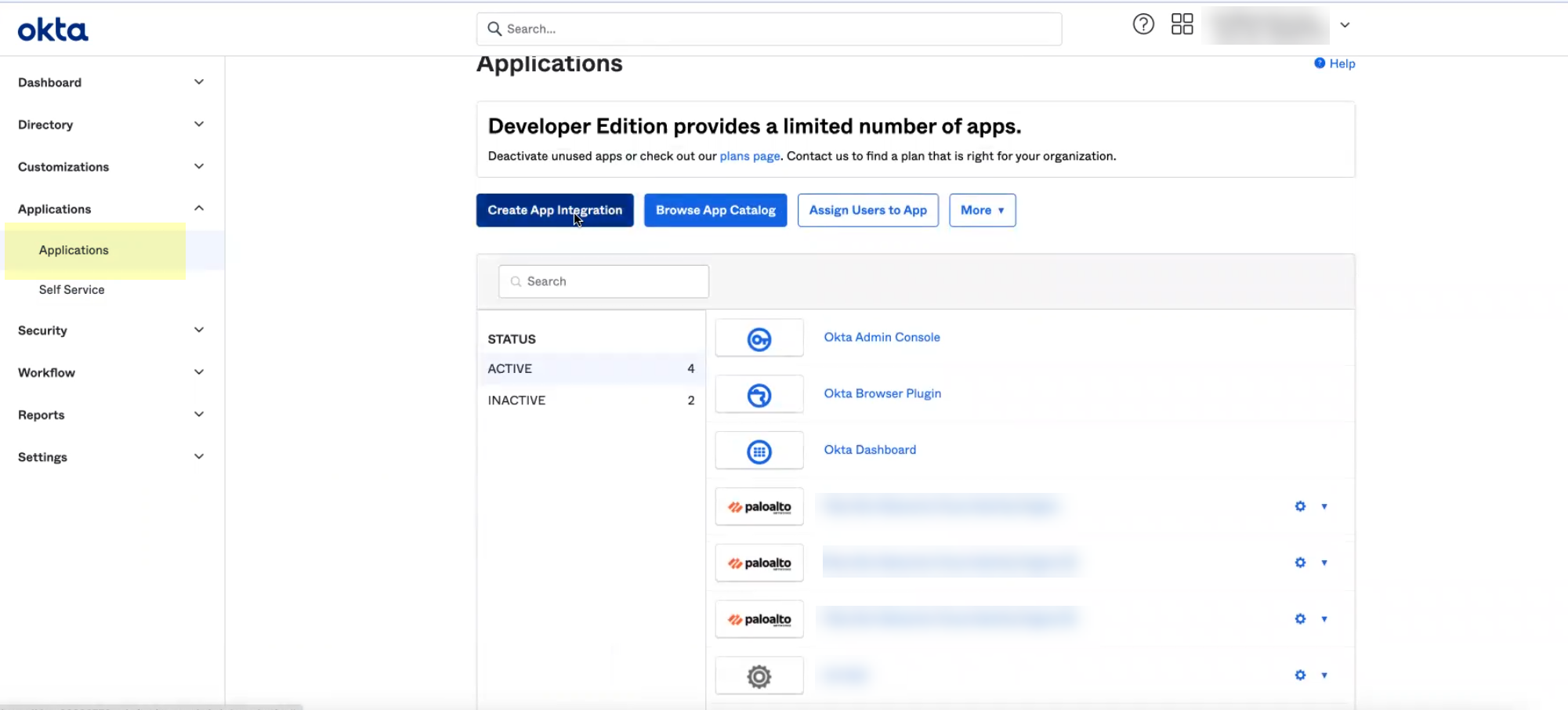
- Click Browse App Catalog .
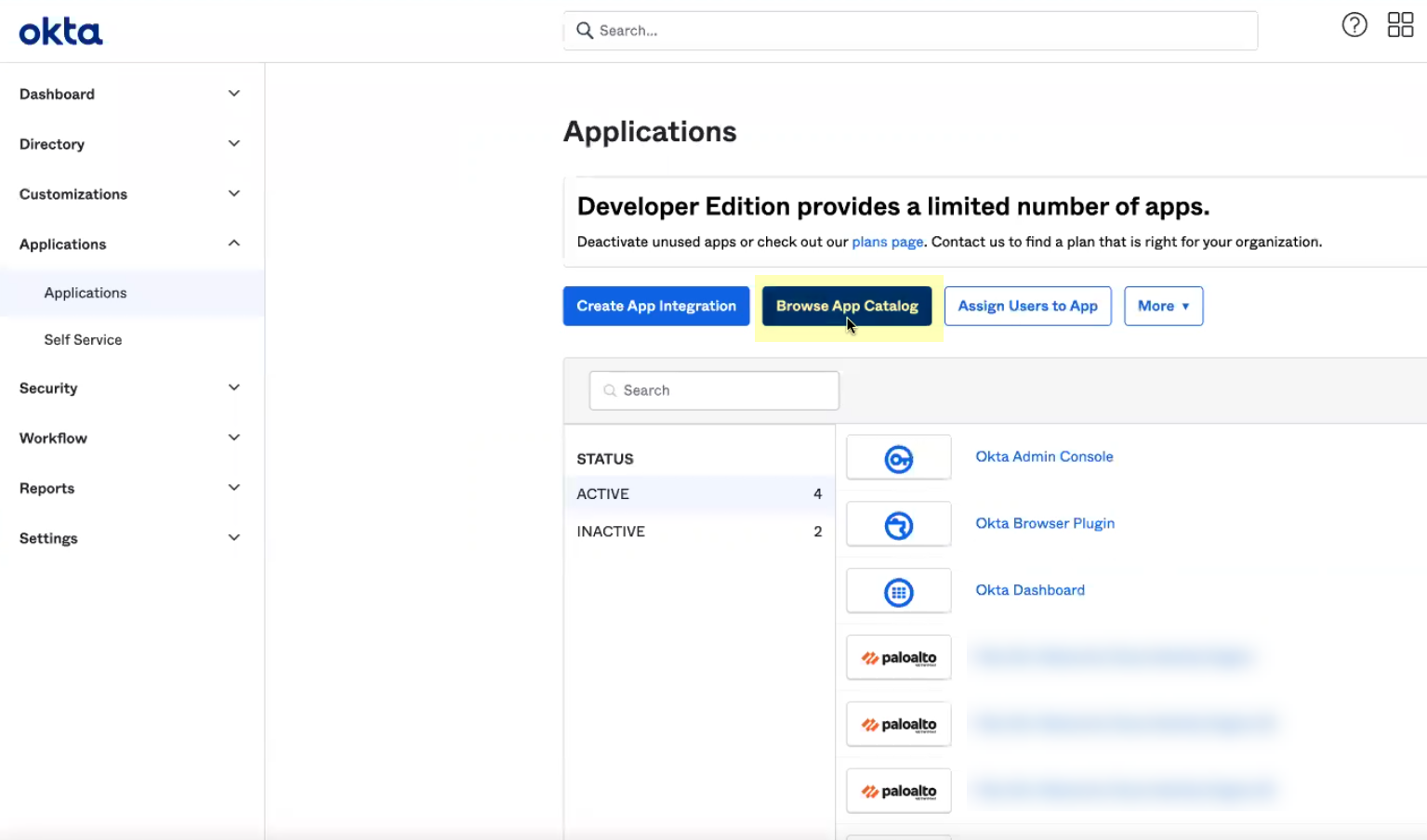
- Search for and select Palo Alto Networks Cloud Identity Engine .
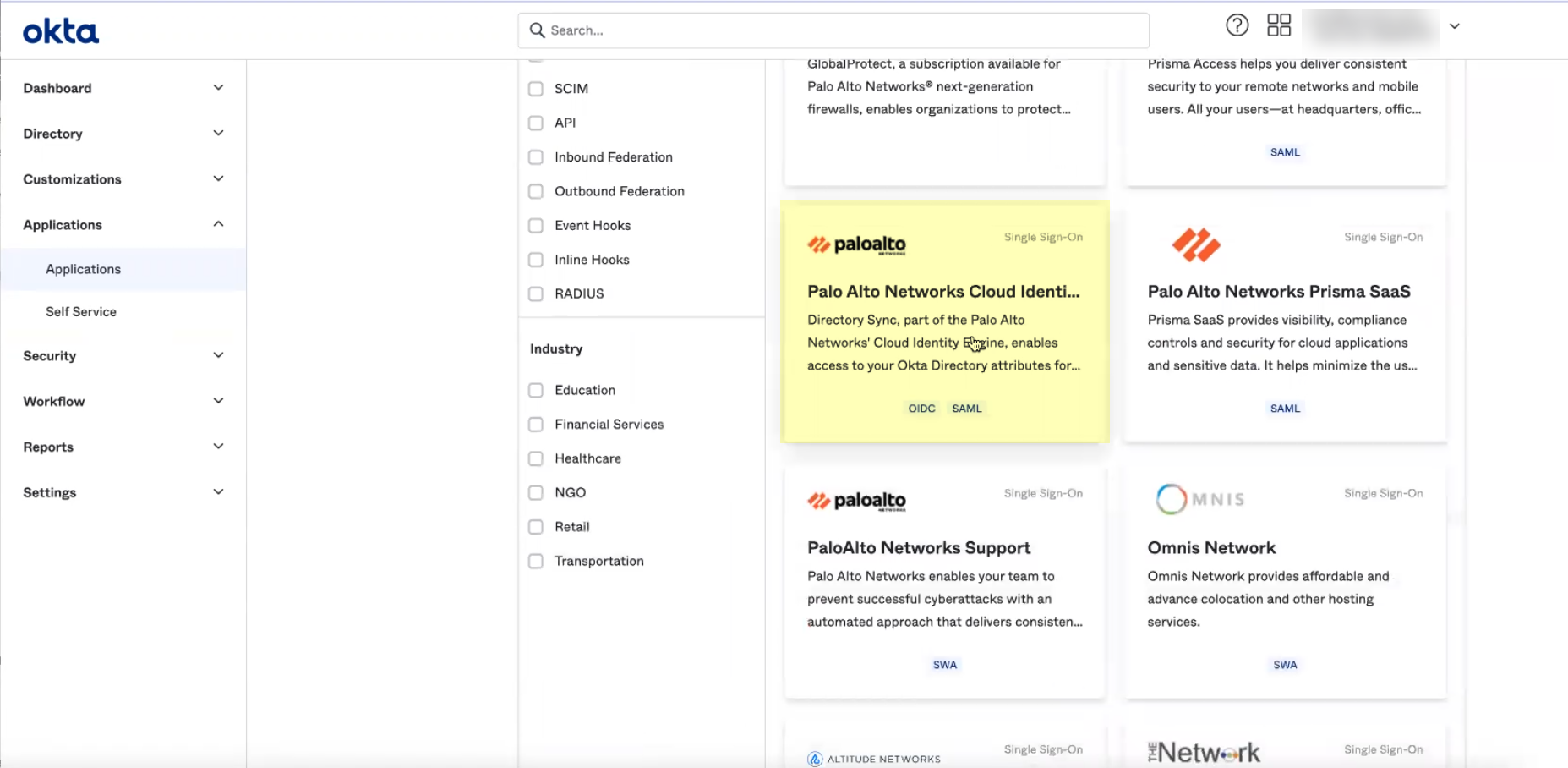
- Click Add Integration .
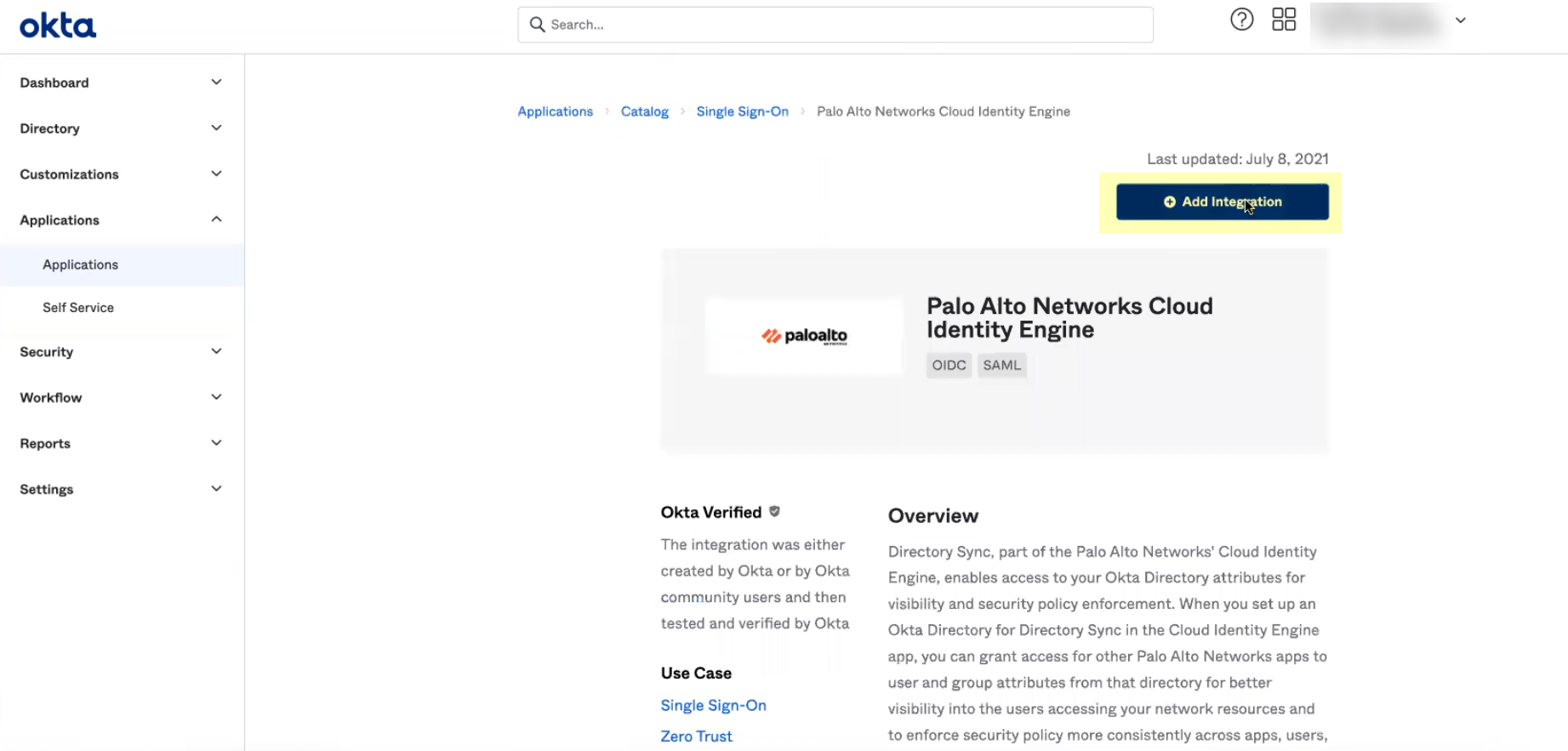
- Optionally edit the application name then click Next .
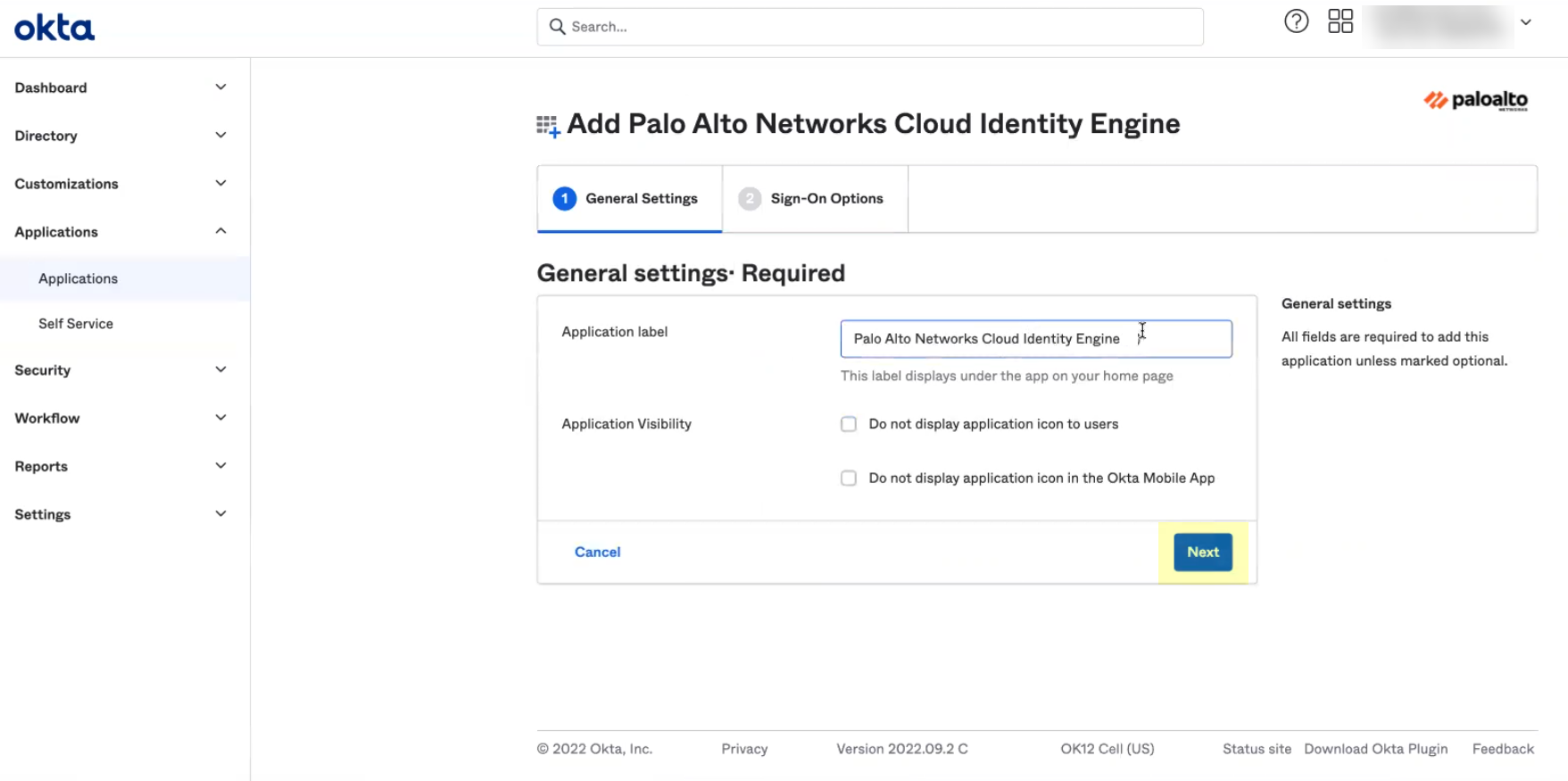
- Verify that SAML 2.0 is the sign-on option type.
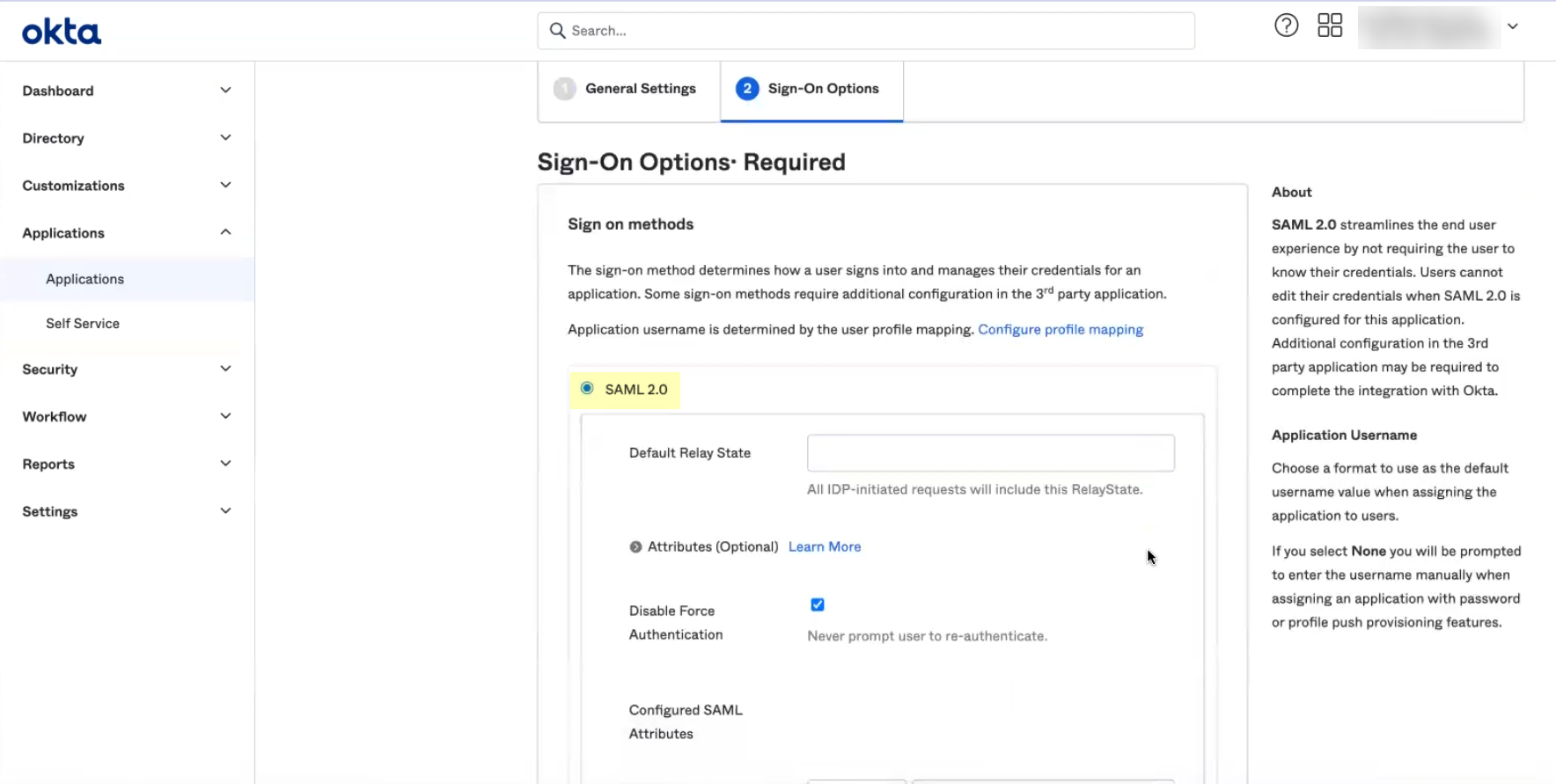
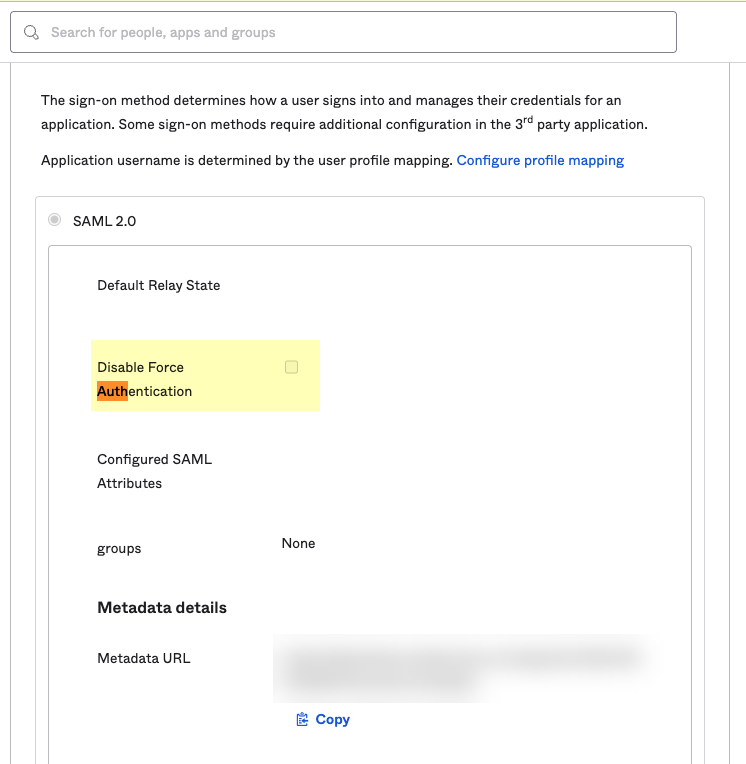
- If you enabled Force Authentication in step
6
, select Applications , select the app you created, select Sign-On , Edit the Settings , and uncheck Disable Force Authentication .
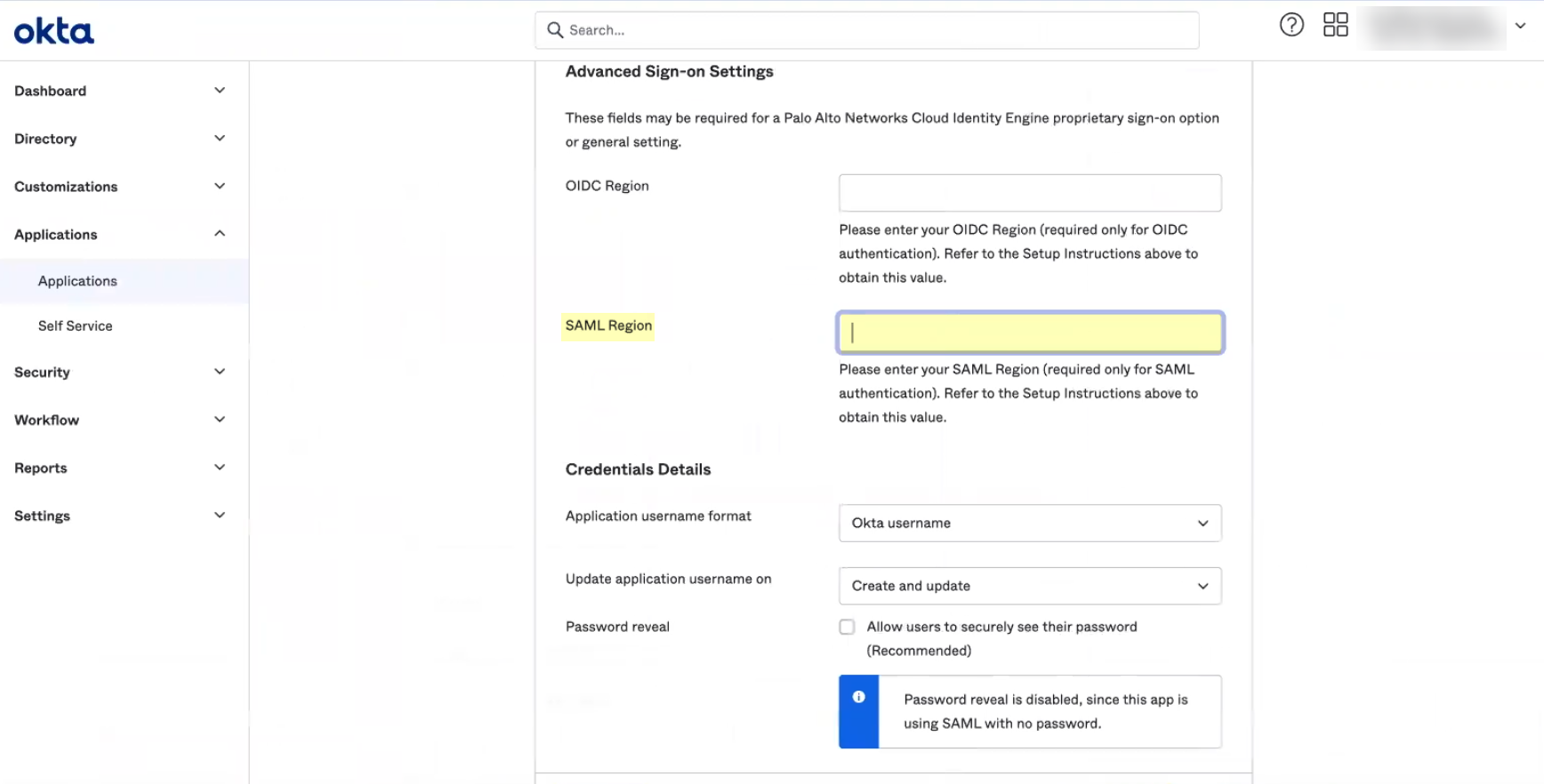
- Edit and paste the SAML Region .
The SAML Region is based on the Entity ID in the SP Metadata. To obtain the SAML Region, enter only the text between the backslash in the Entity ID and the paloaltonetworks.com domain. For example, if the Entity ID is https://cloud-auth.us.apps.paloaltonetworks.com/sp , the SAML Region is cloud-auth.us.apps .
- Select the Application username format that you want to use to authenticate the user. For example, Email represents the UserPrincipalName (UPN) format.
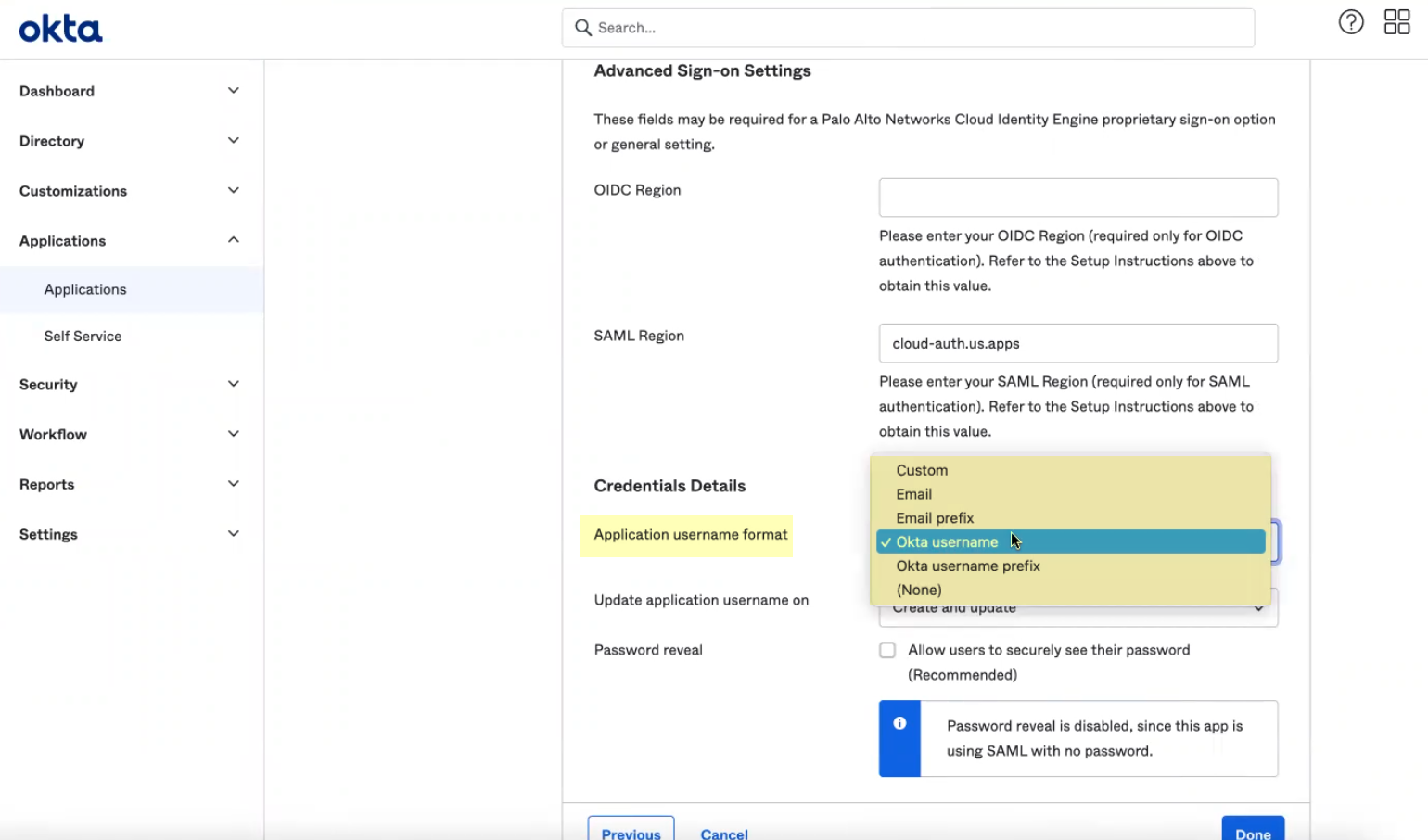
- Click Done .
- (Optional) If you want to configure other attributes in addition to the username, refer to the Okta documentation .
Integrate Okta as a Custom Application
Palo Alto Networks strongly recommends that you
Integrate Okta as a Gallery Application
. However, if you want to configure the Okta integration as a custom application, complete the following steps.
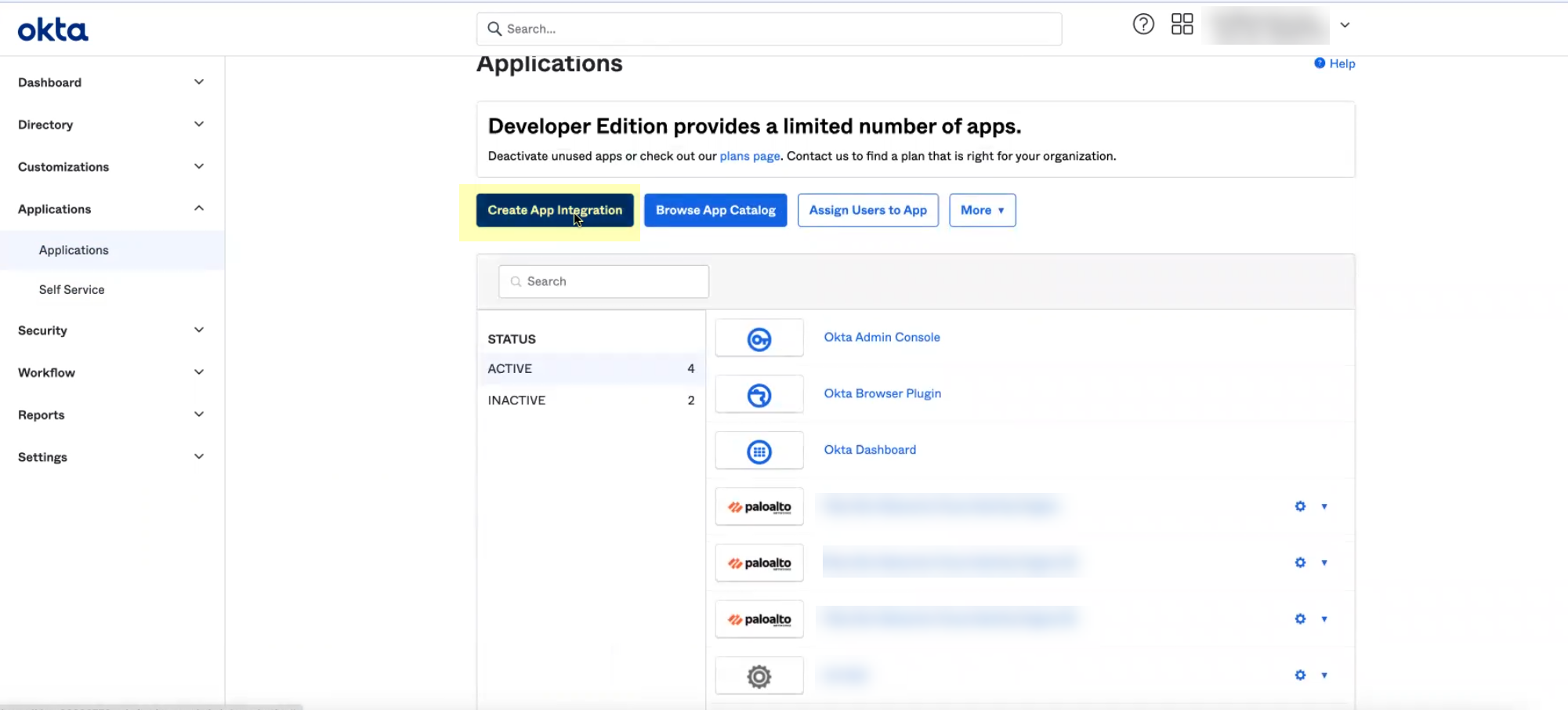
- Log in to the Okta Admin Console and select ApplicationsApplications .

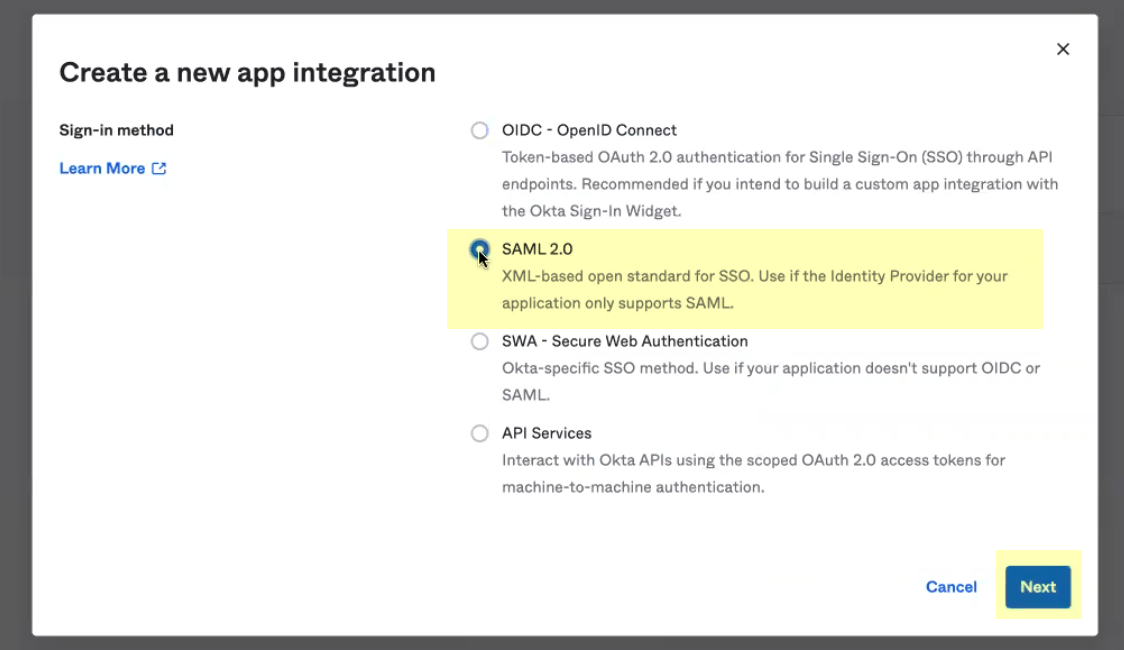
- Click Create App Integration .
- Verify that SAML 2.0 is the sign-on method then click Next .
- Enter an App name then click Next .
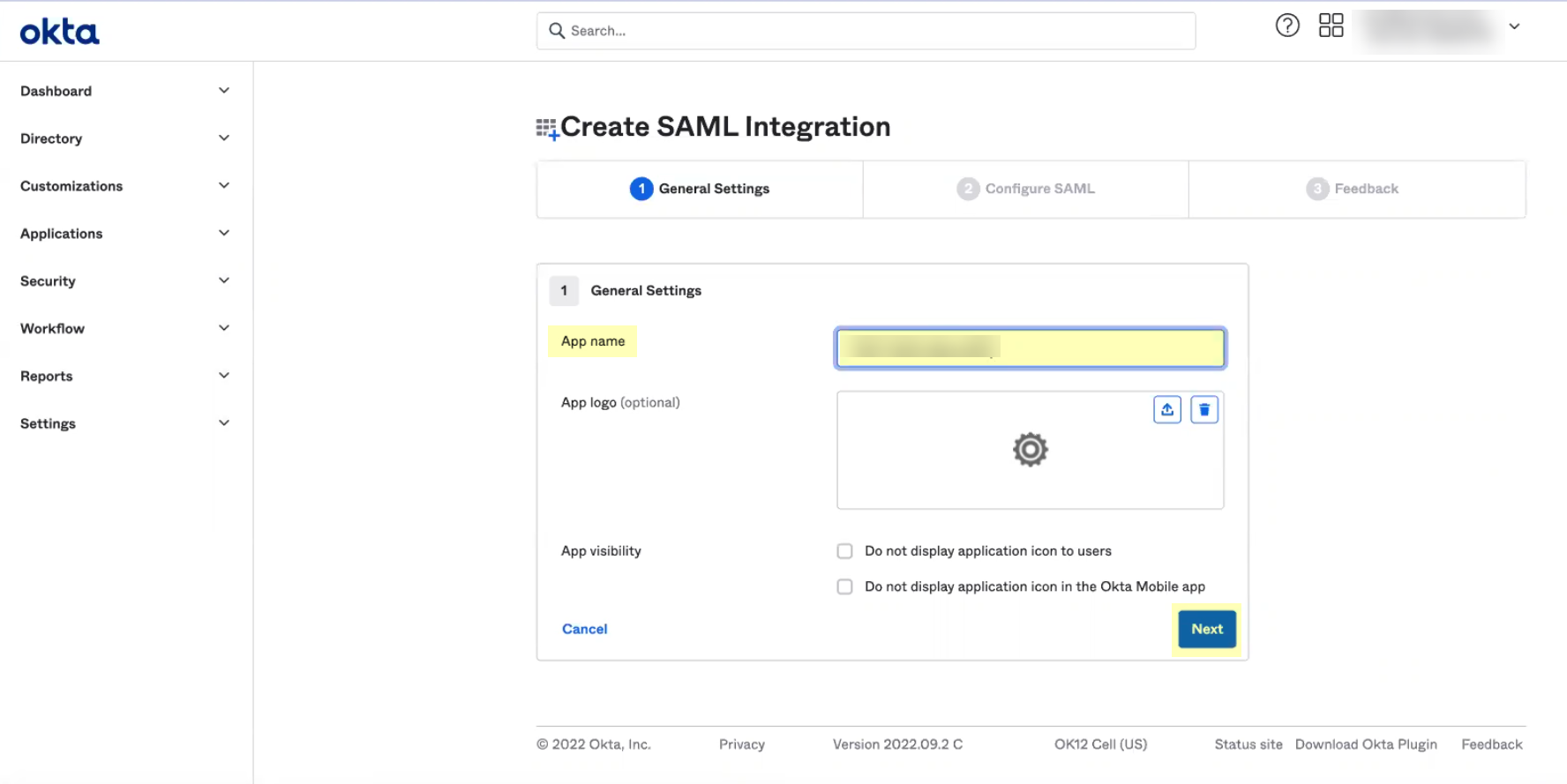
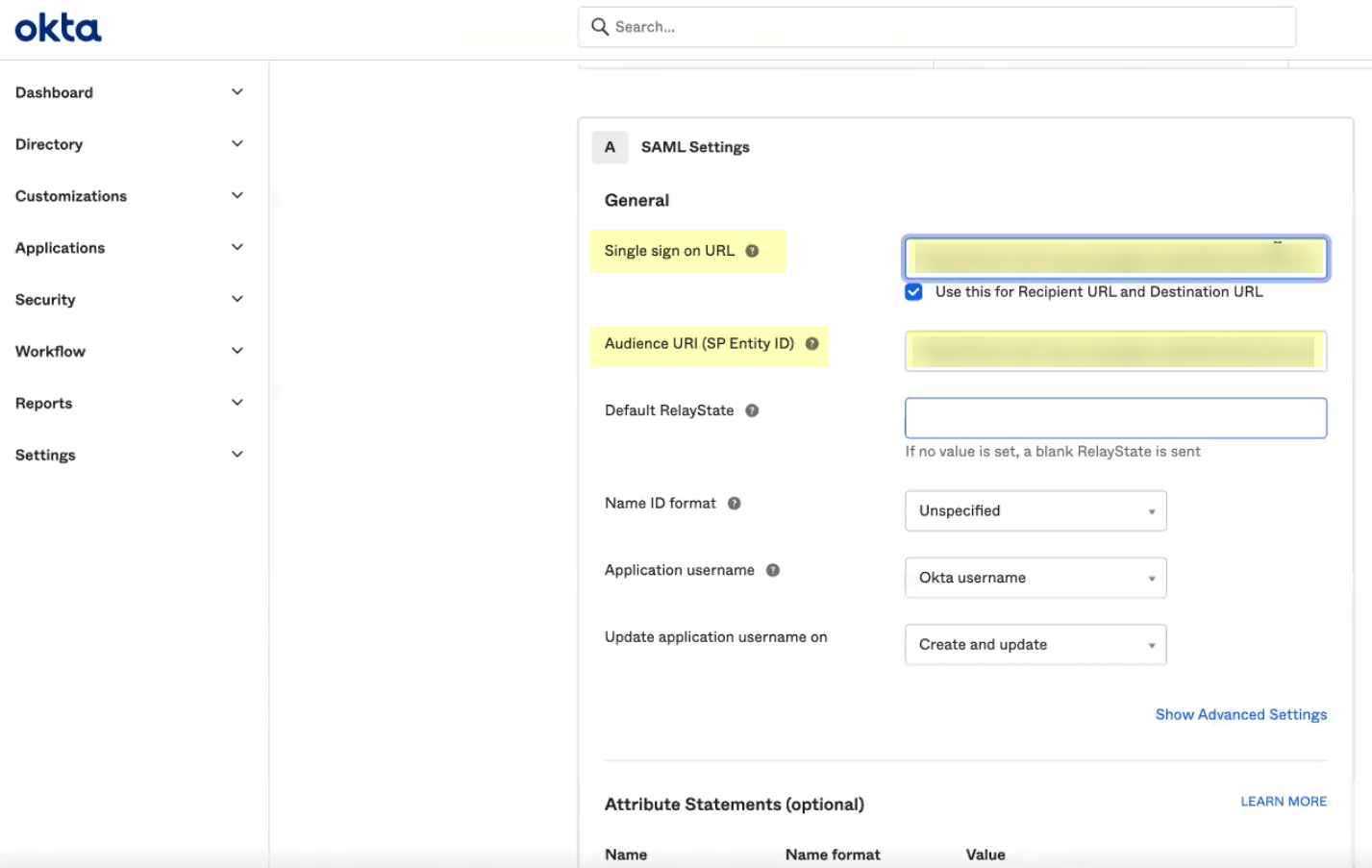
- Copy the SP Metadata information from the Cloud Identity Engine and enter it in the Okta Admin Console as described in the following table:
|
Copy from Cloud Identity Engine |
Enter in Okta Admin Console |
|
Copy the Entity ID from the SP Metadata page. |
Enter it as the Audience URI (SP Entity ID) . |
|
Copy the Assertion Consumer Service URL . |
Enter the URL as the Single sign on URL . |
-
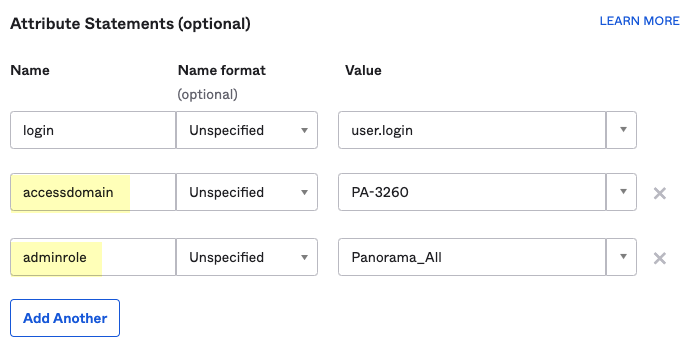
- ( Required for custom app ) Select a Value for the user attributes ( Attribute Statements (optional) ) and optionally enter a Filter for the group attributes ( Group Attribute Statements (optional) ) to specify the attribute formats.
You must configure at least one SAML attribute that contains identification information for the user (usually the username attribute) for the attributes to display in the Cloud Identity Engine. To configure administrator access, you must also enter values for the accessdomain attribute and for the adminrole attribute that match the values on the firewall.
- Click Next , specify whether you're a customer or partner, then click Finish .
- Click Add Rule to define a Sign On Policy that specifies which users and groups must authenticate with the Okta IdP using the Cloud Identity Engine.
- Select Assignments and Assign the users and groups that you require to authenticate using the Cloud Identity Engine. Save and Go Back to assign more users or groups.
Be sure to assign the account you're using so you can test the configuration when it's complete. You may need to refresh the page after adding accounts to successfully complete the test.
- Select Sign On and View Setup Instructions .
- Select the SAML attributes you want the firewall to use for authentication.
Configure PingOne as an IdP in the Cloud Identity Engine
Configure a profile to configure PingOne as an identity provider (IdP) in the Cloud Identity Engine. After you configure the IdP profile, Configure Cloud Identity Engine Authentication on the Firewall or Panorama .
- Enable the Cloud Identity Engine app in PingOne.
- If you have not already done so, activate the Cloud Identity Engine app.
- In the Cloud Identity Engine app, select AuthenticationSP MetadataDownload SP Metadata and Save the metadata in a secure location.
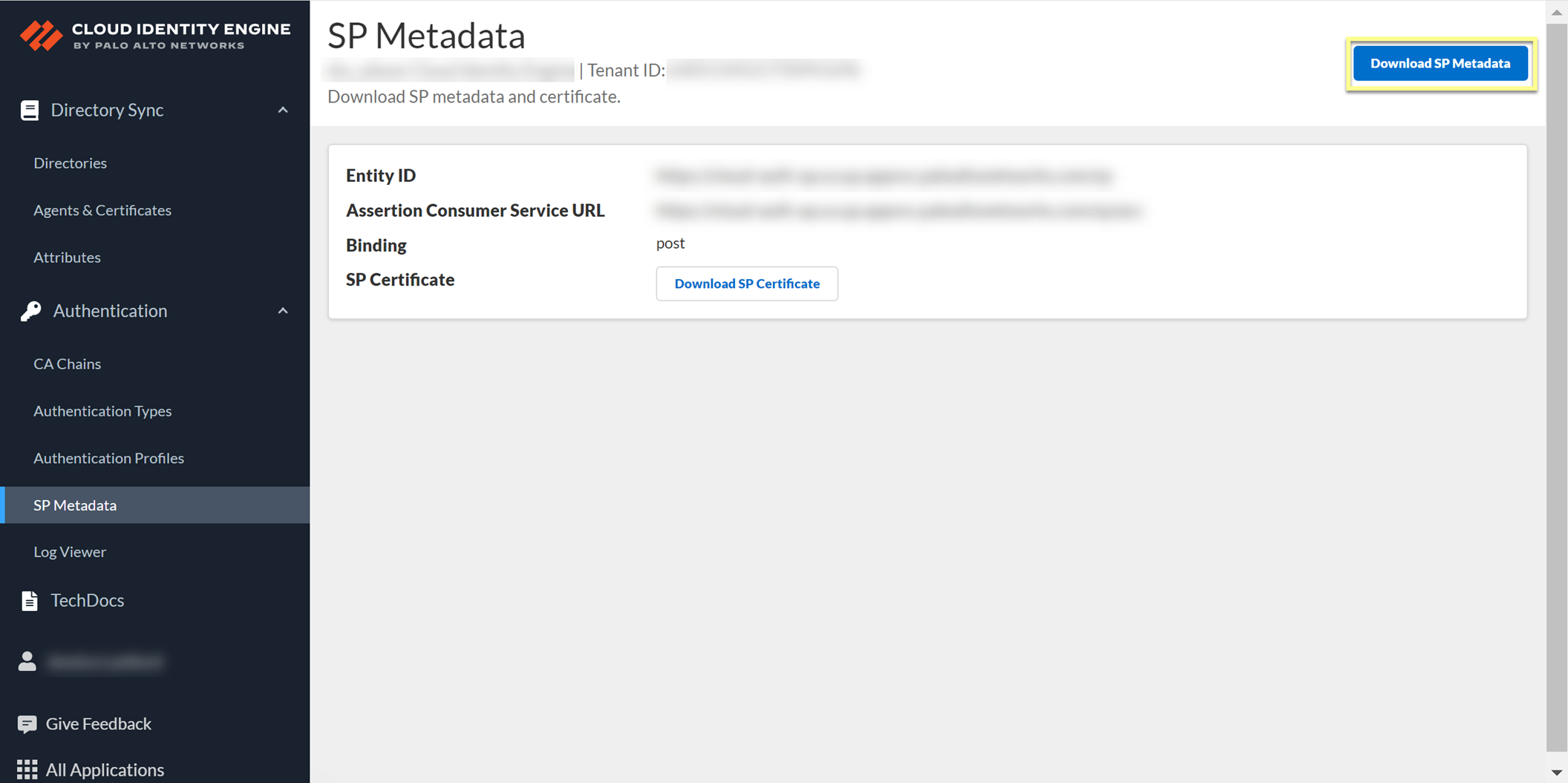
- Log in to PingOne and select ApplicationsMy ApplicationsAdd ApplicationNew SAML Application .
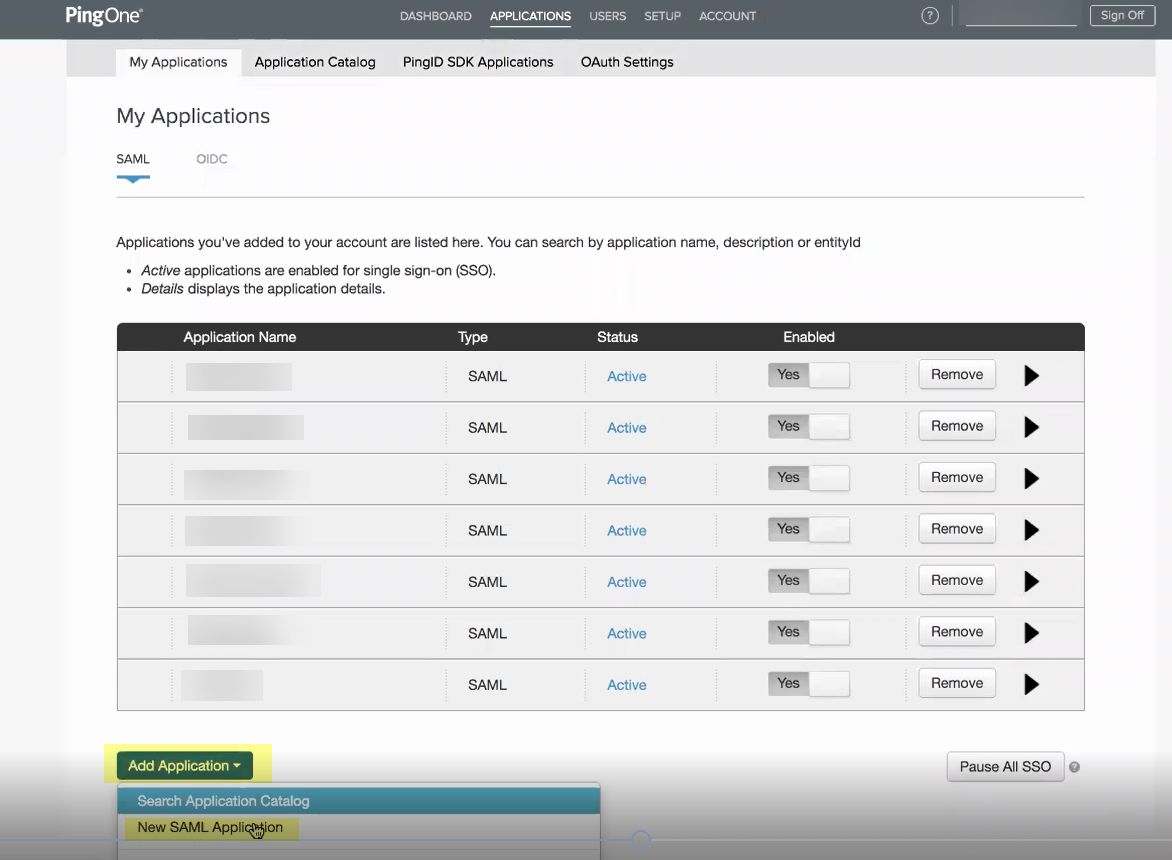
- Enter an Application Name , an Application Description , and select the Category then Continue to Next Step .
- Select I have the SAML configuration and ensure the Protocol Version is SAML v 2.0 .
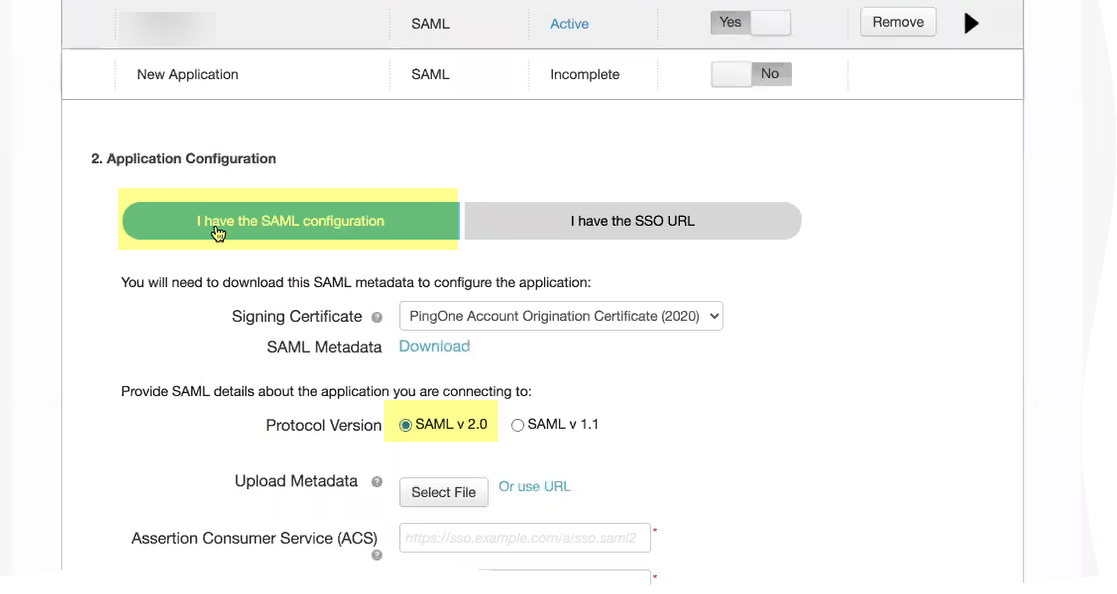
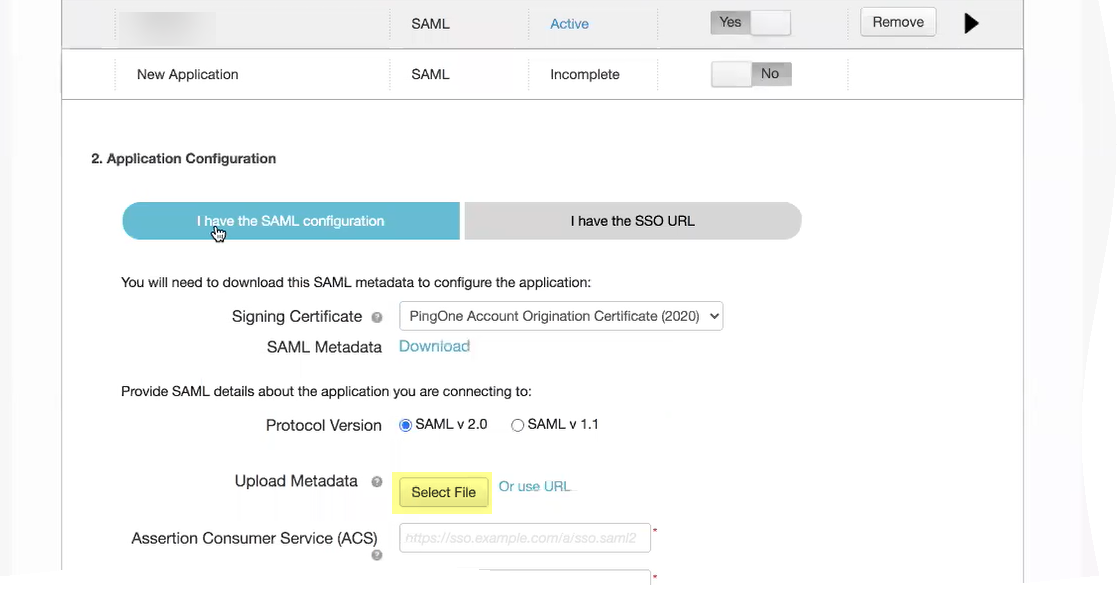
- Click Select File to Upload Metadata
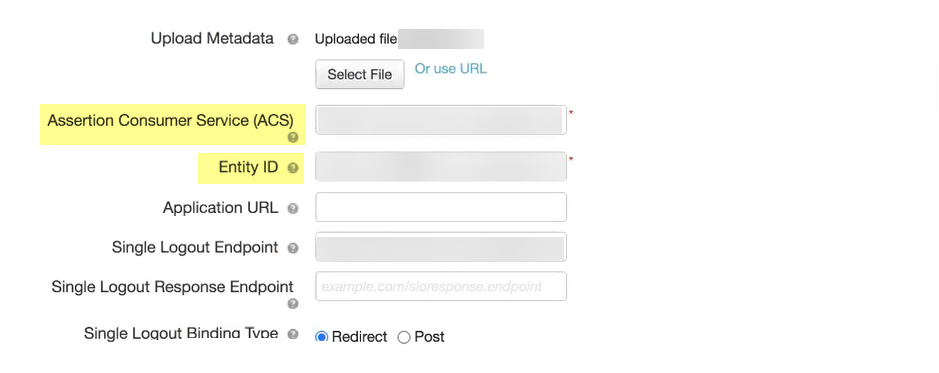
- Copy the metadata information from the Cloud Identity Engine and enter it in PingOne as described in the following table:
|
Copy from Cloud Identity Engine |
Enter in PingOne |
|
Copy the Entity ID from the SP Metadata page. |
Enter it as the Entity ID . |
|
Copy the Assertion Consumer Service URL . |
Enter the URL as the Assertion Consumer Service (ACS) . |
-
- Select either RSA_SHA384 or RSA_SHA256 as the Signing Algorithm .
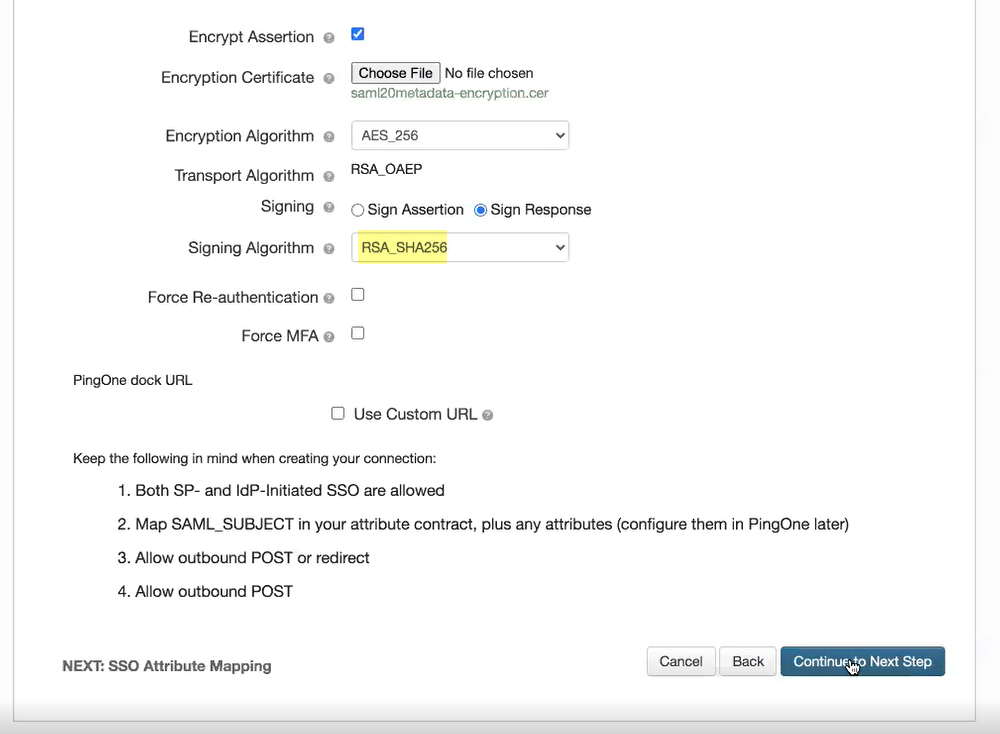
- If you want to require users to log in with their credentials to reconnect to GlobalProtect, select Force Re-authentication .
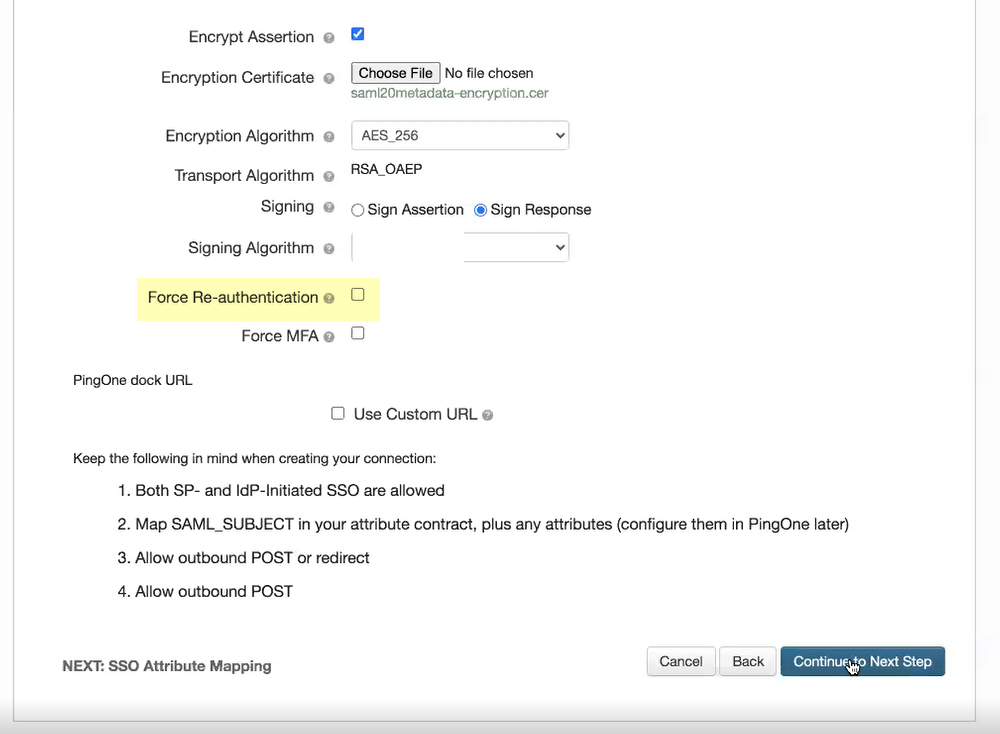
- (Required for MFA) If you want to require multi-factor authentication for your users, select Force MFA .
- Click Continue to Next Step to specify the attributes for the users you want to authenticate using PingOne.
- Specify the Application Attribute and the associated Identity Bridge Attribute or Literal Value for your user then select Required .
Be sure to assign the account you're using so you can test the configuration when it's complete. You may need to refresh the page after adding accounts to successfully complete the test.
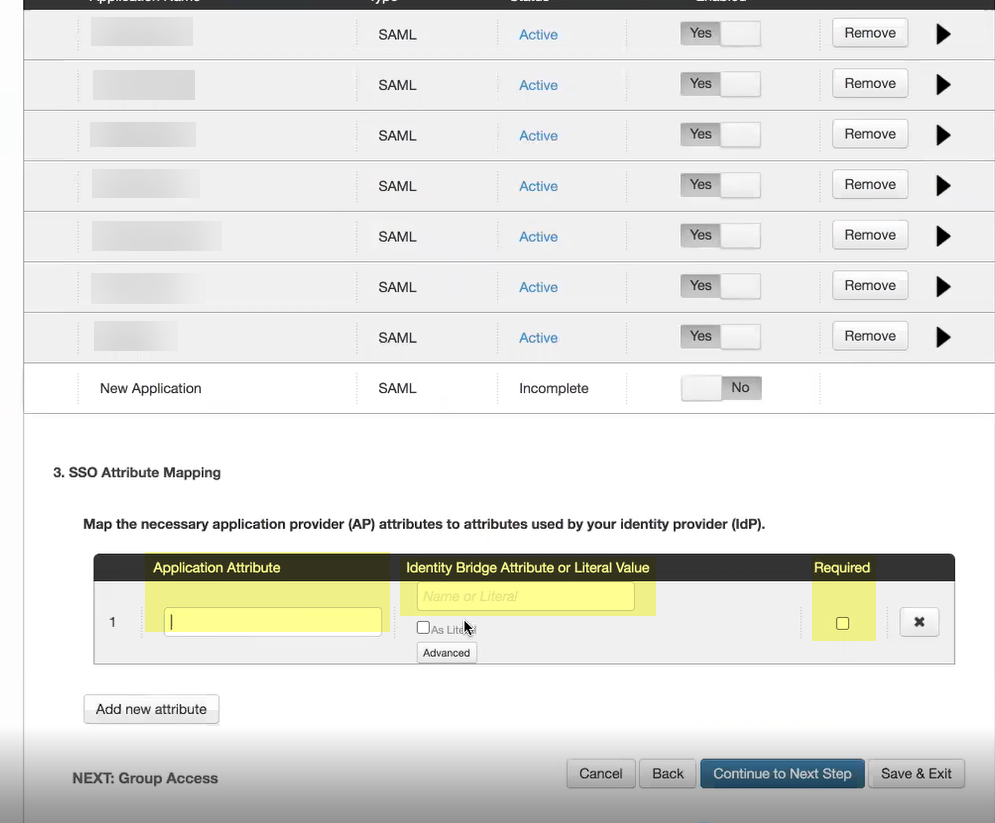
- Click Add new attribute as needed to include additional attributes then Continue to next step to specify the group attributes.
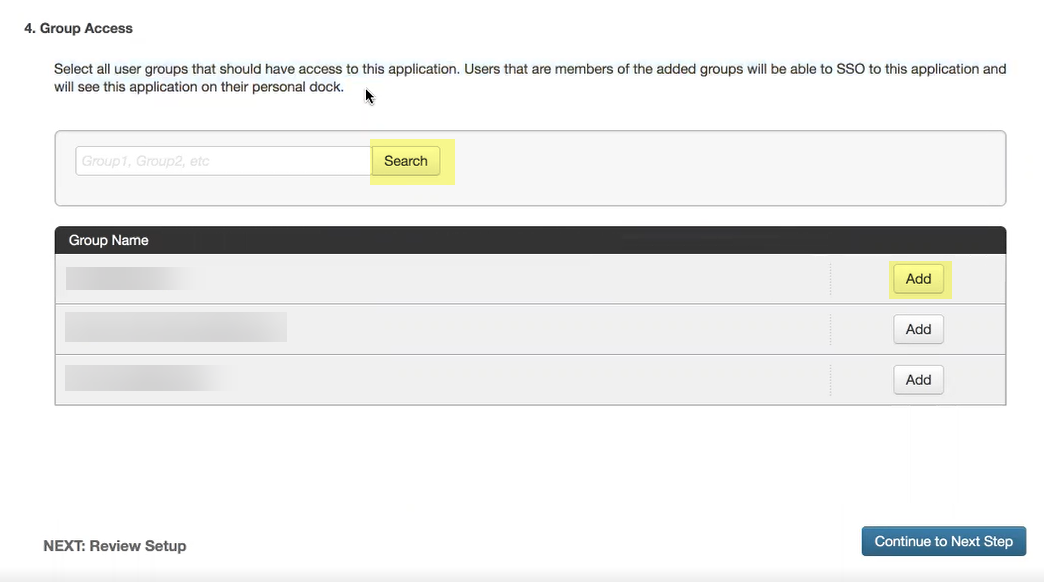
- Add the groups you want to authenticate using PingOne or Search for the groups you want to add then Continue to next step to review your configuration.
- Add PingOne as an authentication type in the Cloud Identity Engine app.
- Select Authentication Types and click Add New Authentication Type .

- Set Up a SAML 2.0 authentication type.

- Enter a Profile Name .
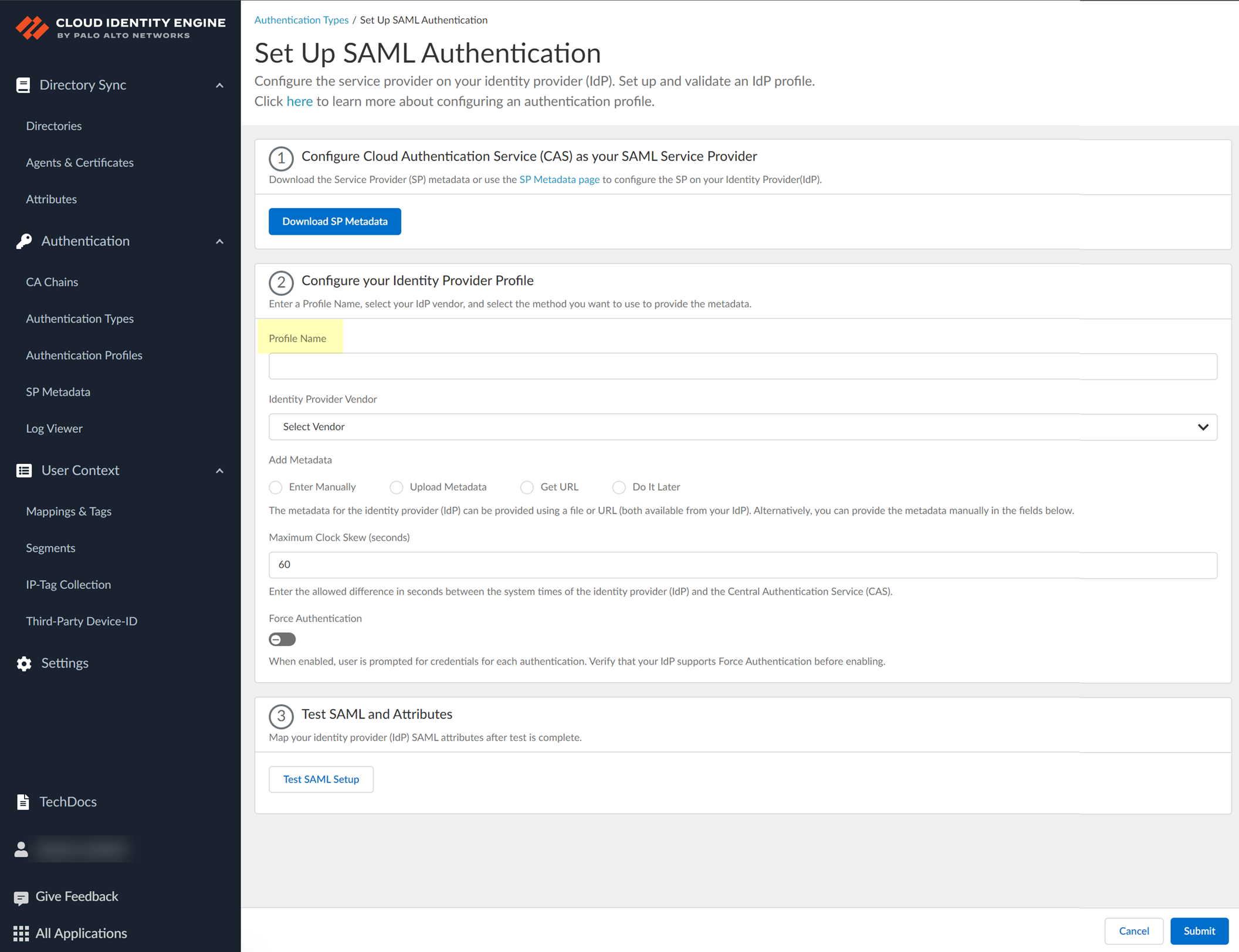
- Select PingOne as your Identity Provider Vendor .
- Select the method you want to use to Add Metadata and Submit the IdP profile.
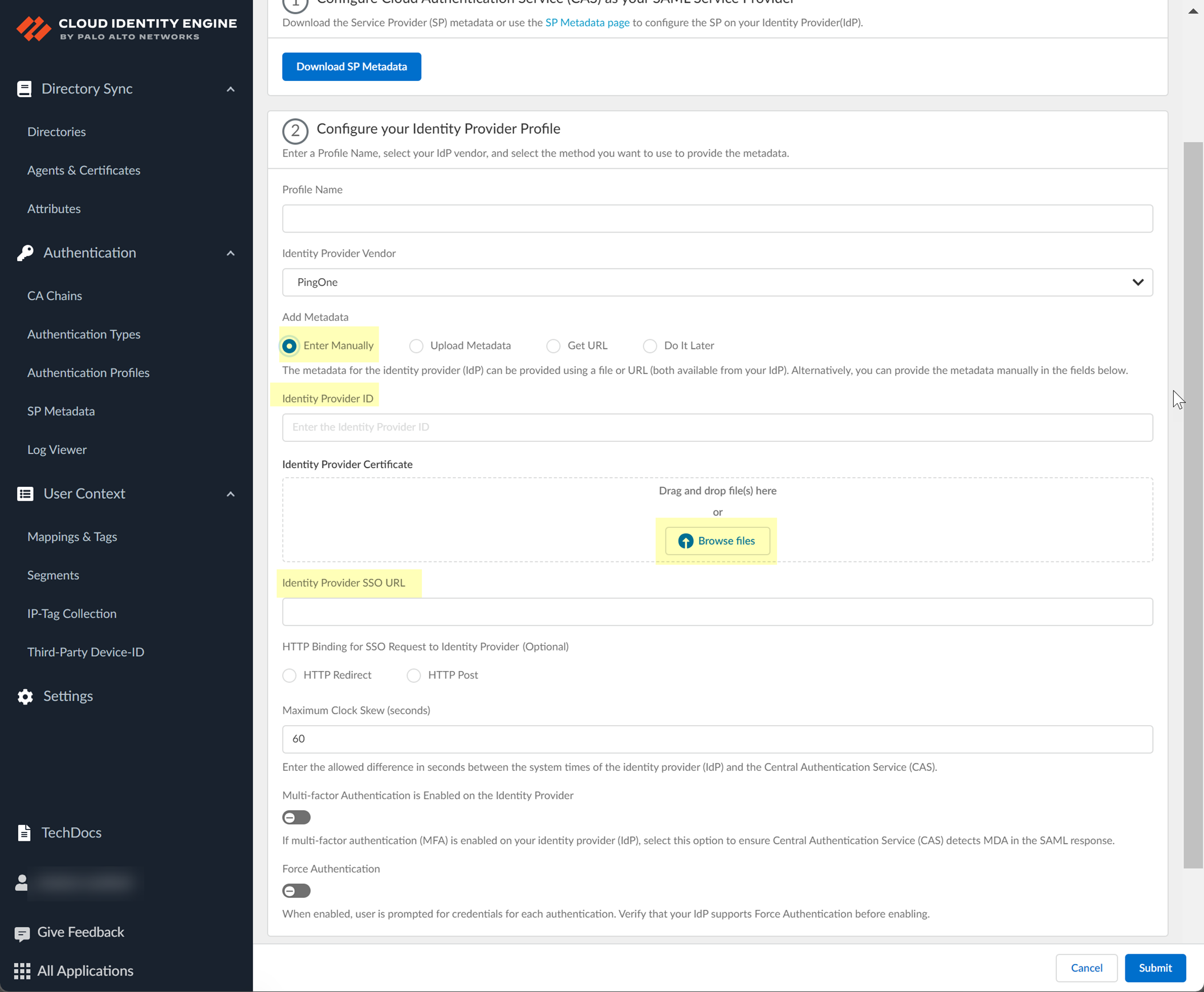
- If you want to enter the information manually, copy the identity provider ID and SSO URL, download the certificate, then enter the information in the Cloud Identity Engine IdP profile.
- In PingOne, select ApplicationsMy Applications then select the Cloud Identity Engine app.
- Copy the necessary information from PingOne and enter it in the IdP profile on the Cloud Identity Engine app as indicated in the following table:
|
Copy or Download from Okta Admin Console |
Enter in Cloud Identity Engine IdP Profile |
|
Copy the Issuer ID. |
Enter it as the Identity Provider ID . |
|
Download the Signing Certificate . |
Click to Upload the certificate from the Okta Admin Console. |
|
Copy the Initiate Single Sign-On (SSO) URL . |
Enter the URL as the Identity Provider SSO URL . |
-
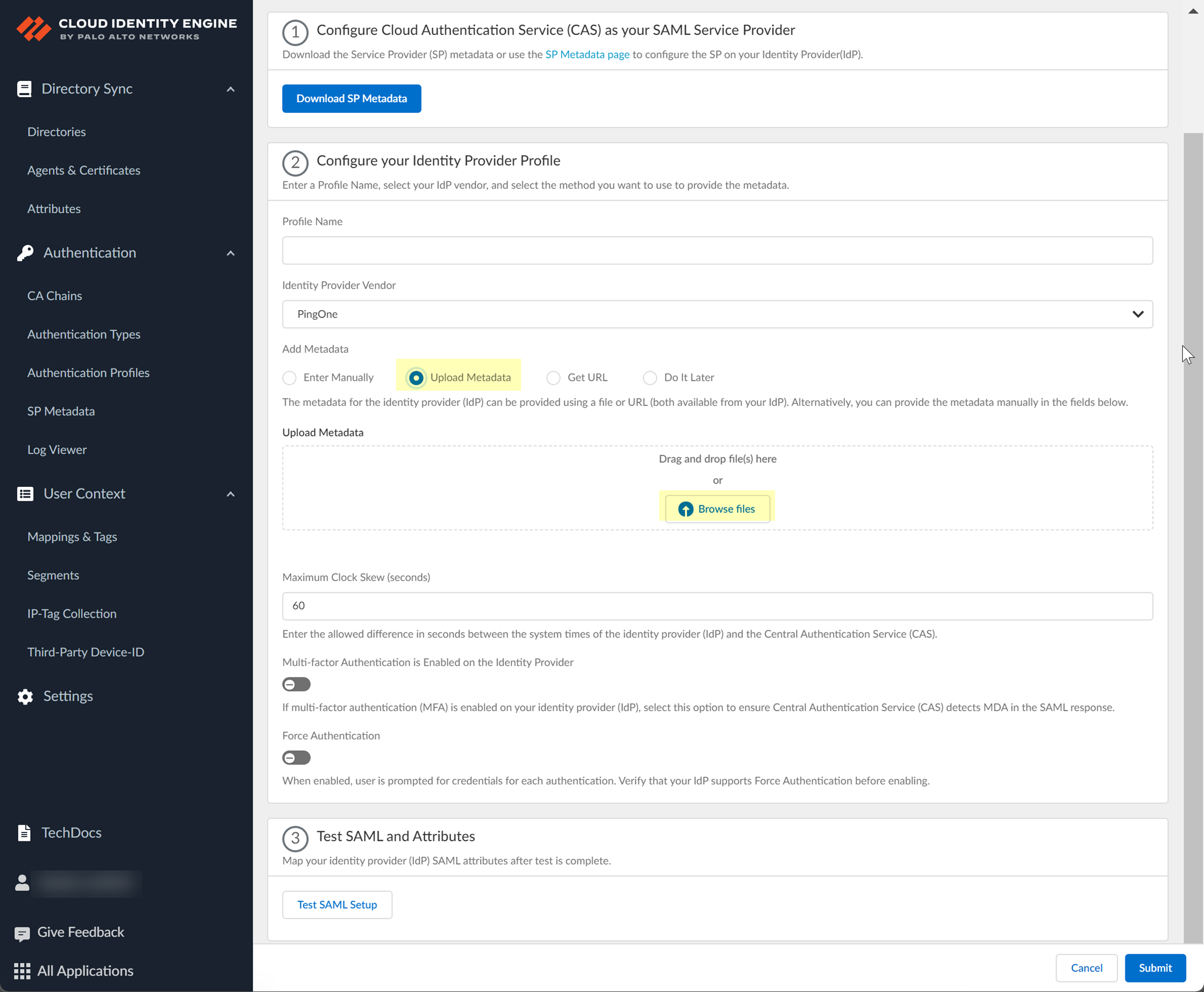
- If you want to upload a metadata file, download the metadata file from your IdP management system.
- In PingOne, select ApplicationsMy Applications then select the Cloud Identity Engine app.
- Download the SAML Metadata .
- In the Cloud Identity Engine app, click Browse files to select the metadata file, then Open the metadata file.
- To use the Get URL method, copy the URL from your IdP and enter it in Cloud Identity Engine.
- Log in to Ping One using your administrator credentials.
- Select Applications then select the application you created in step
1.c
.
- Copy the SAML Metadata URL and save it in a secure location.
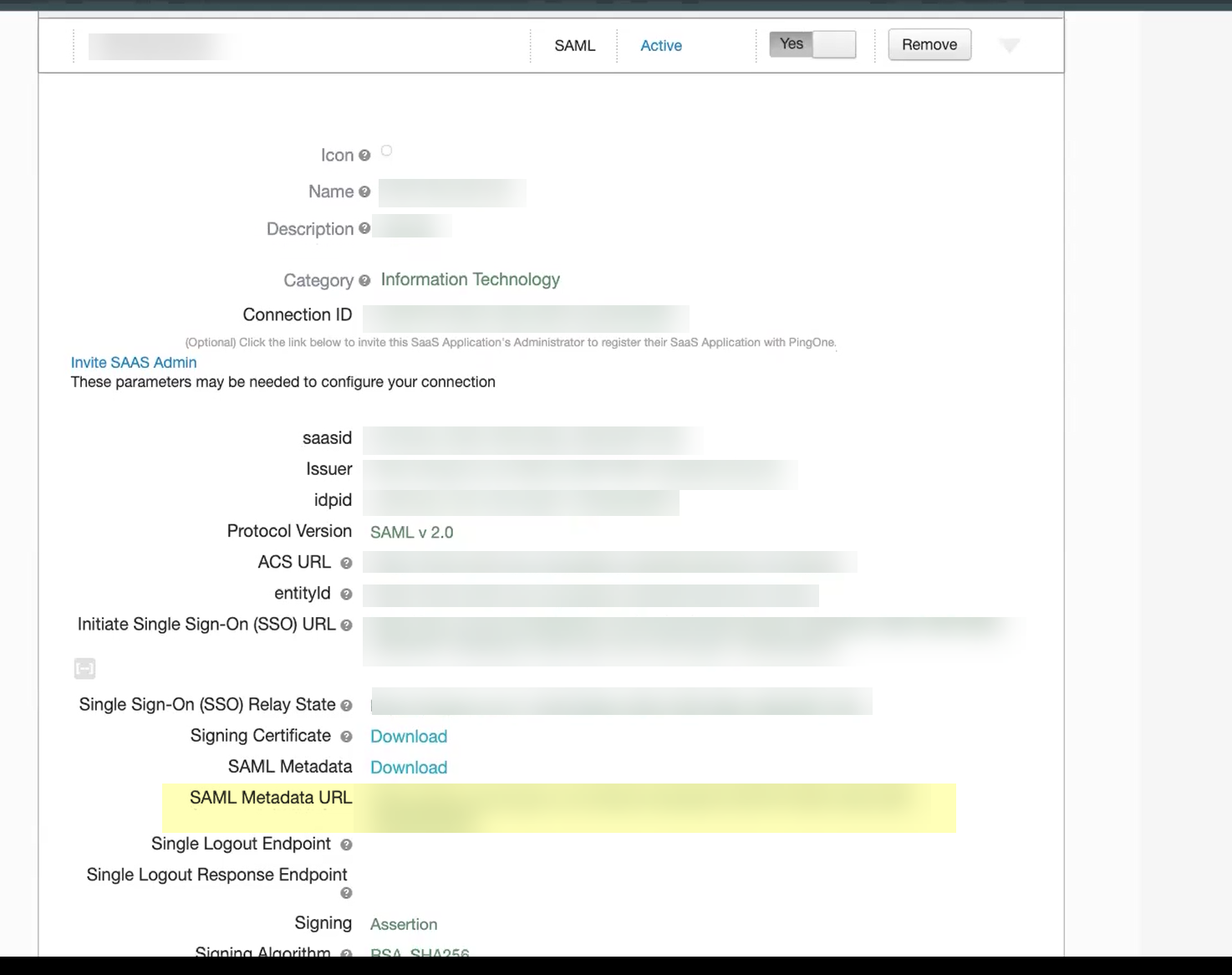
- In the Cloud Identity Engine, select Get URL and the Add Metadata method and paste the URL you copied in the previous step as the Identity Provider Metadata URL .
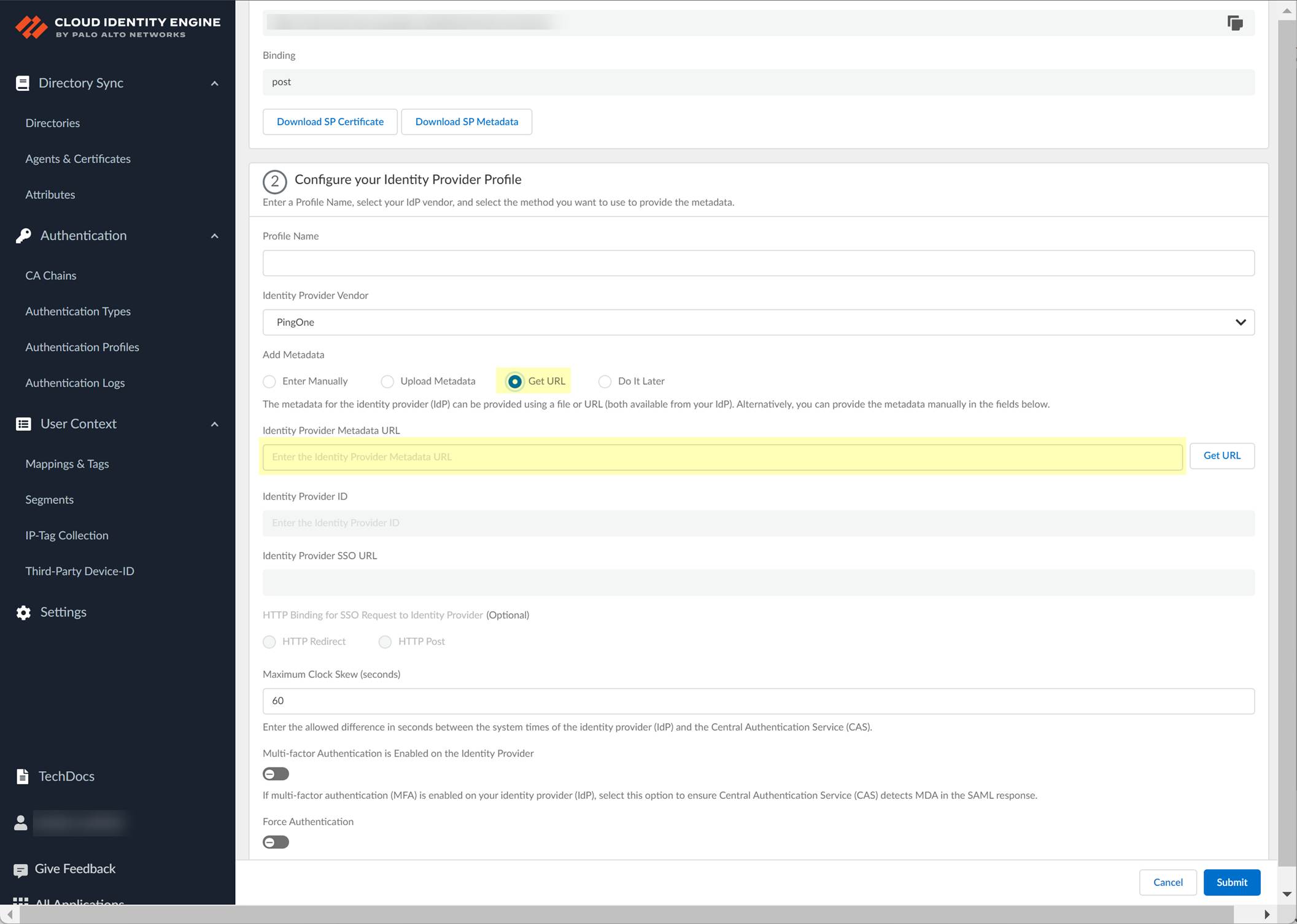
- Click Get URL to confirm the URL and populate the Identity Provider ID and Identity Provider SSO URL .
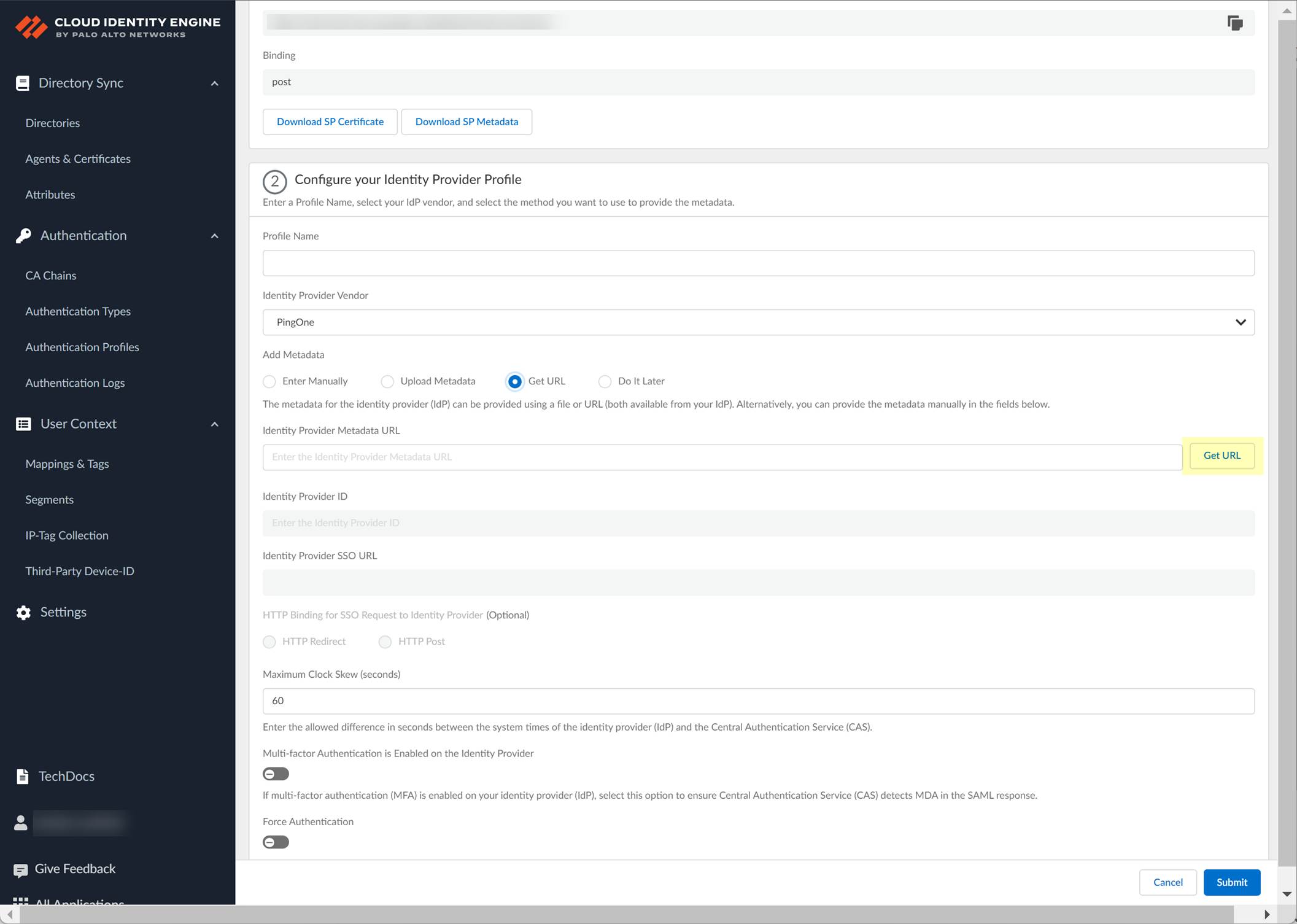
- If you don't want to enter the configuration information now, you can Do it later . This option allows you to submit the profile without including configuration information. However, you must edit the profile to include the configuration information to use the authentication type in an authentication profile.
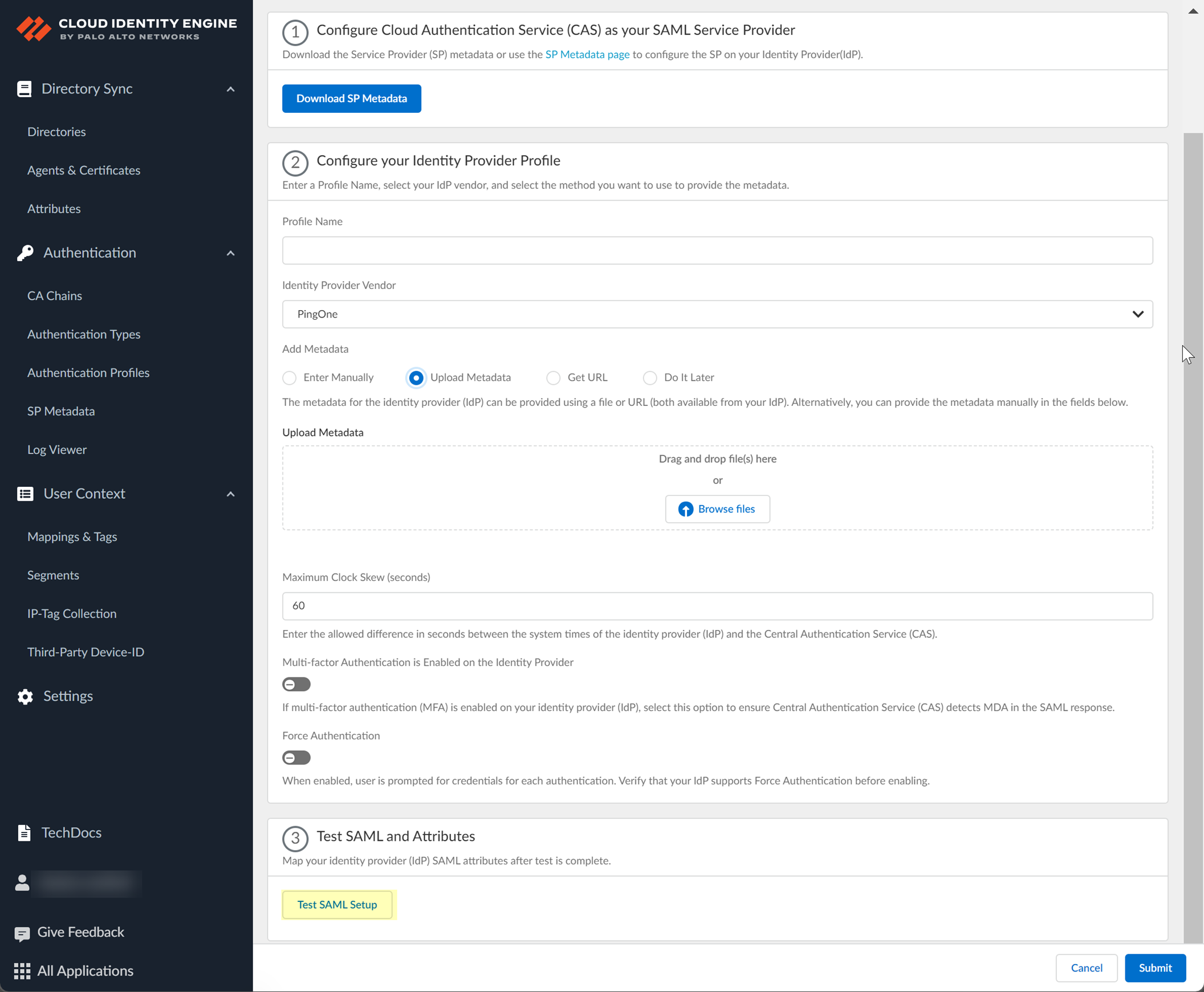
- Select the HTTP Binding for SSO Request to IdP method you want to use for the SAML binding that allows the firewall and IdP to exchange request and response messages:
- HTTP Redirect —Transmit SAML messages through URL parameters.
- HTTP Post —Transmit SAML messages using base64-encoded HTML.
- Specify the Maximum Clock Skew (seconds) , which is the allowed difference in seconds between the system times of the IdP and the firewall at the moment when the firewall validates IdP messages (default is 60; range is 1–900). If the difference exceeds this value, authentication fails.
- If your IdP requires users to log in using multi-factor authentication (MFA), select Multi-factor Authentication is Enabled on the Identity Provider .
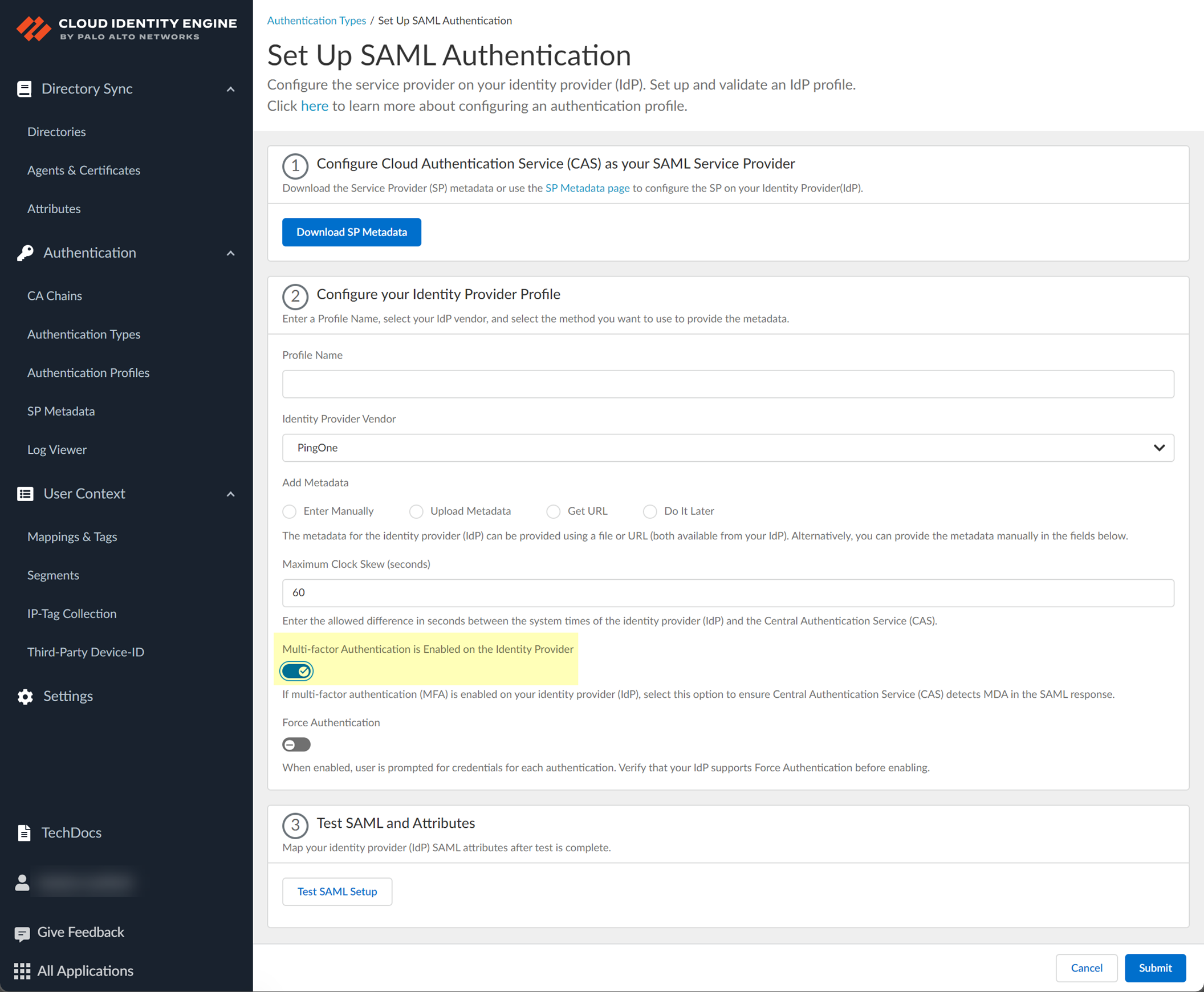
- If you enabled the Force Re-authentication option in step
1.9
, enable the Force Authentication option to require users to log in with their credentials to reconnect to GlobalProtect.
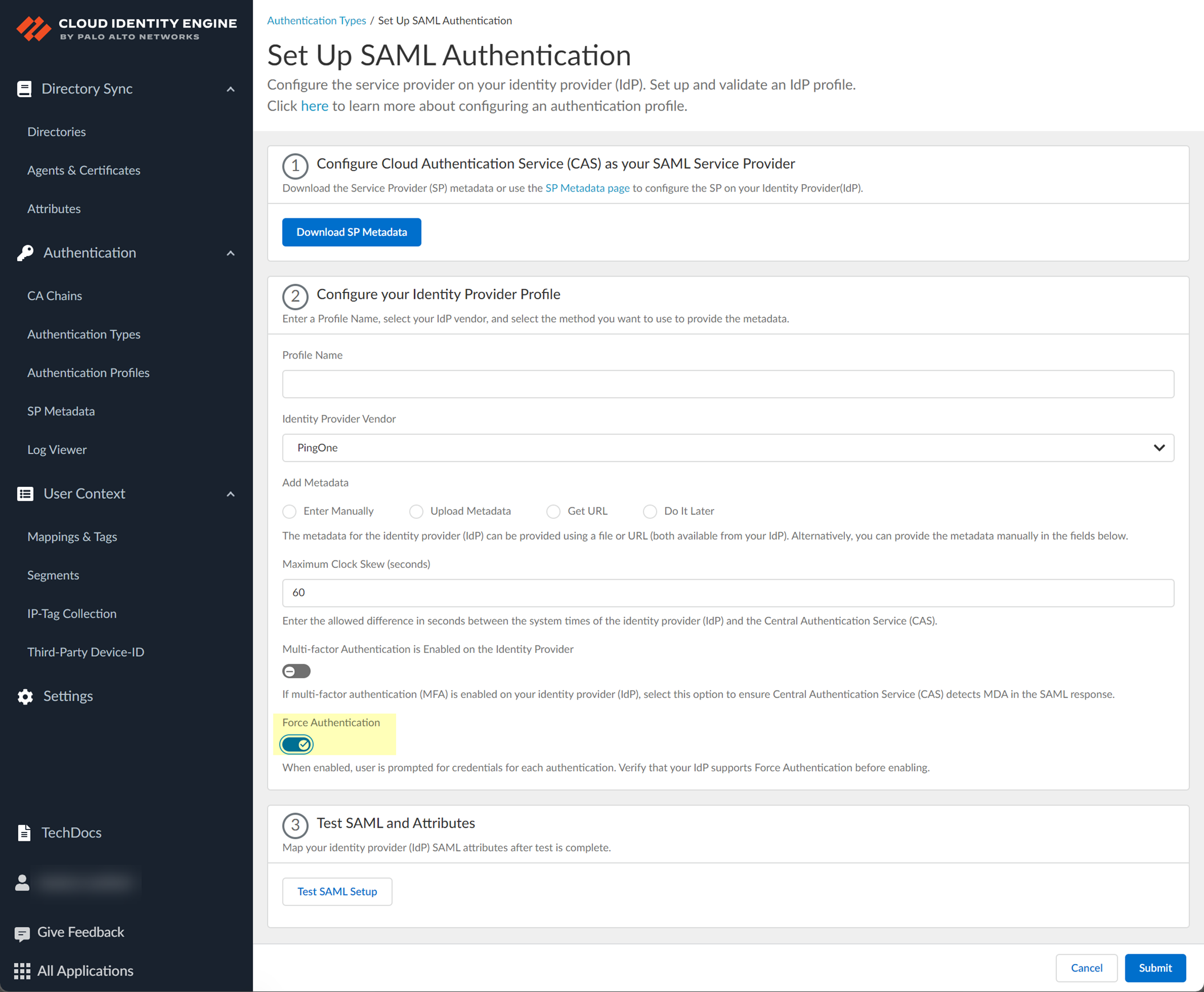
- Test SAML setup to verify the profile configuration.
This step is necessary to confirm that your firewall and IdP can communicate.
- Select the SAML attributes you want the firewall to use for authentication and Submit the IdP profile.
- In the Okta Admin Console, Edit the User Attributes & Claims .
- In the Cloud Identity Engine, select the Username Attribute and optionally, the Usergroup Attribute , Access Domain , User Domain , and Admin Role , then Submit your changes.
You must select the username attribute in the Okta Admin Console for the attribute to display in the Cloud Identity Engine.
Configure PingFederate as an IdP in the Cloud Identity Engine
- Prepare the metadata for the Cloud Identity Engine app in PingFederate.
- If you have not already done so, activate the Cloud Identity Engine app.
- In the Cloud Identity Engine app, select AuthenticationSP MetadataDownload SP Metadata and Save the metadata in a secure location.
- Log in to PingFederate and select SystemSP AffiliationsProtocol MetadataMetadata Export .
- Select I am the Identity Provider (IdP) then click Next .
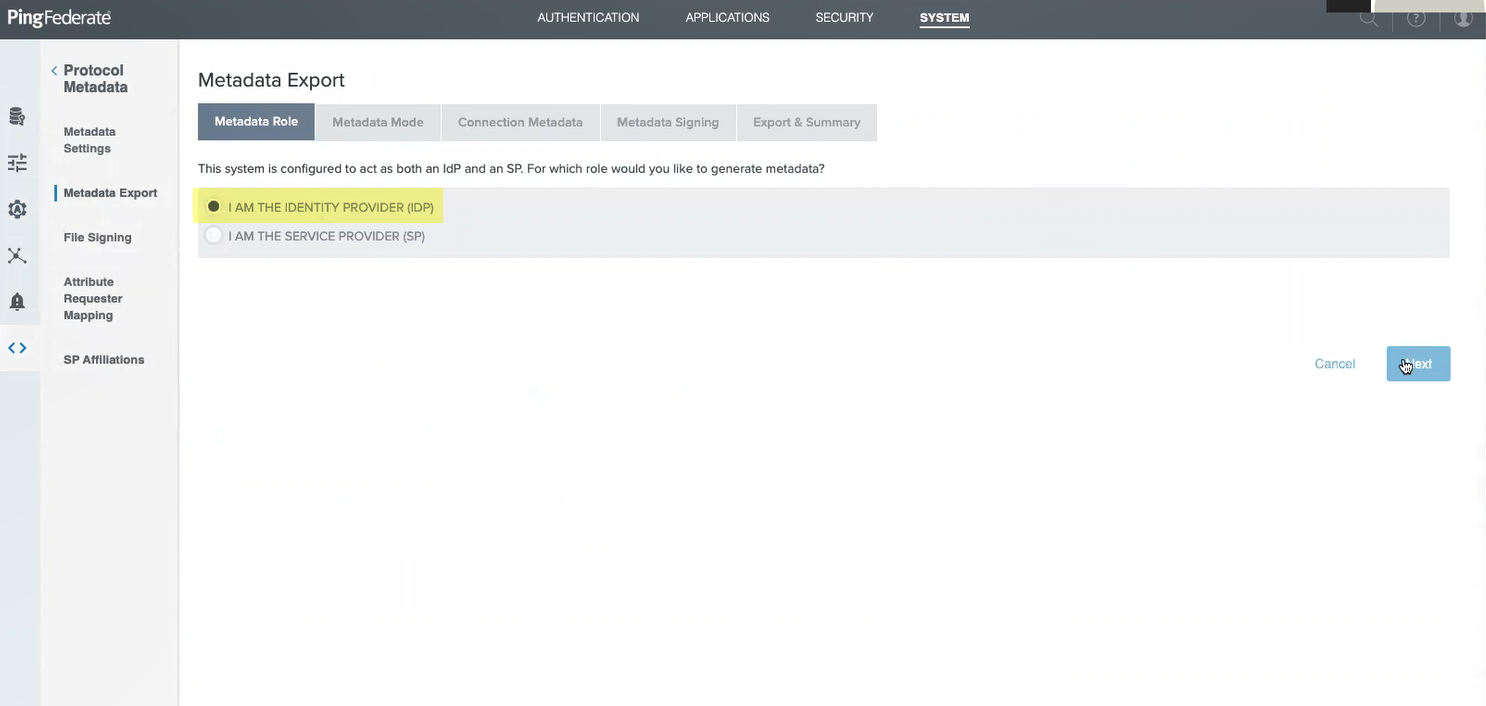
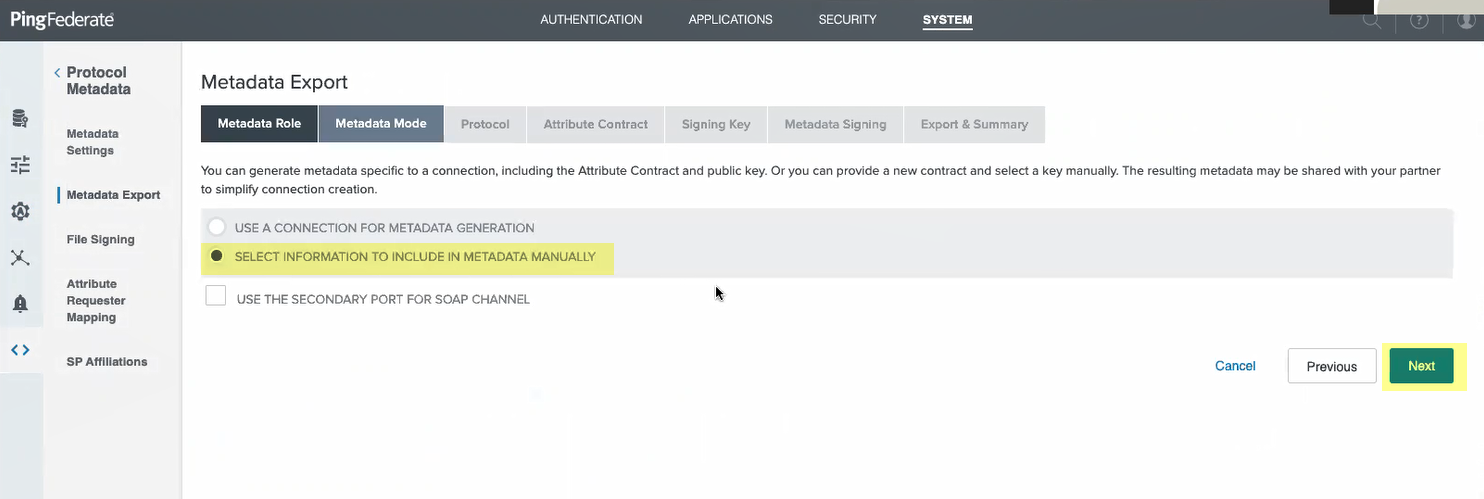
- Select information to include in metadata manually then click Next .
- Select the Signing key you want to use then click Next .
- Ensure that SAML 2.0 is the protocol then click Next .
- Click Next as you don't need to define an attribute contract.
- Select the Signing Certificate and that you want to Include this certificate’s public key certificate in the <key info> element .
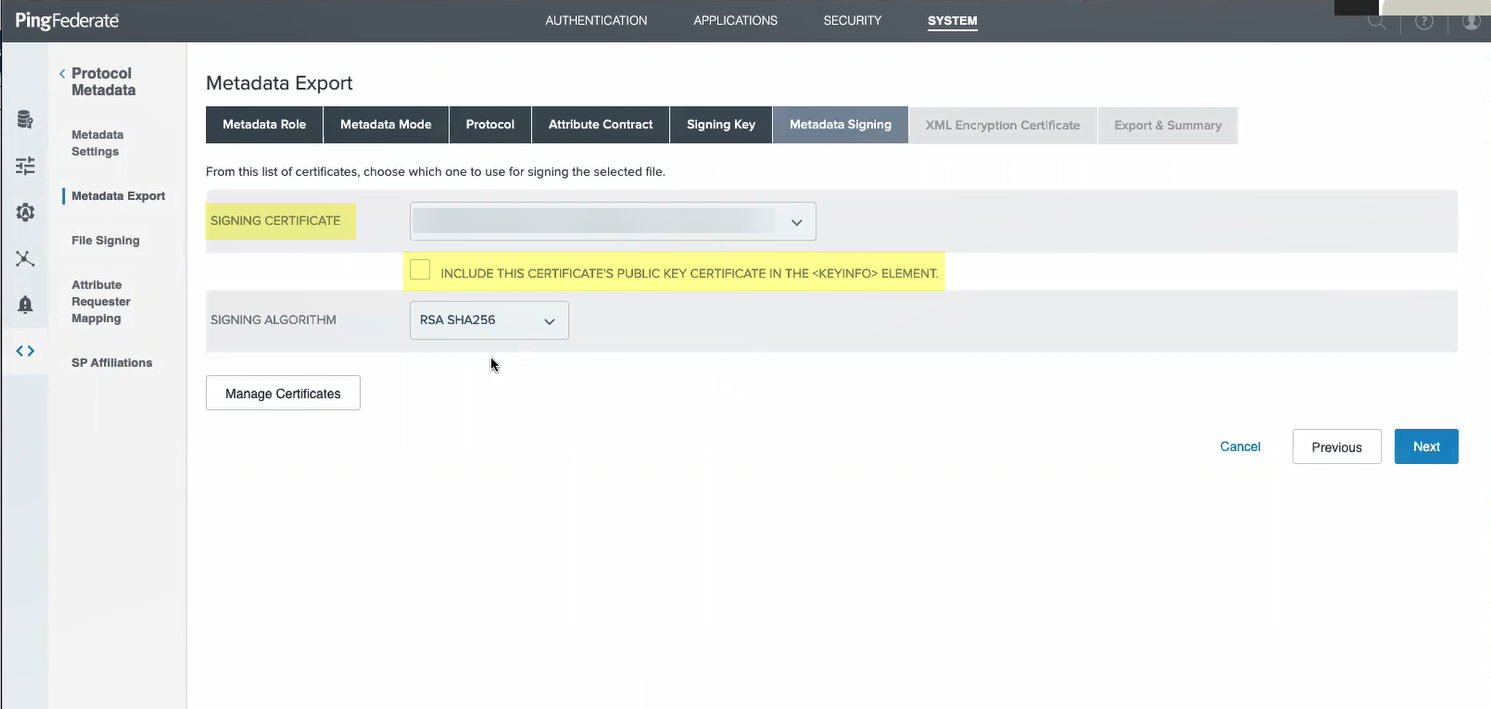
- Select the Signing Algorithm you want to use then click Next .
- Select the same certificate as the Encryption certificate then click Next .
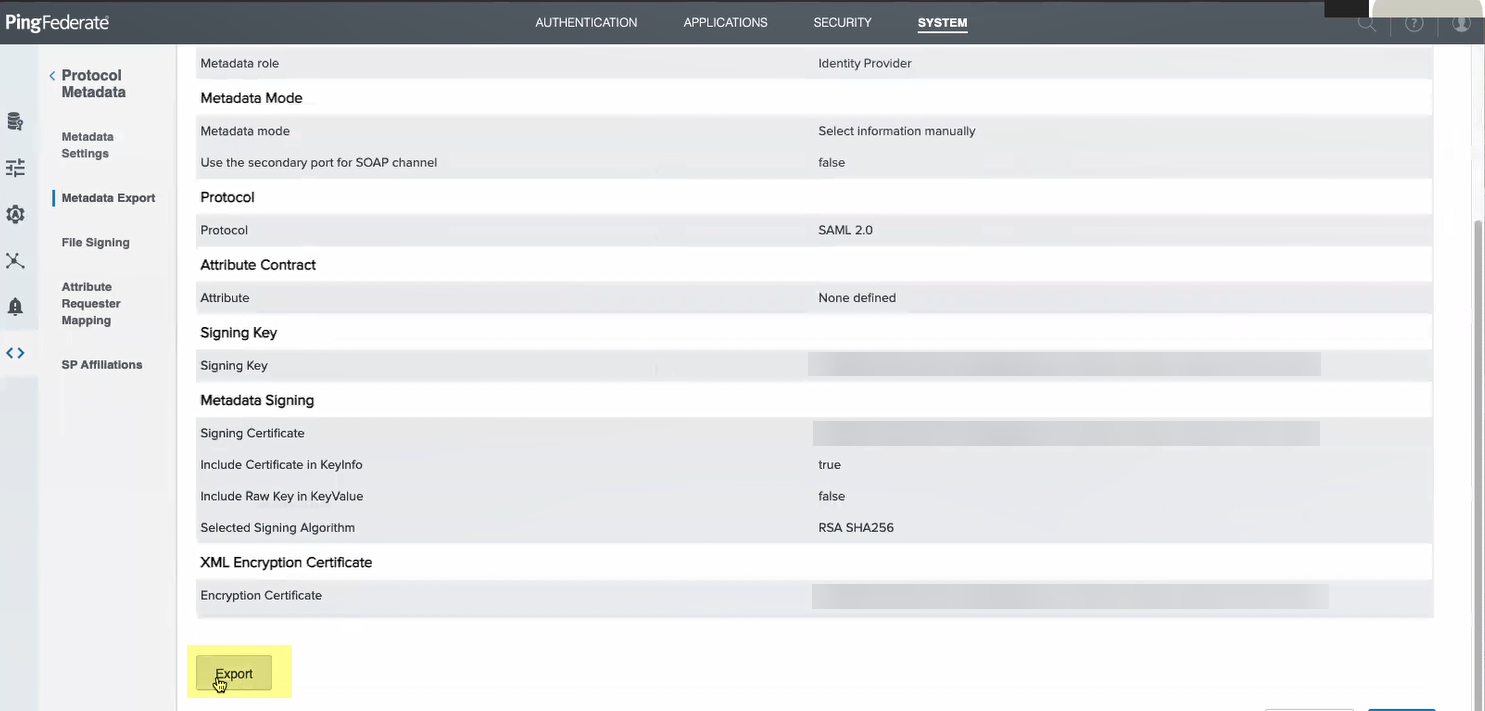
- Review the metadata to verify the settings are correct then Export the metadata.
- Add PingFederate as an authentication type in the Cloud Identity Engine app.
- Select Authentication Types and click Add New Authentication Type .

- Set Up a SAML 2.0 authentication type.

- Enter a Profile Name .
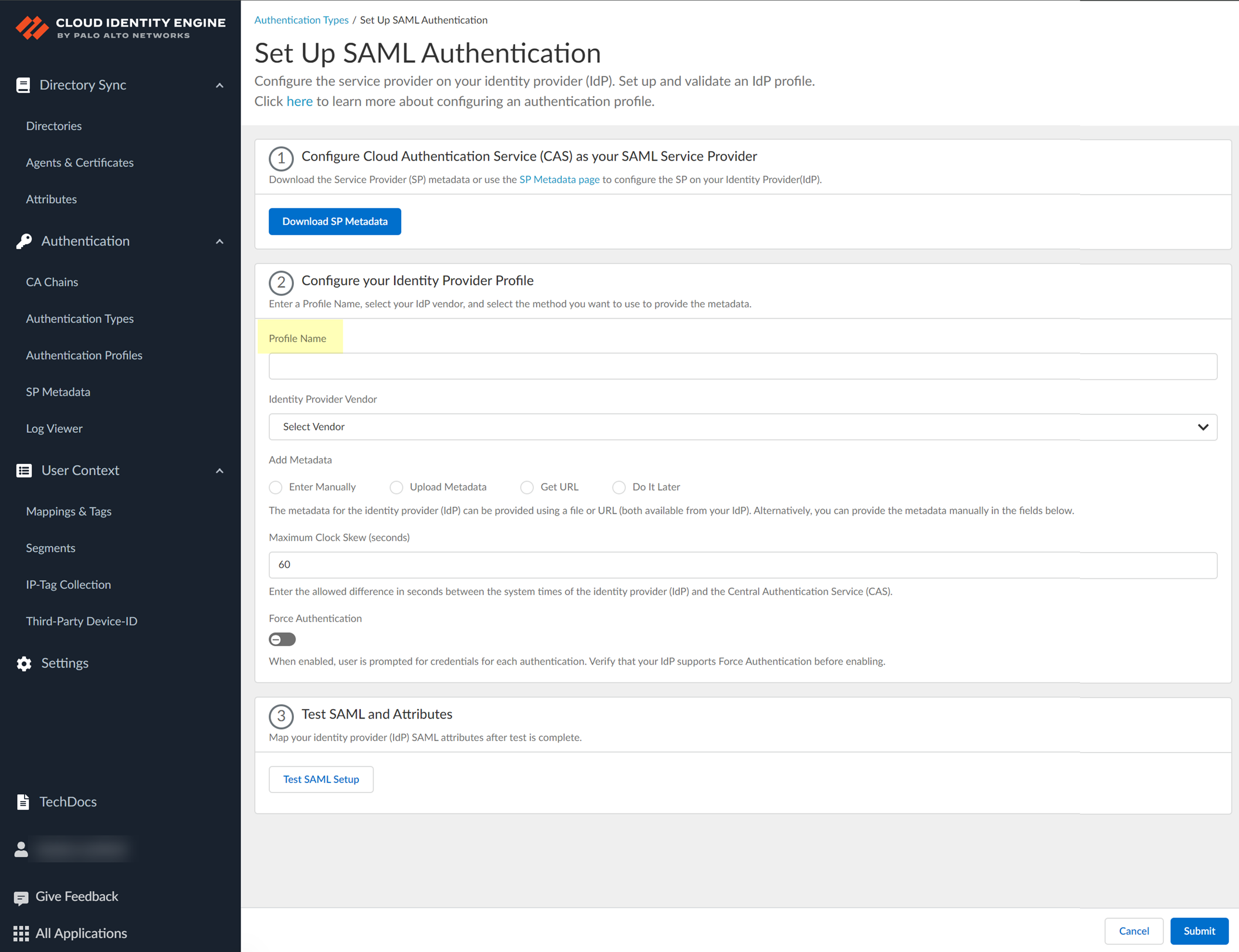
- Select PingFederate as your Identity Provider Vendor .
- Select the method you want to use to Add Metadata and Submit the IdP profile.
- If you want to enter the information manually, copy the identity provider ID and SSO URL, download the certificate, then enter the information in the Cloud Identity Engine IdP profile.
- In PingFederate, select SystemOAuth SettingsProtocol Settings to copy the Base URL and SAML 2.0 Entity .
- Copy the necessary information from PingFederate and enter it in the IdP profile on the Cloud Identity Engine app as indicated in the following table:
|
Copy or Download from PingFederate |
Enter in Cloud Identity Engine IdP Profile |
|
Copy the SAML 2.0 Entity ID. |
Enter it as the Identity Provider ID . |
|
Copy the Base URL . |
Enter the URL as the Identity Provider SSO URL . |
-
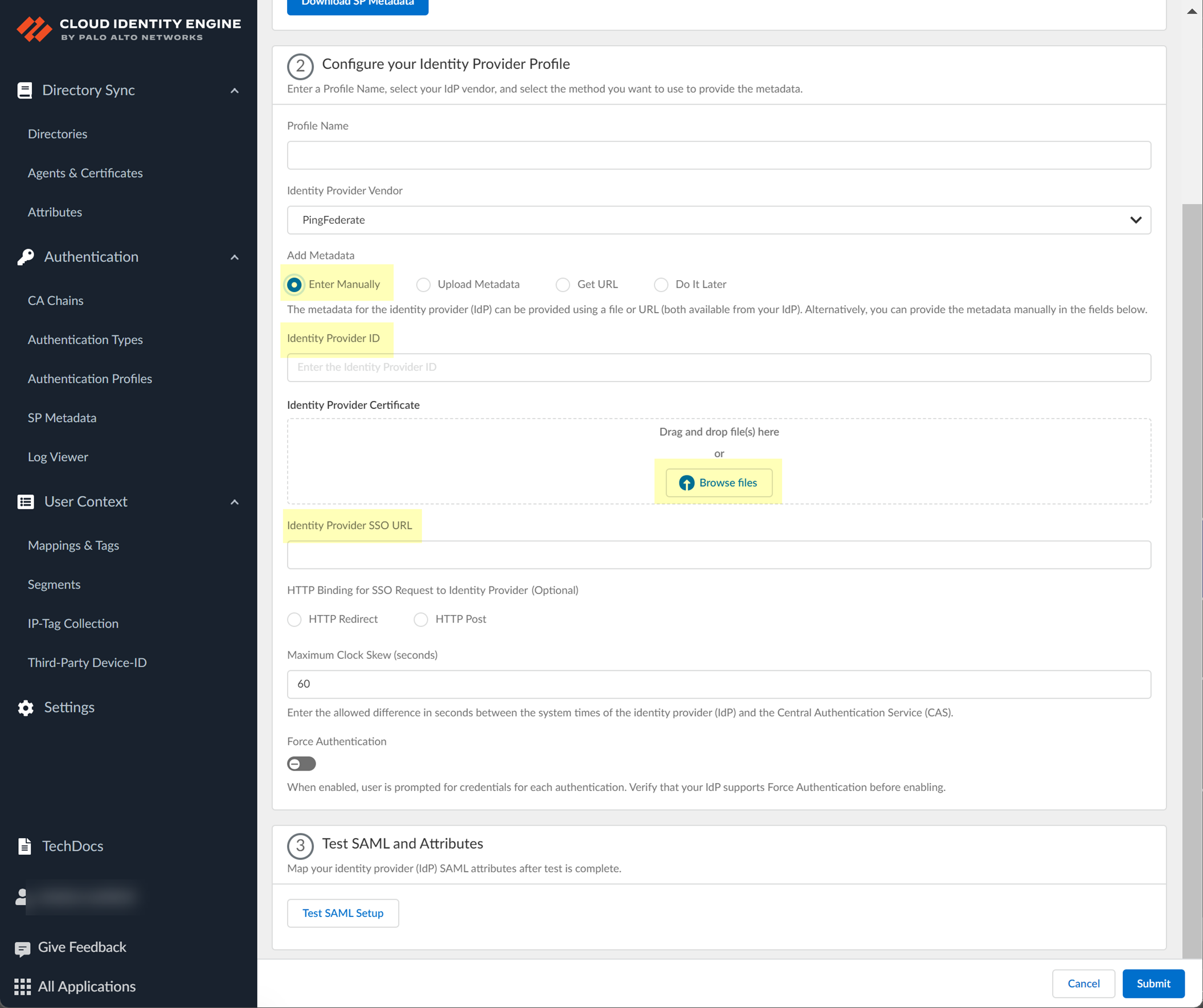
- In PingFederate, select SecuritySigning & Decryption Keys & Certificates to Export the certificate you want to use.
- In the Cloud Identity Engine app, click Browse files to select the PingFederate certificate.
- Select the HTTP Binding for SSO Request to IdP method you want to use for the SAML binding that allows the firewall and IdP to exchange request and response messages:
- HTTP Redirect —Transmit SAML messages through URL parameters.
- HTTP Post —Transmit SAML messages using base64-encoded HTML.
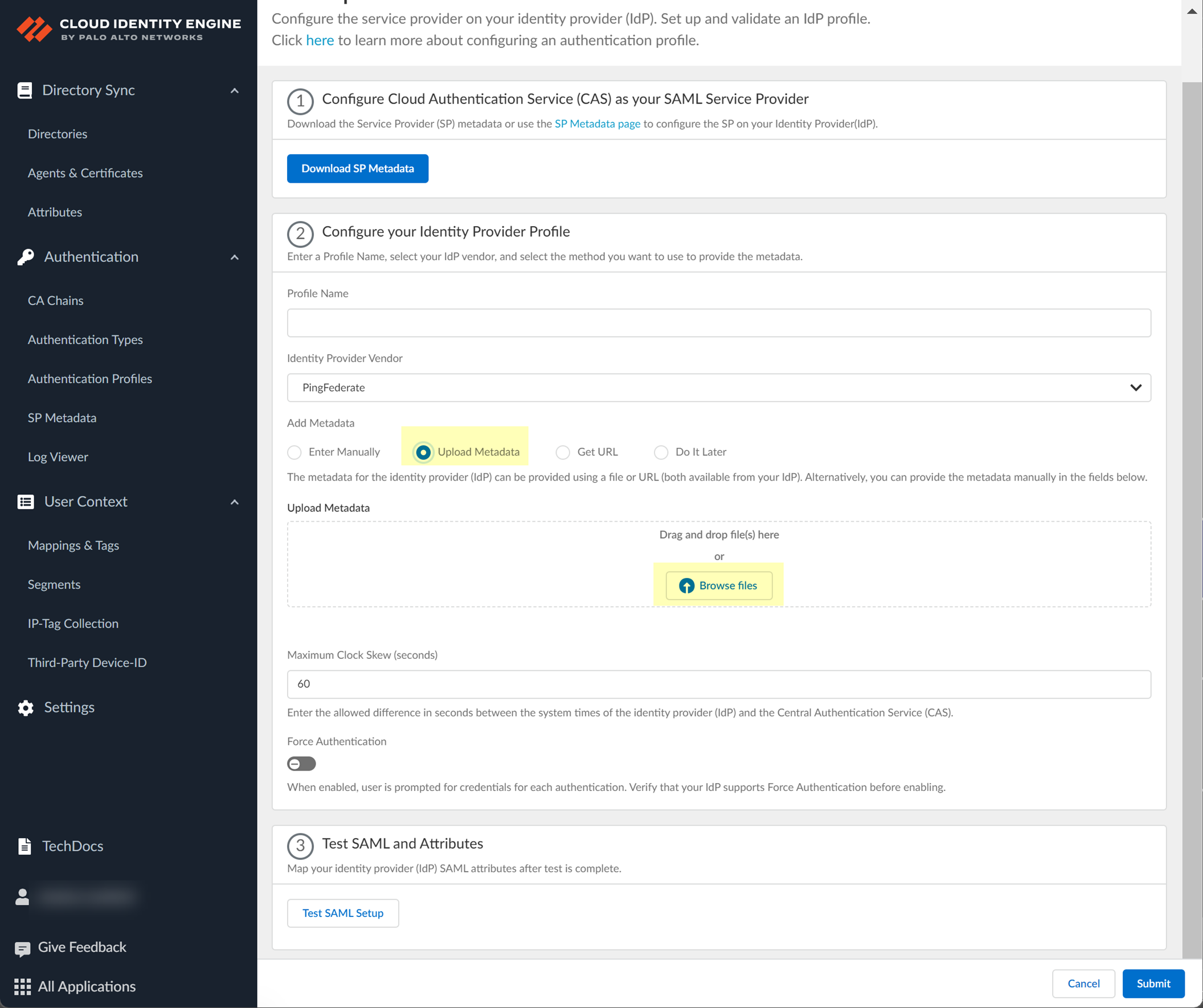
- If you want to upload a metadata file, download the metadata file from your IdP management system.
- Locate the metadata file from the first step.
- In the Cloud Identity Engine app, click Browse files to select the metadata file, then Open the metadata file.
- If you don't want to enter the configuration information now, you can Do it later . This option allows you to submit the profile without including configuration information. However, you must edit the profile to include the configuration information to use the authentication type in an authentication profile.
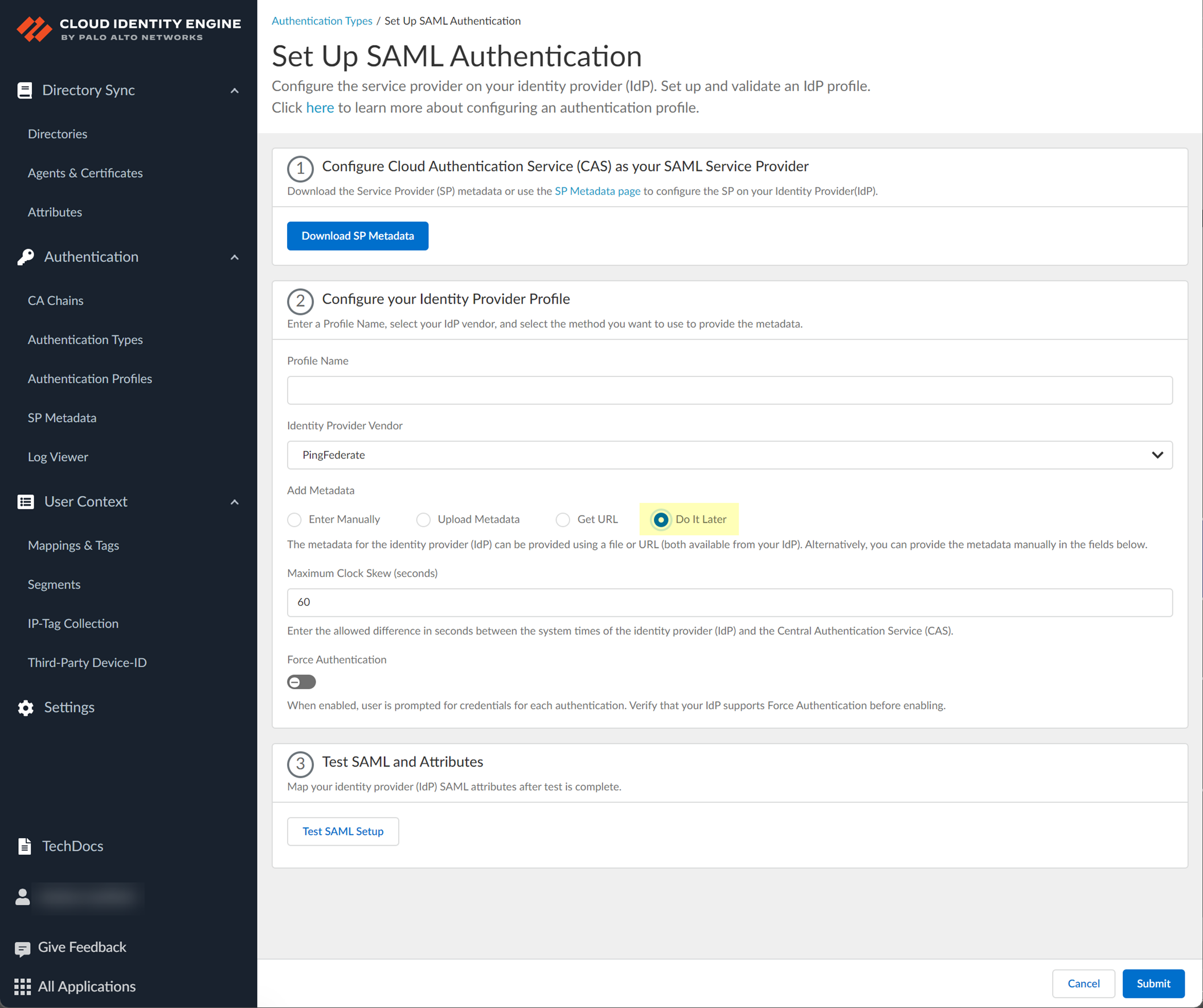
- The Cloud Identity Engine does not currently support the Get URL method for PingFederate.
- Specify the Maximum Clock Skew (seconds) , which is the allowed difference in seconds between the system times of the IdP and the firewall at the moment when the firewall validates IdP messages (default is 60; range is 1–900). If the difference exceeds this value, authentication fails.
- To require users to log in using their credentials to reconnect to GlobalProtect, enable Force Authentication .
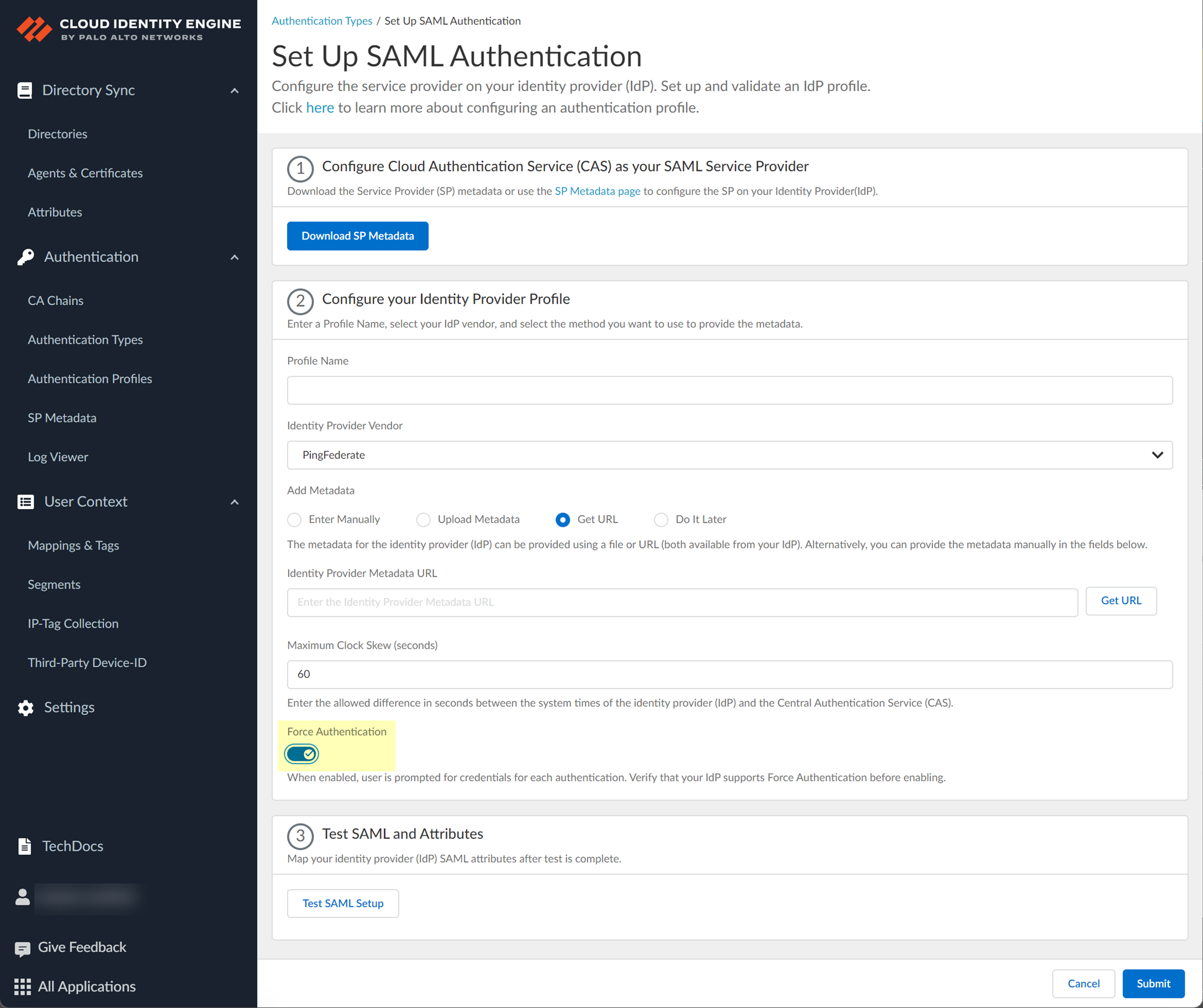
- Test SAML setup to verify the profile configuration.
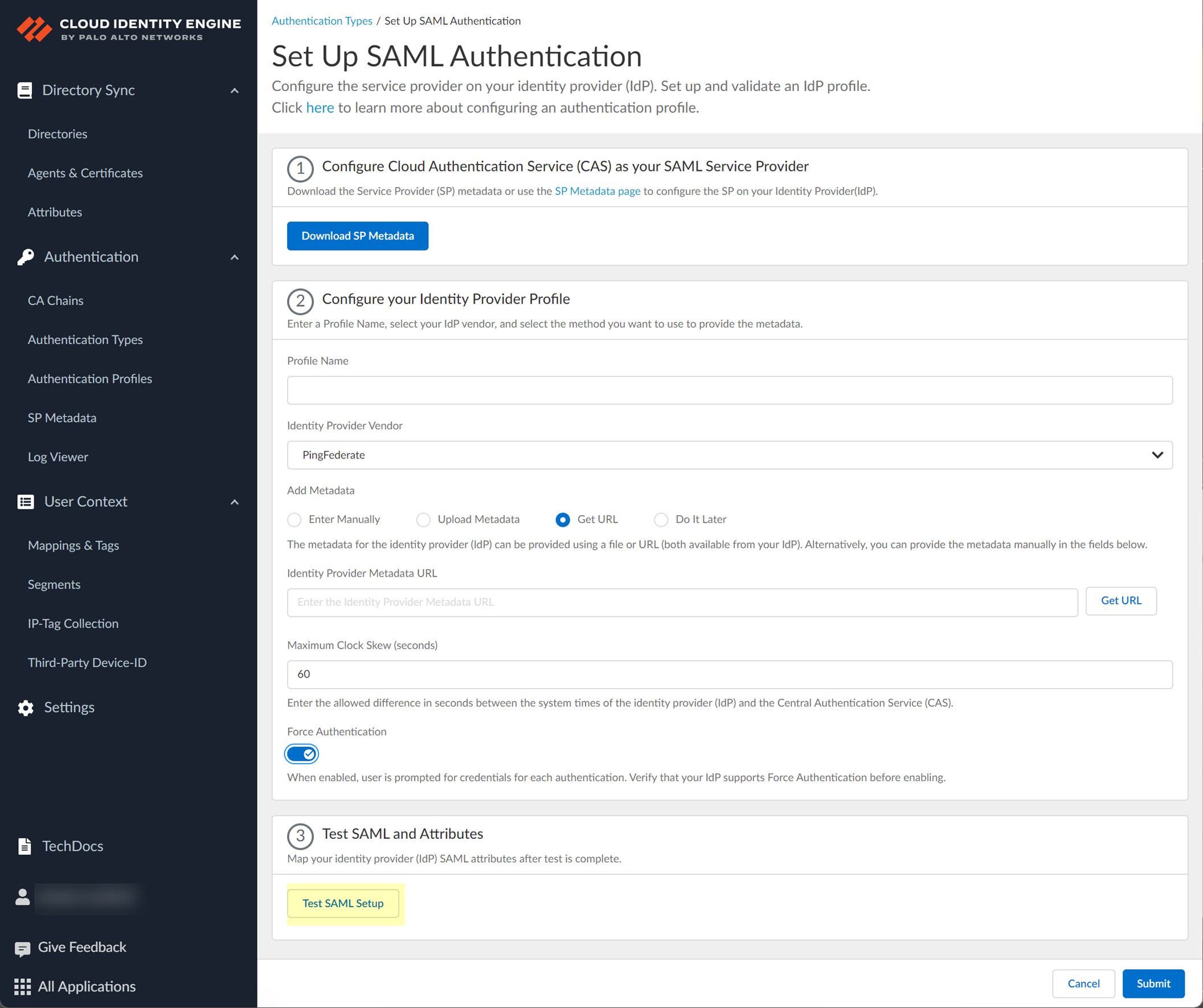
This step is necessary to confirm that your firewall and IdP can communicate.
- Select the SAML attributes you want the firewall to use for authentication and Submit the IdP profile.
- In the Cloud Identity Engine, select the Username Attribute .
- (Optional) Select the Usergroup Attribute , Access Domain , User Domain , and Admin Role .
